In this article:
Shingles is a skin condition caused by the varicella-zoster virus. This virus can remain inert in the body for a long time after an infection and may get reactivated by certain factors, leading to shingles. (1)(2)
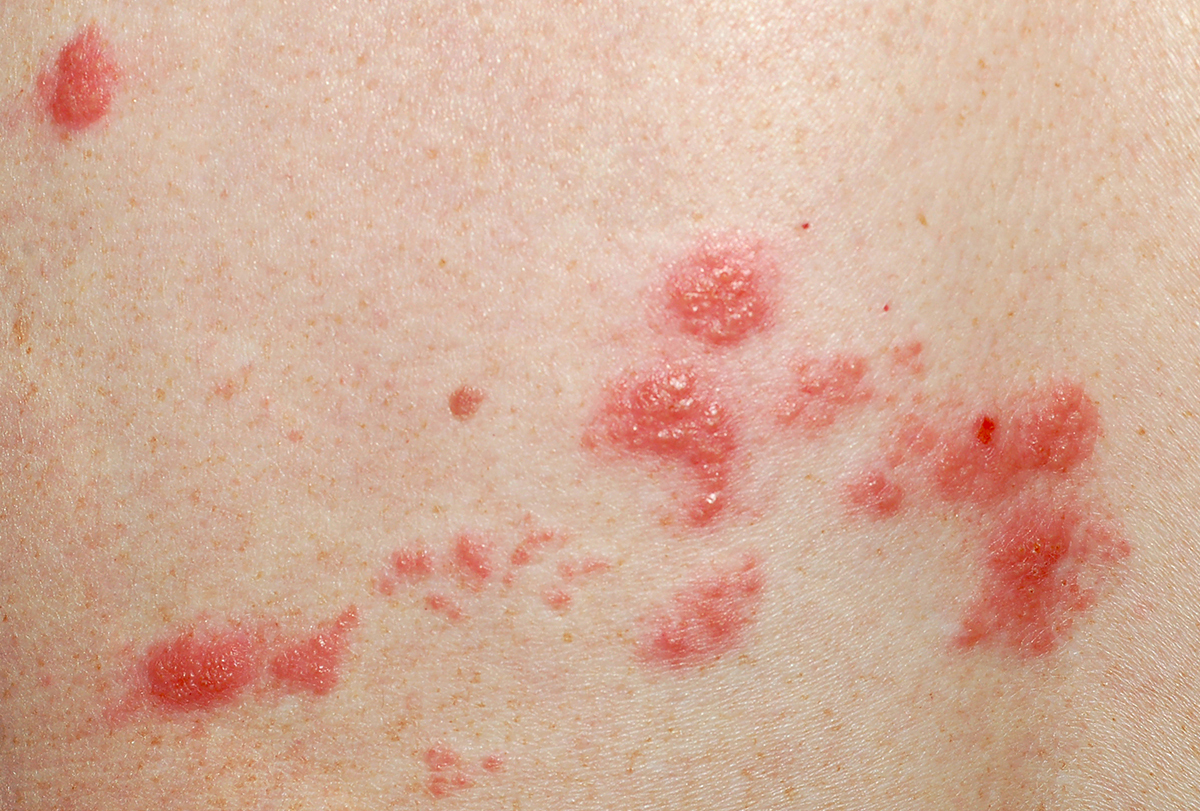
The varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox in children and may cause herpes in adults. It commonly causes shingles in middle-aged and elderly people. (3)(4)
Home Remedies for Shingles
Certain home remedies can help you heal from shingles fast. However, they are not a substitute for medical treatment and should be used only to help relieve the symptoms.
1. Apply a capsaicin-based ointment
Capsaicin creams are made of capsaicin, a chemical compound derived from chilies.
Capsaicin is an effective pain relief agent and can be used to soothe the pain associated with shingles rash and blisters. (5) It is available over the counter in most places. (6)
How to use:
- Apply a small amount of capsaicin cream to the blisters and rash at least 2–3 times a day.
- Wash your hands with soap afterward. (7)
Disclaimer: It is advisable to wear gloves when applying the ointment. (7)
2. Use licorice

Licorice contains a compound called glycyrrhizin, which is associated with viral-inhibiting properties and can help stop the replication of the varicella-zoster virus.
Note that, although licorice may be safe to use topically, it is not known if it can cause side effects when taken orally. (5)
How to use:
- Add a few drops of water to 1 teaspoon of licorice powder.
- Apply this paste to the affected areas.
- Wash it off after drying.
- Wash your hands with soap.
3. Give eucalyptus oil a try
Eucalyptus oil is well known for being an effective inhibitor of viral replication. It has potent antimicrobial properties that help fight infections. (8)
Note: Do not use eucalyptus oil without diluting it with a carrier oil as it can irritate the skin.
How to use:
- Add ½ teaspoon of eucalyptus oil to 2 tablespoons of coconut oil.
- Apply this mixture to the affected area twice a day.
4. Use calendula topically

Calendula flowers are widely known for their medicinal properties.
Calendula extract exhibits antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory qualities. It can help soothe the itching and pain in the shingles rash as well as help decrease viral replication. (9)
How to use:
Apply a small amount of calendula lotion or gel to the affected area twice or thrice a day.
5. Try using apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is another natural agent that exhibits strong antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps soothe the rash and fight the infection. (10)
How to use:
- Apply an apple cider vinegar compress to the affected area.
- Alternatively, you can add a couple cups of apple cider vinegar to your bath water and soak in it.
6. Neem leaves can help

Neem leaves have traditionally been used as a shingles cure in Ayurvedic medicine. They have antiviral properties and can help decrease the infection and inflammation associated with the condition. (11)
How to use:
- Crush a few neem leaves to make a paste, and apply it to the affected area.
- Alternatively, you may take a bath in neem leaves soaked in water.
Causes of Shingles
The varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox in children. However, when you recover from the condition, this virus can remain inactive in the nerves for years.
Certain conditions such as the onset of chronic disease, weakened immunity, and infections can activate this virus and cause a painful rash with blisters known as shingles.
Symptoms of Shingles
Here are some common symptoms of shingles:
- Red rash in a localized area
- Pain, tingling, and itching
- Blisters
- Slight fever
- Pus
- Diarrhea (12)
Treatment for Shingles

Common treatments prescribed for shingles include:
- Antiviral medicines can decrease the viral load and help your body fight off the infection. It can help decrease the severity of the rash as well. (13)
- Pain-relieving medications such as capsaicin ointments and lidocaine patches may be prescribed by your doctor in severe cases. (14)
- A shingles vaccine has been approved in 2018 for use in adults above 50 years of age.
Prevention for Shingles
The best way to protect yourself from developing shingles is to take the shingles vaccine. (15) This vaccine is administered in two doses over 6 months and is most useful in people over 50 years of age. (16)
If you or anyone you know develop shingles, make sure to follow certain precautions:
- Avoid contact with people who have a compromised immunity: people with cancer, chronic illness, or HIV infection and pregnant women.
- Do not touch the rash, and keep it covered. (17)
Risk Factors for Shingles
There are a few common risk factors associated with a herpes zoster breakout. The severity of the disease and its associated risks may vary due to a number of factors such as the age of the patient and their immunity.
Here is a list of some common complications associated with shingles: (18)(19)
- Scratching the blisters may lead to secondary bacterial infections.
- A shingles rash on the face may spread to the eyes and cause serious eye problems, even blindness.
- Inflammation and fluid accumulation may occur in the brain.
- Lung infections may also occur. (20)
Note: In rare cases, untreated shingles may lead to death.
Most-Asked Questions About Shingles
How is shingles treated?
Shingles is usually treated with antiviral medications. Your doctor may also prescribe pain-relieving medicines to help dull the pain. (21)
Why do shingles keep returning?
The varicella-zoster virus can remain inactive in the body for a long time. Compromised immunity, chronic illnesses, etc., can activate the virus and cause a return of shingles. (18)
Does having chickenpox make you immune to shingles?
No, people who have had chickenpox can develop shingles. (2)
How long will it take for my shingles rash to go away completely?
The time of treatment can depend on your age, overall health, how soon you start medical treatment, and other factors. (12)
Is shingles contagious?
Shingles itself is not contagious. However, the varicella-zoster virus is contagious. (22)
Final Word
Shingles is a common condition but can lead to serious complications in immunocompromised individuals.
It is important to seek medical treatment as soon as possible to prevent the rash from spreading. With proper treatment, shingles should resolve in a few days. You can try the home remedies given above to accelerate the rate of recovery. (22)
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


