In this article:
Eggs are among the most universal and versatile dietary staples. Chickens eggs are the most popular variety in the United States. However, various cultures around the world eat eggs from other birds, such as ducks, ostriches, and quail.

The complexity of eggs allows them to have a range of functions in food while also providing nutrients necessary for optimal health.
The Inside of an Egg
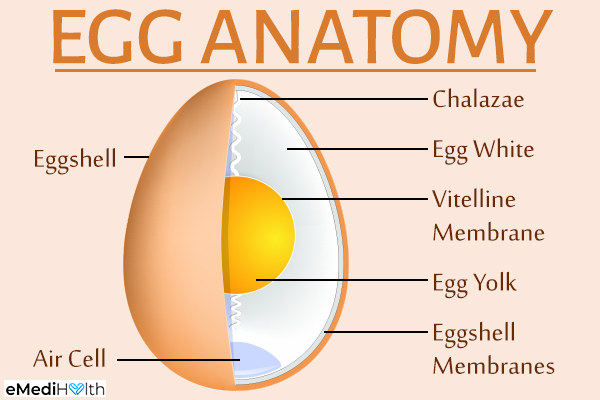
The egg is made up of two-thirds egg white and one-third yolk. Egg whites are classically labeled as “diet food” because they are low in calories, fat-free, and high in protein. On the other hand, the egg yolk is demonized for its high cholesterol content.
However, recent research shows that cholesterol in foods does not necessarily correlate with blood cholesterol levels. (1) Therefore, it is more important to optimize the type of fat in the diet rather than minimizing dietary cholesterol. (2)
While one large egg yolk contains 1.5 grams of saturated fat, it also has 3.5 grams of healthy, unsaturated fat, including omega-3 fats. Therefore, egg yolks can safely be included in a heart-healthy diet plan.
Nutritional Value of Eggs
With only 70 calories, one egg provides 12% of the daily value of protein. Eggs have one of the highest biological values, of 93.8%. This means that they supply amino acids in a pattern almost exactly fit to what the body needs.
Moreover, eggs are rich in riboflavin, biotin, vitamin B12, iodine, selenium, and choline. Eggs also provide vitamin D, vitamin A, folate, phosphorous, omega-3 fats, and the antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin. Eggs do not contain any sugar, carbohydrates, or vitamin C.
Eggs contain the following nutrients. (3)
| Nutrient | Amount in 1 Large Egg | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 70 kcal | |
| Protein | 6 g | 12% |
| Total Fat | 5 g | 6% |
| Saturated fat | 1.5 g | 8% |
| Cholesterol | 185 mg | 62% |
| Vitamin D | 1 mcg | 6% |
| Phosphorous | 99 mg | 14% |
| Vitamin A | 80 mcg | 8% |
| Riboflavin | 0.2 mcg | 15% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.2 mcg | 20% |
| Biotin | 11 mcg | 15% |
| Iodine | 28 mcg | 20% |
| Selenium | 15 mcg | 25% |
| Choline | 150 mg | 25% |
Types of Eggs

Eggs must be chosen, handled, stored, and prepared properly to enjoy their benefits. Some of the types of eggs on the market include:
- Conventional cage eggs: Hens live in a climate-controlled room with 60–80 square inches to move around in.
- Cage-free eggs: Hens live in a climate-controlled room with about twice the space as conventionally caged hens.
- Free-range eggs: Hens live in a barn that also has access to an outdoor area where they can roam freely.
- Pasture-raised eggs: Hens have at least 108 square feet to roam outdoors.
- Organic eggs: Hens are usually free-range or pasture-raised and are given certified organic feed. Organic feed is produced without pesticides and other chemicals.
- Nutritionally enriched eggs: Hens are fed extra omega-3 fats or vitamins such as vitamins D and E. The eggs from these hens have higher levels of these nutrients.
- Processed eggs: The eggs are deshelled and processed into an egg product. Processed eggs include liquid, dried, and frozen eggs.
- Brown eggs: The color of an egg is determined by the breed of hen and type of poultry feed. Color does not reflect the nutritional value.
- Local eggs: Produced by farmers in your area. These eggs are often available at farmers’ markets.
- Grade AA, A, and B: Grading reflects the quality of the egg, but not the nutritional value. Grade AA is the highest quality, and grade B is the lowest.
- Size: Chicken eggs range in size from peewee to jumbo. Large eggs are the preferred sizes in most recipes.
The type of egg you choose depends on your needs and priorities.
Benefits of Eating Eggs
Eggs provide a variety of nutrients and therefore have many health benefits.
1. Improve brain function

Lecithin found in egg yolks is made up of fatty acid, a phosphate group, and choline. Adequate choline intake is associated with better memory and learning abilities. (4)(5)
Choline and vitamin B12 participate in the chemical reaction that prevents the buildup of homocysteine in the body, (6) thus reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. (7)
2. Aid in maintaining a healthy weight
Many people find that eating eggs helps them feel more satisfied on a low-calorie diet. This allows them to lose weight without feeling hungry and deprived.
Eggs are nutrient-dense, provide high-quality protein, and contribute to overall diet quality. High-quality protein, such as that found in eggs, promotes maintenance of muscle mass during moderate weight loss. (8)
3. Facilitate muscle building
Research confirms that protein is essential for muscle recovery and growth. (9) The high-quality protein in eggs can be quickly absorbed and efficiently utilized to optimize muscle growth.
It is also important to consume the yolk along with the egg white as it contains various nutrients and proteins, contrary to the belief that the yolk contains only fat. (9)
Caution: The myth that eating raw eggs is better for muscle building is not true. Eggs may contain Salmonella that can cause sickness or death, so never consume them raw. Always cook eggs or buy pasteurized products.
4. Promote a healthy pregnancy
Many of the nutrients needed to nourish the chicken embryo also benefit a human fetus during pregnancy.
Choline is needed for cell reproduction, growth, and brain development. (10)(11) Moreover, eggs provide other essential nutrients, including omega-3 fats and protein, that help with healthy fetal development.
Caution: Pregnant women should not consume eggs that are raw or unpasteurized due to the risk of Salmonella infection.
5. Strengthen bones
Calcium, milk, phosphorus, and vitamin D are important for building and maintaining strong bones. One egg provides 15% of the daily value of phosphorus and 6% of the daily value of vitamin D.
A study in 2018 found that daily egg consumption was associated with greater bone density in 13-year-old adolescents. (12)
6. Improve mood
Low levels of B vitamins are associated with depression. (13) Eggs are a reliable source of B12 and other B vitamins. Omega-3 fats have also been found to reduce depression. Studies show that 1.5–2 grams of omega-3 fats per day effectively improves mood. (14)
7. Protect eye health
The antioxidants in eggs, namely, lutein and zeaxanthin, are found in the eye pigments of the retina. These antioxidants prevent cell damage in the retina and reduce the risk of macular degeneration.
Eating eggs has shown to significantly increase retina pigment concentrations of lutein and zeaxanthin. (15)(16)
ALSO READ: Eye Health: 6 Important Nutrients and 10 Best Foods for Your Eyes
8. Promote skin and hair health

Eggs can be a beneficial addition to your beauty routine. Many of the nutrients in eggs promote healthy skin, nails, and hair:
- Consuming eggs provides protein and collagen that help keep skin taut and wrinkle-free.
- Phosvitin and phosphoglycoprotein are proteins in the egg yolk that control excessive melanin production and thus prevent pigmentation. (17)
- Biotin helps keep skin and hair cells healthy. Eggs contain 15% of the daily value of biotin.
- Eggs can even be used as a shampoo. It is high in protein and nutrients that cleanse, shine, and nourish hair.
How to Use Eggs in Your Recipes
In addition to adding flavor, color, and texture, the unique chemical makeup of eggs makes them useful in many cooking applications. Here are a few of the many ways that eggs are useful in the kitchen:
1. Eggs are natural emulsifiers
An emulsifier helps water and fat mix together when they normally separate. This quality is useful in salad dressing, mayonnaise, ice cream, and baked goods.
2. Eggs provide leavening
The egg white produces foam when whipped and can incorporate air into baked goods, including waffles and sponge cakes.
3. Eggs are binders
When eggs coagulate, they bind the ingredients of a recipe together. This keeps meatloaf, crab cakes, and baked goods from being crumbly.
4. Eggs are used as a glaze
When brushed on baked goods, an egg wash gives products a shiny crust.
5. Eggs are thickening agents
Eggs thicken pudding, sauces, and custards.
How to Store Eggs

Consider these tips for storing your eggs:
- Eggs should be stored in the fridge on the main shelves, not the door. This ensures they remain at a safe temperature.
- Store eggs in the carton to keep them fresh and to block any contamination.
- Pay attention to the expiration date on the container.
- Unwashed farm eggs have a longer shelf life than washed eggs from the grocery store.
| Egg | Recommended Storage Time |
|---|---|
| Store-bought shell eggs | 3-4 weeks or best by date |
| Unshelled yolks or whites | 2-4 days |
| Hard-boiled eggs | 1 week |
| Egg dishes | 3-4 days |
| Pickled eggs | 1 month |
| Frozen whole eggs | 4 months |
| Unwashed farm eggs | 6-8 weeks unrefrigerated or 3 months refrigerated |
Are Eggs Always Safe to Eat?
While rare, consumption of raw eggs can cause the following problems:
1. Salmonella poisoning
Salmonella in eggs can cause sickness and death. Raw eggs should always be cooked or pasteurized before consumption.
2. Biotin depletion
Overconsumption of raw eggs can lead to a biotin deficiency. This deficiency is characterized by dry skin, rashes, brittle hair, hair loss, and fatigue.
Eating Eggs if You Have Certain Medical Conditions
With careful planning, eggs can be included in the diets of people with medical conditions.
Kidney disease
In proper portion sizes, eggs can provide needed protein for those with kidney disease with or without dialysis. However, an excess of protein can be harmful. Moreover, the yolk is high in phosphorus, which may need to be limited depending on the stage of kidney disease.
ALSO READ: 10 Foods That Are Good for the Kidneys
Diabetes
Eggs do not contain any carbohydrates. When paired with a moderate portion of carbohydrate foods, the protein in eggs can help prevent blood sugar spikes following meals and snacks.
Can Eggs Cause Allergy?
Egg allergy is one of the most common allergies among children. An estimated 1%–2% of children in the United States have an egg allergy. (18)(19)
See a medical provider if the child has any of these symptoms after eating eggs, which indicate an allergy:
- Upset stomach
- Hives
- Itching
- Rash
- Swelling
- Tingling mouth
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of tongue or throat
- Wheezing
- Persistent cough
- Dizziness
Fortunately, many children will outgrow an egg allergy by age 6.
Expert Answers (Q&A)
Answered by Lily Chen, MS, RDN, APD, FAND
In general, eggs offer a wealth of benefits. Boiled eggs, in particular, are a great choice as a nutritious snack or as an integral part of the main meal eaten daily.
All foods should be consumed as part of a balanced diet. An egg or two a day is a great way to meet protein and nutrient needs.
Eating eggs daily by itself is not the main culprit for weight gain as its high amount of protein helps to keep you full and satisfied. It is usually what you eat with your eggs, which causes weight gain.
Instead of processed meats such as bacon or sausage, pair eggs with nutritious sides such as a vegetable, fruit, or whole grains.
Eggs are a source of high-quality protein that helps with body growth and repair, including hair.
Final Word
Eggs add high-quality protein and an array of nutrients to a well-balanced, healthy diet. With the number of health benefits and uses of eggs in the kitchen, it is no wonder they are eaten and loved worldwide.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


