In this article:
Pneumothorax is a condition in which air leaks outside of the lungs and collects in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. This air can put extreme pressure on the lung, causing it to collapse.
Different Types of Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax generally has two broad categories depending on the cause, namely, spontaneous pneumothorax (without injury) and traumatic pneumothorax (related to injury).
Spontaneous pneumothorax is further divided into:
- Primary spontaneous pneumothorax: This occurs in patients without a known lung disease.
- Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: This occurs in patients who have an underlying lung condition, such as COPD, cystic fibrosis, and cystic lung disease.
Traumatic pneumothorax is further divided into:
- Iatrogenic: Develops after a procedure or surgery in the lungs or when patients are placed on a ventilator (breathing machine).
- Non-iatrogenic: Develops after an accident or injury to the chest. (1)
Causes of Pneumothorax
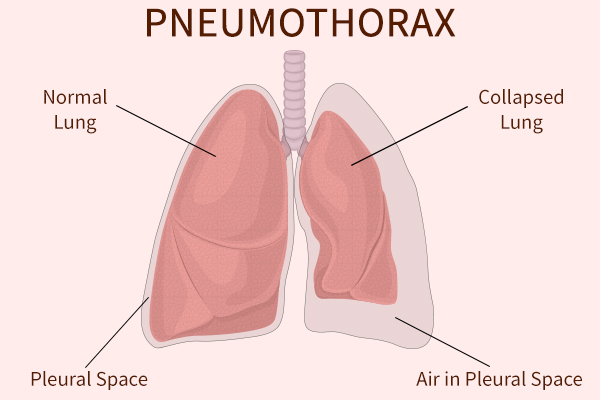
Pneumothorax can develop after a chest or lung injury, generally from an accident or surgery/procedure done near the lungs. It can also develop without injury in patients with certain underlying conditions, which include:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is caused by smoking
- Cystic fibrosis, a congenital condition in children that causes lung injury and frequent infections
- Lung infections
- Cystic lung disease, a condition in which the lung has abnormal air-filled pockets that can burst open
Rarely, patients can develop pneumothorax without any identifiable cause.
Symptoms of Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax can occur without any symptoms, especially if the lung collapse is mild or limited.
Otherwise, the condition is characterized by shortness of breath and sharp, stabbing chest pain on the side of the pneumothorax. Both these symptoms usually have a sudden onset.
Diagnosing Pneumothorax and Treatment
Pneumothorax is usually diagnosed with a chest X-ray. At times, it can be diagnosed with an ultrasound or CT scan of the lung. Pneumothorax can be treated surgically or nonsurgically depending upon the cause, size, and extent of the problem.
Patients with a small pneumothorax without any symptoms can often be managed by giving extra oxygen and monitoring with repeated chest X-rays to see if the condition is resolving on its own.
Patients with a large pneumothorax or symptoms from the condition usually require removal of air from the cavity around the lung. Depending on the size and cause, occasionally, the air can be sucked out using a needle.
In most cases, however, the treatment requires placement of a small tube in the lung cavity through a hole between the ribs to remove the air. This tube generally stays for a few days until all the air is drained out and the leak in the lung has healed. (2)(3)
Precautions to Be Taken When Suffering From Pneumothorax
Once discharged from the hospital, the patient should continue to follow up with their healthcare provider to ensure adequate treatment for pneumothorax and if they have any underlying lung condition.
Patients who had pneumothorax in the past should discuss with their healthcare provider before air travel or scuba diving as it can increase the chances of recurrence. Be aware of the symptoms of pneumothorax, and contact your healthcare provider right away if there is any sudden onset of shortness of breath or chest pain.
Tension Pneumothorax: A Medical Emergency
Tension pneumothorax develops when the pressure inside the lung cavity exceeds atmospheric pressure.
Trapped air under high pressure in the lung cavity can lead to a complete collapse of the lung and can prevent blood flow to the heart chambers, which in turn could keep the heart from pumping effectively.
Tension pneumothorax is a medical emergency, which can cause significant breathing difficulties, low oxygen levels in the body, and very low blood pressure. It usually happens when patients are on a ventilator in the intensive care unit (ICU).
Most-Asked Questions About Pneumothorax
Can pneumothorax heal itself?
Yes. Depending on the cause and size of pneumothorax, it can heal itself with supplemental oxygen and time.
What lifestyle changes should be made when suffering from pneumothorax?
Patients should try to refrain from smoking tobacco and other substances, as these have shown to increase the chances of developing a pneumothorax.
Are smokers prone to pneumothorax?
Yes. Smokers are prone to have primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) as smoking causes airway inflammation. In fact, most people who develop PSP tend to be smokers.
In one study, authors showed smoking increased the relative risk of developing PSP 9 times higher in women and 22 times higher in men. (4)(5)
Why is pneumothorax common in tall, thin men of 20–40 years of age?
PSP, which develops without injury in patients without an underlying lung condition, is more common in tall, thin men of 20–40 years of age. (5) PSP generally happens from the rupture of small blebs (air pockets between lungs and pleura) in the cavity between the lung and chest wall.
It is hypothesized that tall men tend to have more blebs on top of the lung due to the increased stretch during lung development.
Can high stress levels lead to pneumothorax?
No, stress does not contribute to the development of pneumothorax.
Are dietary changes helpful in treating pneumothorax?
No, your diet has no connection with the development of pneumothorax.
Final Word
Pneumothorax can be the result of various reasons, which may or may not be identifiable. It is marked by a buildup of air between the lung and chest wall, which puts pressure on the lung, triggering shortness of breath, chest pain, low oxygen level, and eventual lung collapse in severe cases.
While mild cases are mostly self-resolving with required self-care, more serious ones will require breathing assistance and proper treatment. The treatment for this condition has to be tailored according to each individual case, which requires a proper diagnosis to pin down the root cause and understand the severity of the damage.
Thus, medical consultation must be sought if the condition is suspected. Since certain causes of pneumothorax are recurrent, people who have had this problem once must take proper precautions to avoid future episodes.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


