In this article:
Neem oil contains a unique mix of organic compounds that account for its therapeutic properties. It is widely used in pharmacology and cosmetics and for making a wide range of herbal products that are safe to use. Neem oil has also been used as a natural pesticide for centuries. (1)
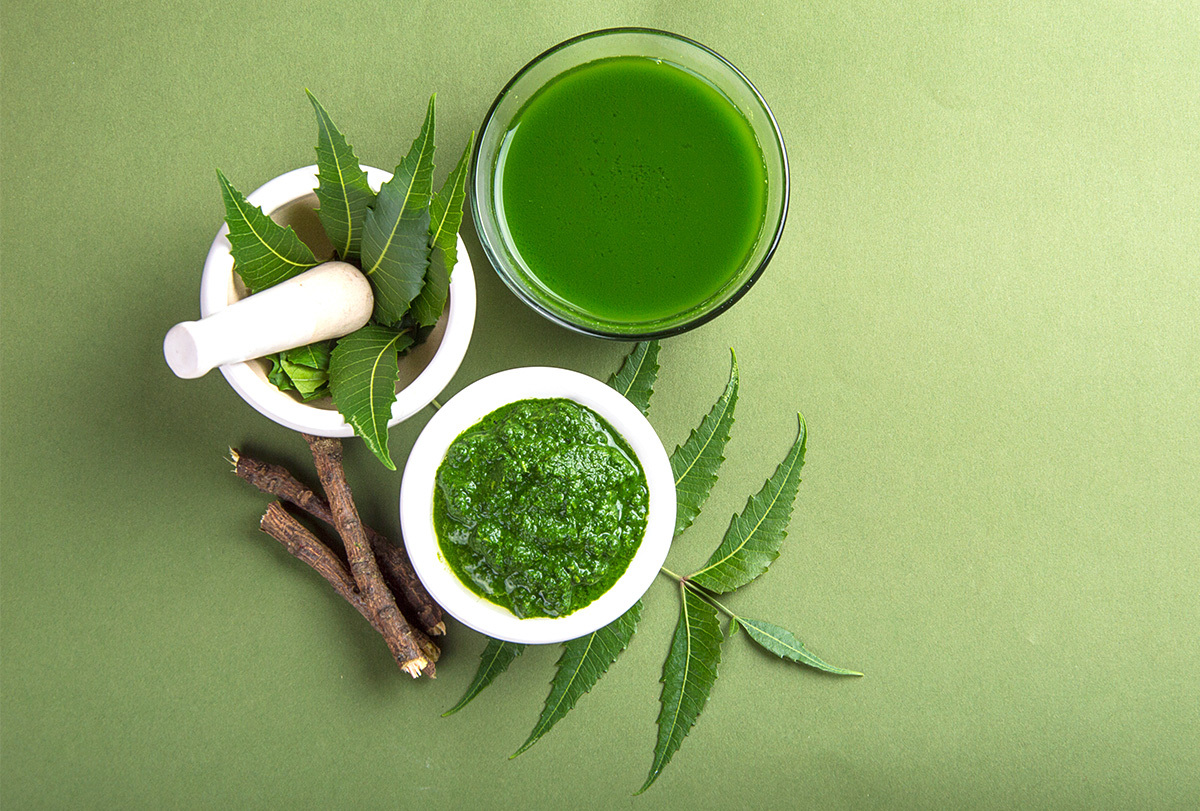

This oil is extracted from the seed kernels of the neem tree, which is native to India, but it has slowly reached other parts of the world too, including the tropics. (2)
Neem oil gives off a pungent garlicky or sulfuric smell and tastes extremely bitter. Its color can range from yellow to brown.
Benefits of Using Neem
Neem is very strong and should be used with care or in a carrier substance, such as a neutral oil. Neem oil should only be taken internally as a tincture (in alcohol) or inside of a capsule, such as a supplement.
The common benefits of neem extract or oil are as follows:
1. Treats dandruff
There are a few reasons neem is suggested to help with dandruff. Neem contains vitamin E, which can help skin cells regenerate and thus lead to a healthier scalp.
Neem extract has also been proven to be an antifungal against (3) several types of human pathogens in a study, one of which was candida. Candida causes a yeast infection, and it is thought that dandruff can be a result of yeast overgrowth.
2. Treats skin problems
Because of its antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties, neem has been shown in a recent review of studies to have an effect on skin conditions, such as acne, psoriasis, and eczema, (4) all of which are conditions of the skin that involve inflammation.
In addition, as mentioned earlier, neem contains vitamin E, which is an antioxidant that is found in most lotions that rejuvenates skin cells.
3. Kills head lice
Some anti-lice shampoos contain neem extract. One study found that a treatment time of only 5 minutes, with even better results after 10 minutes, was enough to kill the larvae in eggs and those that had already hatched. Neem was believed to block the lice from receiving oxygen. (5)
Another reason for such mechanism could be a compound in neem called azadirachtin. This compound interferes with insect hormones and makes reproduction difficult. (6)
4. Promotes oral health

The compounds nimbidin and azadirachtin can help to remove bacteria, and this effect can benefit mouth health.
Certain parts of the neem tree, such as the leaf, have antiseptic and astringent properties. For this reason, they are often used to make toothpaste and mouthwash. (7) Long ago, people even brushed their teeth with neem twigs!
5. Purifies blood
Neem may help purify blood, thanks to all its antioxidant effects, which may play a role in picking up toxins or impurities from the blood and taking them to the liver and the kidney, two organs that are directly responsible for the elimination of toxins from the body. (8)
6. Controls diabetes
Neem may help manage diabetes in several ways. Neem contains quercetin, which has been shown in some studies to lower blood glucose. Neem also contains many flavonoids and polyphenols that are helpful in glucose control.
Human studies are very rare on this topic, and the majority of them have been done in rats or in vitro models. There have been some of these that suggest neem compounds restore B cells needed to produce insulin.
In one human study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, neem was shown to have an effect on lowering blood sugar when used in addition to metformin therapy. (9)
It is generally agreed that people with diabetes should consult their doctor before using neem, since it can lower blood sugar.
7. Prevents intestinal worms
Neem has antiparasitic properties. The mechanism might be similar to how neem can kill lice, via the compound azadirachtin, which, as noted earlier, prevents insects from multiplying.
Neem leaves, seeds, and oil (a component of some lice treatment shampoos) are parts of the plant that can be used to eradicate intestinal worms. You may consume neem tea to get the internal benefits.
8. Relieves arthritis inflammation
There are several ways that neem can benefit arthritis. As mentioned earlier, neem oil contains anti-inflammatory properties and has long been used to soothe arthritic joints.
It is believed the compound called catechin does the job. Other studies suggested it is quercetin that reduces inflammation. (10)
Still others postulate that polysaccharides, which are a type of fat found in oils, are responsible for the reduction in inflammation in joints. Other studies also add that neem reduces not only inflammation but also pain.
9. Fights nail problems
Fungal nail infections are commonly caused by dermatophytes and candida. In a clinical trial, neem oil extract at a 5% concentration was as effective as a standard prescription dermatological cream at treating nail fungus (11) when applied twice daily for 4 weeks.
10. Other benefits
In addition to those already mentioned, neem has been suggested to have antitumor properties, making it potentially useful against cancer. Neem also can boost the immune system and can be used as a form of contraception and birth control.
Nutritional Content of Neem
One cup of neem (Indian lilac) leaves contains less than 50 calories, 2 grams of protein, 8 grams of carbs, and a trace of fat.
Neem leaves are a very good source of fiber, iron, and calcium, one cup providing nearly 30% of the RDA of each of these nutrients. They are also a good source of magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium and low in sodium. Neem oil contains oleic, linoleic, and palmitic fatty acids. (12)
Oleic acid is an omega-9 fatty acid or a monounsaturated fat. Linoleic acid is a polyunsaturated fat, and palmitic acid, also known as palm oil, is a saturated fat.
Ways to Include Neem in Your Diet
Neem comes in the forms of powder, capsule, oil, or juice. You can take it as neem powder or an extract in the form of a supplement. (13) Drinking neem tea is also a common way of consuming neem.
Neem fruits can also be eaten, raw or cooked, and sometimes are made into drinks, including a fermented alcohol drink. The refined neem oil from the plant can be used for cooking.
What Parts of the Neem Tree Are Useful?
Each and every part of the neem tree can be useful in some way or another. Medicines are usually made from its bark, leaves, and seeds and sometimes from its roots, flowers, and fruits.
To date, more than 400 compounds that are beneficial for the body or used for medicinal purposes have been identified and/or extracted from various parts of neem. (14)
Safe Usage
Here are some precautions to be taken when including neem in the daily diet
- Neem should not be used by pregnant women, because it can cause abortions in some cases.
- Neem should also be used with great care by anyone with an immune system condition, particularly autoimmune diseases.
- Neem can stimulate the immune system and, thus, should not be used by people taking immune-suppressing drugs.
- Neem should not be used by children, as severe neurological side effects, including seizures, coma, and even death, have been noted as reactions to neem oil.
- Neem should be used internally in the form of supplements or tea.
- As mentioned earlier, neem is associated with reducing blood sugar. Therefore, if you are diabetic or are taking blood sugar-lowering medications, such as metformin, you should consult your doctor before using neem to avoid the risk of lowering your blood sugar too much.
Side Effects of Using Neem Oil

Although neem oil possesses healing properties, it can have some deleterious side effects. Oral consumption of neem oil is not safe for kids or infants. People with preexisting renal or liver problems should not use neem oil without their doctor’s approval.
Plus, neem oil is known to have a slight sedative effect, which can cause drowsiness and fatigue. So, it is important to use it properly, carefully, and in recommended doses. It’s best to consult your doctor before starting the medicinal use of neem oil to avoid such side effects.
Final Word
Every part of the neem tree has some medicinal benefit, which is why it is often referred to as “nature’s drugstore.” In fact, this plant has long been used in Ayurveda for treating a variety of ailments.
Neem oil packs considerable healing potential and can be used for treating a variety of skin, hair, and body ailments.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


