In this article:
A thick head of hair can boost your self-esteem and is one of the most desired beauty traits for both men and women.

Everyone tends to have more or less the same number of hair follicles, but not necessarily the same quality or type of hair. Whether you have curly, straight, or wavy hair depends entirely on the hair follicle.
No matter what your hair type is, you must adopt a proper hair care regimen to maintain or improve the quality of your hair and undo the daily damage induced by environmental pollutants and aging. Thus, the quality of hair care will determine the strength and beauty of your hair.
Your hair care routine should be customized according to your hair type and the extent of hair damage that needs to be undone, but it must include the nourishment, moisturization, and well-being of the scalp as well.
Only a healthy base will sprout a strong, shiny strand of hair. (1) Multiple factors can impact the rate of your hair growth, which may range from genetic and lifestyle contributors to your age, daily diet, and general health.
Hair Structure
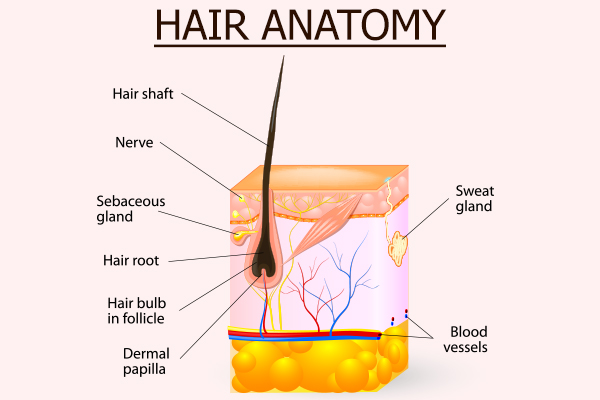
Hair is essentially made up of a tough structural protein called keratin and each strand consists of the following parts:
- The shaft emerges out of the scalp and is visible to the eye.
- The invisible root is embedded inside the scalp, from where it stretches down to the deeper layers of skin.
- The root is enclosed within a thin covering of connective tissues and skin known as a hair follicle. The hair follicle not only protects the hair root but also provides anchorage to the exposed outgrowing part of the hair, which is the shaft.
- The hair follicle is attached to a sebaceous gland right underneath the scalp surface. The oily secretions of these glands help to keep the scalp naturally moisturized.
- The lower end of the hair root expands to form a bulb-like structure, which is the hub of new hair cell generation.
- An indentation at the bottom of the hair bulb, called hair papilla, is lined with multiple capillaries that supply blood, oxygen, and nutrients to the hair root. The hair papilla is primarily responsible for hair nourishment with little to no cell division.
Stages of Hair Growth
The hair growth cycle has three phases.
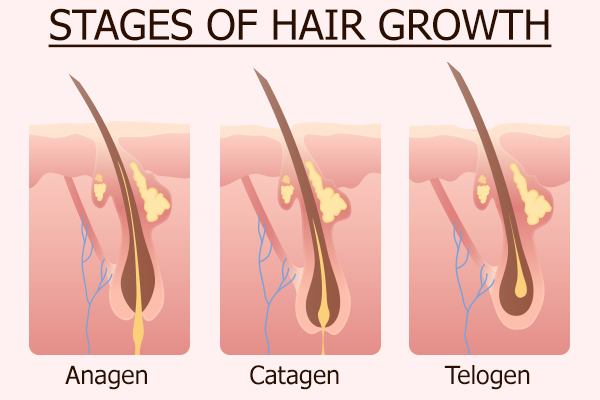
1. Anagen or the growth phase
This phase is not only the most active phase of the hair growth cycle but also the longest, lasting for nearly 2–6 years.
During this phase, there is a rapid multiplication of hair cells at the base of the hair follicles, which translates into the development of new hair shafts and elongation of existing ones. The longer the anagen phase, the longer the hair.
2. Catagen or the transition phase
This phase marks the end of active hair growth and triggers the regression of the hair follicle. During this stage, the bottom of the follicular sheath shrinks and attaches itself to the hair shaft, cutting off blood and cell supply to the root. Thus, the hair eventually turns into a club hair.
Catagen is the shortest phase of the hair growth cycle, which lasts for only 1–2 weeks before the hair enters the final phase. Only 1% of hair is found in this stage.
3. Telogen or the resting phase
Once the hair is completely formed, it enters this final stage. At a time, almost 10% of the hair on your head is fully mature. The hair sticks for approximately 3 months on the scalp, before naturally falling out.
Normally, people lose around 100 strands of hair per day and new hair starts forming in their place instantly. The empty hair follicle becomes a place for rapid hair cell proliferation leading to the growth of new hair.
Factors That Can Slow Hair Growth

Negligent hair care is not the only factor responsible for weak, unhealthy hair. Numerous other things can contribute to stunted hair growth or excessive hair loss, such as:
- Unhealthy or nutritionally deficient diet
- Side effects of certain drugs
- Elevated stress
- Exposure to environmental pollutants or radiation
- Hormonal imbalances
- Smoking
- Increased stress levels
Medical Treatments for Hair Growth

If you are suffering from hair loss, talk to your medical provider. The following treatments may be prescribed to promote hair growth:
1. Medication
Certain medicines may help reduce hair loss and promote hair growth to a certain extent.
The most common over-the-counter medication for treating androgenetic alopecia (AGA) in women is topical minoxidil, but it only promotes patchy hair growth on the top of the scalp but not around the forehead area.
Moreover, melatonin is a strong antioxidant and hair growth modulator that can serve as a potential alternative to minoxidil, as demonstrated in both in vitro and in vivo studies. (2)
Note: Pregnant women and those with heart conditions can suffer dangerous side effects from these medicines and are therefore advised to stay off them. Consult your healthcare provider before considering such medical intervention for your hair problems.
2. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy
PRP therapy may be an effective treatment strategy for hair regeneration. This intervention involves injecting the patient’s own blood into the scalp to promote natural hair growth.
The blood is drawn from some other part of the body, such as the arm, and the plasma containing the platelets is separated from the rest of the contents. The PRP concentration is then administered into the balding areas of the scalp. (3)
3. Surgery
Surgery can be considered as a last-resort treatment when all other measures fail to bring the desired hair growth.
Medical Conditions Related to Hair Loss
It is completely normal to experiences some degree of hair loss on a daily basis, but some people have it far worse than others. In some cases, the hair shedding qualifies as an actual medical problem.
1. Androgenic alopecia
Androgenic alopecia, or male pattern baldness, is a genetic disorder that is brought on by the activity of the male sex hormones called androgens. (4) Women also have trace amounts of androgens in the body and can suffer from this condition, especially if it runs in their family. (4)
The level of androgens in the body changes as one grows older or due to other factors such as menopause, ovarian cysts, and taking androgen-based oral contraceptives.
A hormonal imbalance of this kind can lead to the shrinking of hair follicles, which renders them incapable of growing new hair when the old strands fall out. While men suffer from noticeable patterns of baldness, women tend to have a more gradual and diffused thinning of hair.
2. Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune skin disorder wherein the immune system launches an attack on the hair follicles, thereby suppressing hair growth. This condition is characterized by hair fall that occurs in patches. (5)
Final Word
Few things can be as satisfying as sporting beautiful and bountiful hair. Attractive hair seems to have a life of its own and adds an extra zest in your personality.
When it comes to hair care, you have to focus on both the inward and outward well-being. Consciously making favorable dietary and lifestyle choices while using suitable hair products will help your hair reach its maximum growth potential and reduce hair fall.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


