In this article:
Antibiotics are a class of medication with a chemical formulation that kills or inhibits bacterial growth. (1) They can be in the form of topical ointments, oral pills, and sprays and may be available over the counter or with a prescription.

The first antibiotic pill was created in the 1940s, (2) and its use has only increased over the years, so much so that the entire medical world is overwhelmingly dependent on these medications for treating a wide array of bacterial infections.
The excessive use of antibiotics has rendered them ineffective against multiple strains of bacteria that have evolved and learned to surpass the mechanism of these medications. Plus, the fact that they are basically chemicals means that they come with side effects and increase the toxic load of your kidneys.
Moreover, they kill the good bacteria along with the harmful ones, disrupting the healthy microbiome inside the body and leading to adverse health effects. Thus, too much reliance on antibiotics is counterproductive and must be avoided.
While you cannot do away with these life-saving drugs altogether, there are ways to minimize their use. This can be done by trying some natural ingredients that are credited with strong antibacterial properties.
For centuries, traditional medicine has employed the healing power of such ingredients to combat various bacterial infections, and many holistic doctors still swear by them.
However, much of this is based on anecdotal evidence and lacks adequate scientific support. More rigorous research needs to be conducted to understand the mechanism, efficacy, and safety of such unconventional antibiotics.
So, it is always a good idea to run them by your doctor before using them.
Natural Antibiotics and How to Use Them
Here are some natural ingredients that may help treat bacterial infections.
1. Garlic
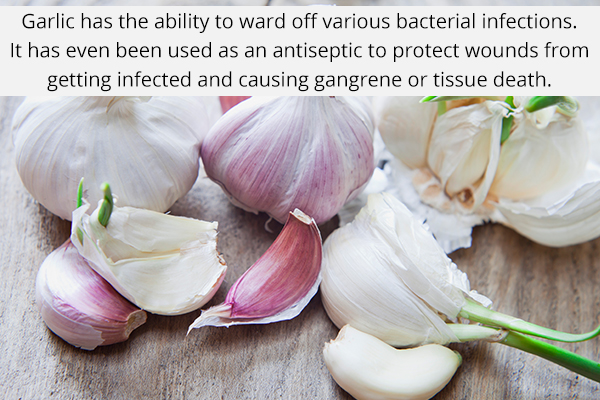
The medicinal use of garlic goes back to various ancient civilizations including the Romans, Greeks, Babylonians, and Egyptians. For thousands of years, this natural ingredient has been used in Chinese medicine and Ayurveda to address a variety of illnesses and infections. (3)
Thus, it’s safe to say that the healing potential of garlic has stood the test of time. Much of it can be attributed to its main active compound allicin, which is found in the root bulb of the plant, along with other sulfur compounds.
One such therapeutic effect of garlic is its ability to ward off various bacterial infections. It was even used as an antiseptic during the first two world wars to protect wounds from getting infected and causing gangrene or tissue death.
The good thing is that this natural ingredient provides potent antibacterial effects with minimal side effects, which is not the case with conventional antibiotics.
How to use:
- Crush and eat 2–3 raw garlic cloves every day to build your immunity against bacterial as well as other types of infections. (4)
- You can also add freshly crushed garlic to your salads, soups, and beverages.
Note:
- Garlic releases allicin when it is crushed, so you must crush raw garlic right before consumption to maximize its antibiotic effects.
- Cooking garlic will only destroy the allicin due to the heat and thereby reduce the healing potential of garlic. So, it’s best to consume it raw and crushed.
2. Honey

Honey exhibits unique antibacterial properties that inhibit infections on several levels, making it harder for bacteria to develop resistance against it. (5)
The therapeutic effect of honey can be attributed to its content of hydrogen peroxide, natural sugars, and polyphenolic antioxidant compounds as well as its acidic nature.
Thus, honey uses different mechanisms to launch a multipronged attack against infection-causing germs but without affecting the essential growth of good bacteria, which is not the case with conventional antibiotics.
This helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome and saves you from the undue digestive distress that is associated with antibiotic drugs. Plus, good bacteria are important for maintaining your immunity and overall health.
Honey can also kill those strains of bacteria that have developed resistance to multiple antibiotic drugs, but this remedy works better when used along with an antibiotic. Another advantage honey has over traditional antibiotics is that it does not cause undue side effects and is also effective against viruses. (6)
How to use:
- Eat a mixture of equal amounts of honey and cinnamon once a day to bolster your immunity during an infection.
- Use honey to sweeten your tea, smoothies, and juices, which is another easy way to incorporate it into your daily diet and reap its health benefits.
3. Grapefruit seed extract

Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) is credited with exceptional broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity that can kill more than 800 different strains of bacteria and viruses as well as more than 100 different strains of fungus and parasites. (7) This covers a wide range of both gram-negative and gram-positive microbes. (8)
GSE is also loaded with antioxidants that can neutralize free radicals, strengthen immunity, and help relieve chronic digestion problems.
How to use:
- For skin infections: Mix 8–10 drops of GSE in 1 tablespoon of water, and then apply to the infected area for 15–20 minutes before rinsing it off.
- For acne treatment: Dampen your face and palms, pour 2–3 drops of grapefruit seed extract into your hands, lightly massage it in your face, leave it on for 5–10 minutes, and then rinse it off.
- For internal use: Add 10–15 drops of GSE in ½ glass of water, mix it well, and drink this solution 2–3 times daily.
4. Oregano/oil of oregano

Oregano is rich in several phytonutrient compounds such as phenols, terpenes, and terpenoids that exhibit potent antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Carvacrol, a monoterpenoid, is the most abundant of all the phenols found in oregano and has the ability to kill a wide range of infection-causing microbes. Thymol is yet another monoterpenoid phenol in oregano that is credited with natural antifungal and immunity-boosting effects.
The therapeutic potential of oregano is most concentrated in the oil extracted from it, known as oregano oil or caracole. This essential oil is best known for its potent antibacterial activity, which was found to be comparable to many traditional antibiotics. (9)
If that wasn’t enough, it may even prove effective in controlling bacterial infections that are resistant to various antibiotic medications. These include MRSA bacteria, which cause staph infections.
How to use:
- For foot or toenail infections: Fill a tub or bucket with warm water, mix in 2–3 teaspoons of oregano oil, and immerse your feet in it for 30–40 minutes. Do this once a day for a week.
- For sinus and other upper respiratory infections: Boil some water in a pot, add a few drops of oregano oil to it, and inhale the steam. Do this once a day until the infection goes away.
Disclaimer:
- Oregano essential oil is very strong in its pure form and can irritate or burn your skin if applied directly. Thus, always dilute it with a carrier oil before topical use.
- This oil is not to be ingested as it can lead to toxicity.
5. Goldenseal

Goldenseal is a medicinal herb that is commonly used as a digestive aid and natural antibiotic. It is often taken along with another herbaceous plant called echinacea, which also exhibits similar healing properties. Both these ingredients increase each other’s potency to provide better results.
Goldenseal may help increase the number of white blood cells in the body and strengthen its ability to fight bacterial infections, but more studies are needed to confirm this claim.
How to use:
- For internal use: Steep 1 teaspoon of goldenseal powder in 1 cup of hot water, strain, and drink this warm herbal tea once daily.
- For external use: Mix the oil from a few vitamin E capsules with 1 teaspoon of goldenseal powder, mix them well, and apply the paste to the infected area thrice daily.
Note: Do not consume this herb for more than a few weeks at a stretch.
6. Turmeric

Turmeric has widely been used in Ayurvedic and Chinese medicinal systems for centuries to alleviate a variety of ailments. It is quite effective in treating a wide range of bacterial infections due to its strong antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
It even works against some antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria such as MRSA and can be used topically to treat the staph infection caused by them.
Turmeric can also be applied to wounds and skin lesions to make them heal faster. (10) When applied to an open wound, this antimicrobial agent helps protect the damaged skin from getting infected.
Plus, you can take turmeric internally to improve your immunity and help your body fight the infection from the inside.
How to use:
- For wound healing and clearing skin infections: Mix a pinch of turmeric with some organic honey, and apply the mixture to the wound or infected area.
- For better immunity: Add 1 tablespoon of turmeric powder to 5–6 tablespoons of honey, mix them together, and store the mixture in an airtight container. Consume ½ teaspoon of this mixture 2 times a day. You can also ask our doctor to start you on a turmeric supplement. (11)
7. Echinacea

Echinacea is a medicinal herb that has traditionally been used for treating blood poisoning, open wounds, diphtheria, and a wide variety of bacterial infections for thousands of years.
Nowadays, it is mainly known for relieving colds and flu. (12) It works well with goldenseal to fight bacterial infections and bolster your immunity.
How to use:
- For eczema, psoriasis, and open wounds: Apply echinacea cream or ointment to eczema or psoriasis patches and open wounds to protect the sensitive damaged skin from bacterial infection.
- To build immunity: Consume 1–2 cups of echinacea tea daily. You can also ask your doctor to put you on an echinacea supplement.
8. Olive leaf extract

Oleuropein is the chief phenolic compound found in olive leaf that possesses considerable antimicrobial activity against various bacterial strains, including some that are resistant to traditional antibiotics.
Oleuropein is also credited with potent antiviral properties (13) and helps enhance your immunity.
How to make olive leaf extract at home:
- Finely chop a handful of fresh olive leaves.
- Put them in a lidded glass container.
- Pour in enough vodka to completely immerse the leaves.
- Close the lid and keep the container in a dark corner for 4–5 weeks.
- After the waiting period, strain the liquid from the container into another one using a clean cheesecloth.
- Use this homemade olive leaf extract to fight bacterial infections.
Another option is taking olive leaf extract in supplement form, but only after consulting your doctor.
9. Cinnamon

The main component of cinnamon oil is an organic compound called cinnamaldehyde (CAD), which can help clear certain bacterial infections. It works by breaking down the protective layer covering the bacterial cells to destroy them from within.
This effect was studied on the environmental bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which causes a wide range of deadly infections, especially in hospitalized patients.
CAD also inhibits the bacteria’s ability to grow and spread. (14)
How to use:
- Mix some cinnamon and honey in 1 glass of water, and drink this tonic to get rid of colds, coughs, and bladder infections.
- Mix some cinnamon with honey, and apply this paste to acne lesions, insect bites, painful tooth, eczema patches, ringworm rash, and other skin infections.
10. Neem oil

Neem oil exhibits multiple healing properties that have long been used in traditional medicine for alleviating a variety of diseases, but it is most prized for its exceptional antimicrobial activity. It can kill a variety of pathogens, which include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
No wonder neem oil is often used in the treatment of lice, ringworm, scabies, and various bacterial skin infections. It was even found effective in clearing some sexually transmitted bacterial infections such as gonorrhea. (15)
Neem oil can even eliminate bacteria that have developed a resistance to conventional antibiotics. This was demonstrated in a 2016 study wherein neem oil was used on 107 strains of MRSA bacteria that are resistant to a whole class of antibiotic medication. Researchers found that all the bacterial strains were killed within 12 hours of being exposed to neem oil, of which 56 strains were destroyed within 1 hour of exposure. (16)
How to use:
- Use skin and beauty products that contain neem as one of the main ingredients to reduce the risk of skin infections.
- Consult your doctor about taking neem supplements to clear toxins, pathogens, and parasites from the body.
11. Ginger
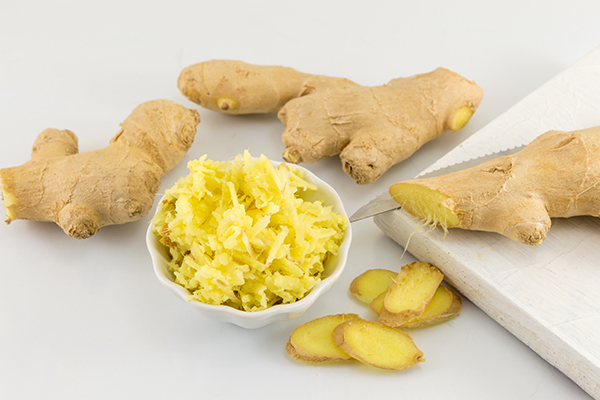

Ginger works as a natural antibiotic to ward off and treat many bacteria-related illnesses. (17)
Fresh ginger is particularly effective against food-borne bacteria such as salmonella. It also exerts antibacterial activity against respiratory and periodontal infections.
How to use:
To prevent bacterial infections:
- Grate a 1-inch piece of fresh ginger and boil it in 1½ cups of water for 10 minutes. Strain the liquid in a cup, mix in some honey and lemon juice to taste, and drink this ginger tea every day.
- Use dry or fresh ginger in your cooking as much as you can.
- Consult your doctor about taking ginger supplements.
Risks of Natural Antibiotics
Natural antibacterial agents rarely cause side effects on their own, but they can interact with other medications, supplements, or foods and cause adverse reactions. They can also exacerbate some preexisting health conditions.
So, exercise caution and consult your doctor before trying any natural antibiotic to manage infections.
Final Word
The invention of antibiotics revolutionized the field of medicine and greatly reduced the severity and mortality rate associated with certain ailments. They continue to be a key part of healthcare. However, many patients treated with antibiotics often suffer from undue side effects that range from mild allergic reactions to serious gastrointestinal distress.
You can try a bunch of natural remedies that are known to exhibit similar bactericidal activity as conventional antibiotics minus the side effects.
Just make sure to consult your doctor before self-treating with these natural antibiotics to make sure they are safe for you and will actually work against your particular infection. They may not be the best choice for serious infections, so don’t take any risks.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


