In this article:
Shortness of breath, also called, dyspnea, is an incredibly uncomfortable condition. The term “dyspnea” is derived from the Greek words “dys,” which means difficult or painful, and “pnoia,” which means breathing. Thus, dyspnea stands for difficulty in breathing.

Dyspnea is a symptom of a disease, rather than a disease itself. It refers to the feeling of insufficient air intake, where you experience a sense of not being able to breathe deeply or rapidly enough, and makes it hard for you to inhale and exhale.
You may experience shortness of breath for a few minutes, but it can also be chronic and last for days and weeks in serious cases. (1)(2)
Take a look at some ways to manage dyspnea by reading on.
How to Manage Dyspnea
Here are some ways that can be helpful in managing shortness of breath.
1. Purse the lips
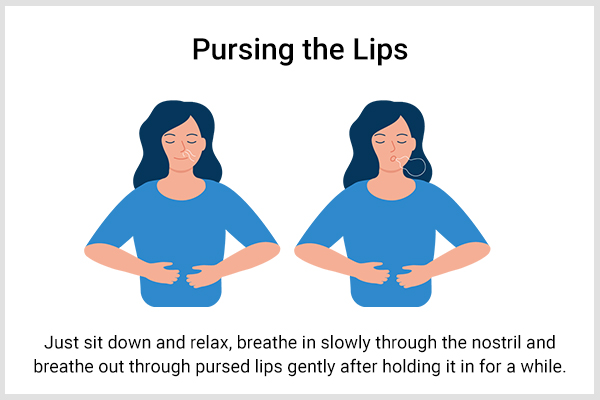
Pursing the lips is a quick and easy way to deal with shortness of breath that may happen when you hyperventilate due to health issues or panic attacks. This can effectively lower the breathing rate and pace, allowing you to take deep breaths that can help you calm down.
Sometimes, air is trapped in the lungs, which can be relieved with this technique.
Pursing the lips is easy to perform. Just sit down and relax, breathe in slowly through the nostrils, hold it in for a while, and then gently breathe out through pursed lips. (3)
2. Sit and relax
Whenever you have difficulty breathing, all you have to do is sit and relax. Support your face with your hands; doing so will help you keep your neck relaxed and will allow your lungs to expand more in the chest.
You can also rest your head and arms on a table or a pillow if that helps more. (4)
3. Stand with support
Standing in a comfortable and supported position can also help you relax and breathe better. You can take support from a wall and relax your arms and shoulders to breathe deeper and more effectively.
This technique is helpful when you can’t find a place to sit. (5)
4. Quit smoking
Your dyspnea may start to resolve itself within a few weeks of quitting smoking. It will be much better after almost a year.
Staying smoke-free is a good way to fight breathlessness. (6)
5. Breathe using your diaphragm
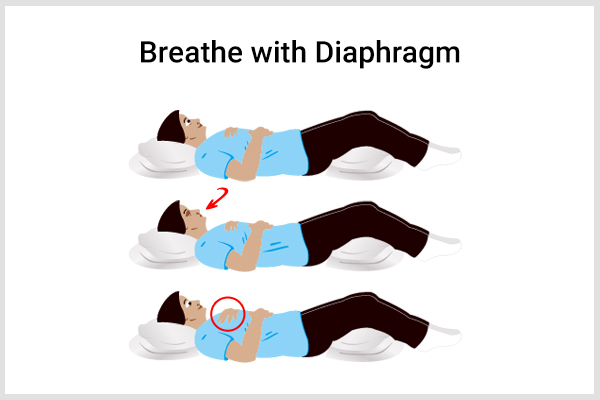
Breathing while involving your diaphragms is helpful in dyspnea management.
To perform this breathing style, first, sit comfortably and relax your body. Keep your hands close to your abdomen, and breathe in slowly as you feel your abdomen move out. Then exhale gently and feel your abdominal muscles move back in.
Remember to breathe in with your nose but exhale with your mouth keeping your lips pursed. (7)
6. Cool air
Researchers have shared that sitting in front of cool air from a fan, vent, or AC can be helpful in managing shortness of breath. You can carry a small battery-operated mobile fan with you if you tend to experience dyspnea more frequently. (8)
7. Caffeine
Caffeine has been found to be helpful in the dilation of the respiratory tract for improved breathing. This is especially true for asthmatic patients.
However, do not consume too much caffeine as it can hinder your sleep cycle due to its stimulating effects. (9)
8. Avoid allergens
Allergies and allergic rhinitis affect your respiratory system. They cause wheezing, itchy nose, sinusitis, sneezing, and shortness of breath.
If you know you are allergic to something, stay away from it to avoid any breathing problems such as dyspnea. (10)
9. Stay in an upright position at night

Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) is a condition where a person wakes up suddenly feeling short of breath after sleeping for 1–2 hours. This condition can be relieved by sitting or standing upright, which helps to ease breathing difficulties.
Experts claim that sleeping in an upright position or using extra pillows to elevate the upper body can help reduce the risk of experiencing PND. (11)
10. Sit leaning forward
People with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may find relief from breathing difficulties by leaning forward while sitting and placing their forearms on their thighs. This position can also be helpful for relaxation during chest physical therapy.
Moreover, studies have shown that sitting in a forward-leaning position can increase lung function compared to sitting leaning back.
Additionally, proper alignment of the head and neck can help reduce airway obstruction and improve breathing. (12)
What Are the Causes of Dyspnea?
Dyspnea can have different causes, which can be classified into four main categories: respiratory, cardiac, neuromuscular, and psychogenic, as well as systemic illness or a combination of these. (2)

1. Respiratory causes of dyspnea may include these conditions:
- Asthma
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism (a blockage in the lung artery)
- Lung cancer
- Pneumothorax (a collapsed lung)
- Aspiration (breathing in food, liquid, or other foreign material into the lungs)
2. Cardiovascular causes of dyspnea may include these conditions:
- Congestive heart failure
- Pulmonary edema (accumulation of fluid in the lungs)
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Pericardial tamponade (fluid accumulation in the sac around the heart)
- Valvular heart disease (one or more of the heart valves are damaged)
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Intracardiac shunting (abnormal blood flow between the chambers of the heart)
3. Neuromuscular causes of dyspnea may include these conditions:
- Chest trauma with fracture
- Obesity
- Spinal cord dysfunction
- Phrenic nerve paralysis, myopathy, or neuropathy (Myopathy refers to muscle disease, while neuropathy refers to nerve damage.)
4. Psychogenic causes of dyspnea may include these conditions:
- Hyperventilation syndrome
- Psychogenic dyspnea (mental or emotional cause of a physical symptom)
- Vocal cord dysfunction syndrome
- Foreign body aspiration
5. Other systemic illnesses that may cause dyspnea include:
- Anemia
- Acute renal failure
- Metabolic acidosis (too much acid in the blood)
- Thyrotoxicosis (thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone)
- Cirrhosis of the liver (scarring and damage to the liver)
- Anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction)
- Angioedema (swelling of the skin and tissue beneath the skin)
6. Other causes can be:
- Anxiety attack
- High altitude
- Sudden temperature change
- Obesity (2)
- Air pollution
- Allergies
- Extreme physical activities
- Chemotherapy
When to See a Doctor
Most of the time shortness of breath can be managed on your own without professional help. However, if you experience the following symptoms, you should seek medical assistance right away:
- Chest pain
- Unstable breathing for a long time
- No improvement in dyspnea
- The feeling of something being stuck in the airway
- Frequently experiencing breathlessness
- Wheezing or tightness in the chest
- Swelling of the ankles
- Fever
- Cough
When is dyspnea an emergency condition?

Dyspnea should be considered an emergency condition if the person experiences uncontrollable shortness of breath. If left untreated, it can be life threatening as prolonged breathing difficulties can cause a decrease in oxygen levels in the body.
Emergency medical help should be sought immediately if dyspnea is accompanied by other symptoms, such as bluish lips or skin, mental confusion, blurry vision, or tightness in the chest.
Most-Asked Questions About Dyspnea
What medications are used for the management of dyspnea?
Shortness of breath can be managed by:
- Inhalers and pumps to dilate the respiratory tract
- Anti-asthmatic drugs if you suffer from asthma
- Antihistamines for allergic symptoms
- Syrups for clearing the lungs and airway
- Drugs for reducing sputum for better breathing
- Antibiotics for infections
What is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a condition where a person has trouble breathing at night while sleeping. It can be fatal, extremely hard to manage, and life-threatening.
In this condition, your breathing stops and starts during sleep by itself, making it hard to fall or stay asleep. It can also be defined as disrupted breathing during sleep. (13)
How is dyspnea treated?
When treating dyspnea, the focus is on addressing the underlying condition that is causing it, especially in cases of sudden onset as it may be a medical emergency.
Diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays, ECG, arterial blood gases, echocardiography, and diabetes screening may be recommended by the doctor to determine the severity of dyspnea and to identify the root cause of the problem. (2)
What is the first-line treatment for dyspnea?
Depending on the underlying cause of dyspnea, your doctor may prescribe medications such as bronchodilators to help open the airways, steroids to reduce inflammation, or pain relievers. (2)
How is dyspnea diagnosed and evaluated?
When diagnosing and evaluating dyspnea, it is important to recognize that it is a subjective experience that can be influenced by emotional factors. There is a distinction made between acute and chronic dyspnea, with the latter persisting for more than 4 weeks.
While history taking, physical examination, and observation of breathing patterns can often lead to an accurate diagnosis, up to 30%–50% of cases may require further diagnostic tests such as biomarker measurements or other ancillary tests.
In cases where there are multiple underlying conditions, establishing a diagnosis may be more challenging. (14)
Can eating fresh ginger help with dyspnea?
There is some evidence to suggest that eating fresh ginger may help with dyspnea.
Ginger contains active components that have been shown to induce bronchodilation, which means they help to open up the airways, by affecting the levels of calcium ions in the muscles that control breathing.
While more research is needed to fully understand the effects of ginger on dyspnea, it is believed that incorporating ginger into the diet may have some beneficial effects on respiratory function. (15)
Final Word
Shortness of breath or dyspnea refers to the inability to breathe properly. It can be described as not being able to get enough air.
Dyspnea is usually associated with heart and lung problems, but it can also occur for many other reasons, which should be addressed to get relief from the condition.
If home remedies are not enough to manage the condition, seek medical help as the doctor will suggest a treatment suitable for you.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


