In this article:
Dermatitis is the medical term for different types of skin inflammation or irritation. It can range from a dry, red, itchy mark on the skin to plaques, scaling, crusting, and extreme itching, known as pruritus.
Dermatitis affects over 30 million people in the United States. The most common form of dermatitis is known as eczema or atopic dermatitis, affecting 4%–10% of adults and 13% of children. (1)
Contact dermatitis, another common form of dermatitis, has a prevalence of 15%–20%. (2)
Types and Causes of Dermatitis
Dermatitis has various types, depending on the cause and symptoms. The most common ones are:
1. Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
It is characterized by inflamed, dry, red, and itchy skin that can develop due to an allergic reaction, genetics, bacterial infection, immune problems, or environmental conditions.
The itchy rash generally appears suddenly and can ooze fluid. In children, eczema appears as a dry rash and scales on the face, generally within 1 year of age. The condition causes severe symptoms with food allergens such as nuts, soy, wheat, cow’s milk, eggs, and fish. (3)
2. Contact dermatitis
It results from contact with allergens or irritants such as perfume, nickel, rubber, preservatives, hair dye, body fluids, detergents, harsh chemicals, friction, and cement.
While allergens trigger an immune response, the irritants can damage the skin barrier and cause symptoms. The symptoms of contact dermatitis may be more severe in those with atopic dermatitis.
3. Seborrheic dermatitis
This is common in people with oily skin or scalp, due to yeast overgrowth on the skin surface. It can also be triggered by stress.
Seborrheic dermatitis is characterized by a greasy, swollen, reddish rash with a yellowish-white crust. It usually flares up in winters.
In infants, seborrheic dermatitis is known as cradle cap and appears as crusty, greasy, scaly, yellowish patches on the scalp. (4)
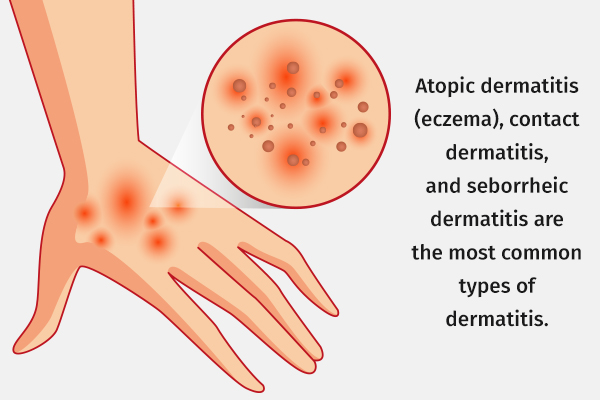
Other less common types of dermatitis include:
- Nummular dermatitis. This generally appears as coin-shaped patches on the skin and occurs due to a skin injury. The irritable patches persist for a few months.
- Stasis dermatitis. Also known as gravitational dermatitis, venous stasis dermatitis, or venous eczema, it causes inflammation of the skin in the lower leg and ankles. The condition is caused by varicose veins and poor blood circulation in the lower leg.
- Neurodermatitis. This form of dermatitis initially doesn’t present any visible symptoms. Instead, the patient first feels an itchy sensation, which causes an urge to scratch the skin, eventually leading to skin damage.
- Perioral/periorificial dermatitis. More common among women, this type of dermatitis manifests as tiny, red bumps around the mouth. This may occur as a reaction to moisturizers, cosmetics, topical steroids, and sunscreen or due to repeated lip licking.
- Diaper dermatitis. It refers to a rash on the baby’s skin due to diaper use. This happens because movement in a wet or full diaper can easily damage the skin.
Symptoms of Dermatitis
Different types of dermatitis exhibit varying symptoms, the most common ones being:
- Itching
- Redness
- Swelling
- Flaky skin
- Blistering
- Creasing
- Skin dryness and cracks
- Rashes
- Skin thickening
- Skin discoloration
- Pain
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Scaling
- Crusting
- Scarring
Medical Treatment for Dermatitis
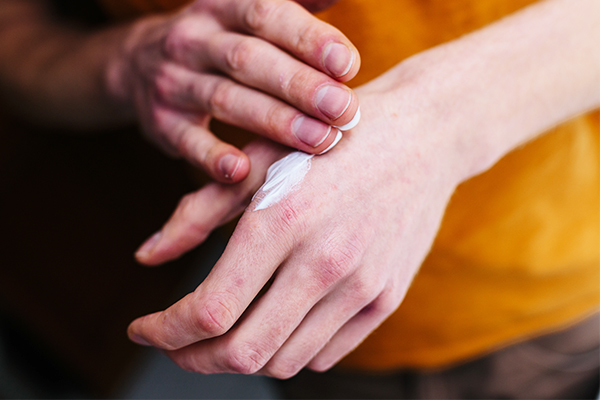

The doctor may prescribe the following treatment modalities, depending on the type and severity of dermatitis:
- Topical steroid creams or ointments. Topical steroids are the most common mode of treatment for dermatitis. Generally, topical steroids are to be applied to the affected areas once or twice daily for 5–15 days.
- Pimecrolimus cream. Pimecrolimus 1% cream exhibits anti-inflammatory effects against atopic dermatitis and has lesser side effects than topical steroids. (5)(6)
- Antihistamines. These are used to help reduce irritation and, therefore, are especially useful at night.
- Antibiotics. Infection-caused dermatitis, such as those due to Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, may require antibiotics such as erythromycin or flucloxacillin.
- Phototherapy. The doctor may suggest phototherapy, which involves the use of UV rays to suppress the immune system. Alternatively, photochemotherapy, a combination of phototherapy and light-sensitizing compounds such as psoralen, may be used.
Diagnosing Dermatitis
Since the symptoms of different types of dermatitis can be similar, it is essential to consult a doctor for the proper diagnosis and suitable treatment. The following tests can help determine the cause and type of dermatitis:
- Physical examination and medical history. The doctor will examine your skin and take note of the location, pattern, and appearance of the rash. He will also inquire about your medical history and allergies, if any.
- Patch test
- RAST testing
- Skin biopsy
Risk Factors for Dermatitis

The following factors can increase the chances of dermatitis flare-ups:
- Medical problems: Health problems such as congestive heart failure, HIV/AIDS, and Parkinson’s disease can increase the risk of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Age: Atopic dermatitis generally develops in infants.
- Hazardous occupation: People whose jobs involve the use of metals, gloves, and cleaning supplies or those that work in healthcare centers are at a higher risk of contact dermatitis.
- Allergies and asthma: People with allergies, asthma, hay fever, or a family history of eczema are prone to atopic dermatitis.
When to See a Doctor
It is recommended to visit a doctor if you develop symptoms of eczema or dermatitis, especially if:
- The skin irritation is hampering your daily activities.
- You have constant pain.
- You have symptoms of a skin infection.
- Home remedies and self-care are unable to improve the infection.
Final Word
Dermatitis is a common skin issue that causes rashes and itchiness on the skin. It can occur due to various reasons, ranging from allergies to infections. Different treatment modalities are available depending on the cause and type of dermatitis.
It is essential to resist the urge to scratch your skin to relieve itching as it can damage the skin, allowing the entry of bacteria, which can infect deeper layers of the skin and cause life-threatening complications. Therefore, it is best to seek timely treatment for all kinds of dermatitis.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


