In this article:
Do you suffer from an uneven skin tone? Don’t worry, you are not alone – millions of people around the world have experienced uneven skin pigmentation at some point in their lives.

Blotchy skin can appear as patches of red, blue, or brown skin and mostly occurs on the back. It can be brought on by temporary factors and in some cases a sign of a serious health issue.
Regardless of the underlying cause, blotchy and uneven skin color may be disconcerting and can affect one’s self-esteem.
Causes of Blotchy and Uneven Skin Tone
Several factors can lead to discolored patches on the skin. Some of these are:

1. Extreme weather conditions
Extreme weather conditions such as extreme heat, cold winds, or excessive humidity can lead to dryness and harsh red patches on the skin.
2. Excessive sun exposure and too-hot showers
Too much exposure to direct sunlight can expose you to harmful UV rays. It may cause dermatitis and sun allergies, heat rashes, red blotches, and unevenly tanned skin.
Extremely hot showers strip away the skin’s natural oils, which ultimately leads to blotchy and uneven skin.
3. Excessive stress
Extreme stress is known to cause skin problems and also aggravate preexisting skin conditions. (1) Rosacea, eczema, and melasma flare-ups can be triggered by stress.
4. Inflammatory skin disorders
Several skin disorders are known to cause patchy and uneven skin tones. These skin disorders include:
- Eczema: Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin disease that causes painful inflammation, irritation, and rash. (2)(3) It can cause scaly red patches and blisters on your skin. Eczema affects 1%–3% of adults worldwide.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disorder that may cause blotchy skin. It mostly affects the kneecaps, elbows, and scalp. (4)(5) Symptoms of psoriasis include redness and inflammation, scaly skin, and itching.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin disorder that is characterized by scaly skin and red patches. It is mostly triggered by an overgrowth of yeast and affects oily areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, chest, and back. (6)
- Rosacea: Rosacea is another very common skin condition that can lead to red patches and uneven skin tone. It causes dilation of the blood vessels, which can make the skin appear blotchy and flushed.
- Pigmentation disorders: Pigmentation disorders cause changes to natural skin color and may lead to an uneven skin tone. Skin color is determined by a pigment known as melanin, which is produced by specialized cells in the body called melanocytes. Changes in melanin production can cause skin pigmentation disorders, which can significantly affect one’s social life and lead to body image issues. (7)
- Melasma: Melasma is one such hyperpigmentation disorder that can cause brown patches on the skin. It may occur due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, melanocyte destruction due to sun exposure, (8) and several other factors.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: Many people suffer from post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) after an acne flare-up. It is characterized by brown to purplish spots on the skin. It is caused by the skin’s healing process after bouts of inflammation such as acne and dermatitis. It can be triggered by UV light exposure. (9)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an inflammatory disease in which the immune system fails to recognize the body’s own tissues and starts attacking them. This condition is an autoimmune disorder that can affect the entire body, (10) including the skin. Lupus can cause a scaly, butterfly-shaped rash on the cheeks.
Treatment Options for Blotchy and Uneven Skin
Many treatment options are available to cure hyperpigmentation. Here is a comprehensive list of the most commonly prescribed medications and procedures for this condition:
Topical treatment:

1. Azelaic acid
Azelaic acid is a medication usually prescribed to cure post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). Tyrosinase is an enzyme required for the production of melanin. Azelaic acid is a tyrosinase inhibitor and effectively reduces melanin production. (11) This leads to a more even skin tone.
2. Metronidazole cream
Metronidazole cream is an antibiotic and anti-inflammatory medication that is used in the treatment of rosacea. (12) It helps reduce inflammation and redness.
3. Ferulic acid serums
Ferulic acid is a natural compound found in the cell walls of plants. It is an antioxidant (13) that can improve the overall look of the skin. Ferulic acid is also a tyrosinase inhibitor and can decrease melanin production to brighten your skin.
4. Niacinamide
Niacinamide, also known as vitamin B3, helps decrease hyperpigmentation (14) and smoothen your skin texture. It slows down the action of melanin on the skin and brightens your skin tone.
5. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is another tyrosine inhibitor that helps decrease melanin levels in the body. (15) It has antioxidant properties that are useful in the treatment of acne scars and redness.
6. Hydrocortisone creams
Hydrocortisone creams are topical steroid formulations used in the treatment of skin irritation, inflammation, and rashes. They are used as a low-potency steroid treatment for itching and irritation caused by eczema.
Higher-potency hydrocortisone creams may be used in the treatment of other conditions such as eczema.
Note: High-potency corticosteroids should not be used during pregnancy unless advised by an obstetrician as they can affect the weight of the baby. (16)
In-office treatment:
1. Chemical peels
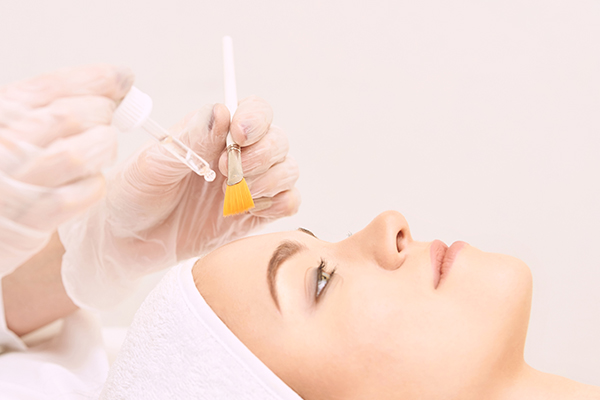
Chemical peels promote skin regeneration by removing the outer layer of epidermal cells from the skin surface. This helps achieve an even skin tone and brighter complexion. (17) Most chemical peels contain one or more of the following acids:
- Glycolic acid is absorbed deeply into the skin and helps cure common skin issues such as wrinkles, acne, and hyperpigmentation. (18) Glycolic acid peel is the most common alpha-hydroxy acid peel, also known as fruit peel.
- Salicylic acid (19) is a well-known exfoliating agent that helps get rid of damaged cells. It is commonly used in the treatment of blotchy skin and hyperpigmentation.
- Lactic acid can help cure uneven skin tone by removing the outer skin layer, stimulating collagen production. It is an excellent exfoliant and can help reduce dark spots and can make your skin look younger.
- Mandelic acid is one of the largest alpha hydroxy acid peels and penetrates the skin slowly and uniformly, making it an ideal peeling agent of choice for sensitive skin. (20) Mandelic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid peel (AHA peel) that can be a better choice for sensitive or aging skin over glycolic acid and other AHAs as it works at a more moderate and steadier pace.
- Ferulic acid is a powerful antioxidant and helps cure dark spots and discoloration by inhibiting melanin production. (21)
2. Intense pulsed light treatment
Intense pulsed light therapy is a nonsurgical procedure that has multiple healing effects on the skin. It helps promote collagen production, (22) constricts blood vessels, (23) decreases melanin synthesis, etc. The overall result is a younger, brighter-looking skin tone.
3. 1,064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser
This laser treatment works by focusing a laser beam on unhealthy skin cells to kill them.
A Q-switched Nd:YAG laser generates a 1,064-nm wavelength of light with strong pulses. This laser is effective in killing the targeted diseased area without affecting other skin cells. Thus, it is widely used in the treatment of hyperpigmentation and other pigmentation issues. (24)
4. Microneedling
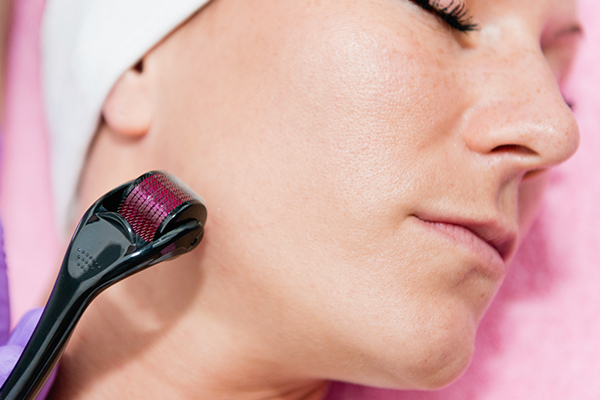

Microneedling, as the name suggests, is a procedure in which the skin is pricked with tiny needles to activate the skin’s healing process. This stimulates the production of new skin cells, elastin, and collagen, making the skin tighter and brighter. (25)
Final Word
Blotchy and uneven skin can cause embarrassment and self-consciousness. But keep in mind that most cases of hyperpigmentation are temporary and resolve with time.
Contact a doctor immediately if you do not see an improvement in the condition of your skin even after trying over-the-counter medications.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


