In this article:
The air that you breathe in or out travels throughout the respiratory system via an expansive web of respiratory tubes called bronchi (singular bronchus).

The windpipe or trachea splits into the left and right bronchus, each of which branches into several smaller airways that extend all the way to the lungs.
What Is Bronchitis?
The inner walls of your respiratory airways or bronchi are lined with mucous membranes that produce a viscous, sticky substance called mucus.
In a healthy body, this mucus helps to trap any unwanted germs or irritants that may enter the respiratory tract. In the event of respiratory infection, the lining of these passages may swell up and produce excess mucus as an immune response to the incoming pathogen. This inflammation of the bronchial lining is referred to as bronchitis.
What Is Chronic Bronchitis?
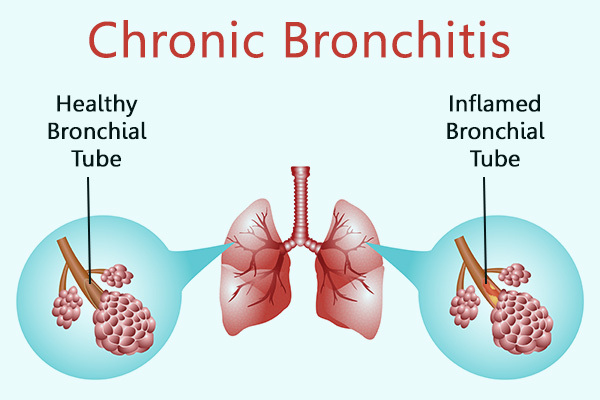
People with bronchitis develop a cough due to the inflammation of the bronchi or airways. If this cough lasts more than 3 months for 2 consecutive years, it is referred to as chronic bronchitis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in more general terms. (1)
Difference Between Acute and Chronic Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchi and is generally self-limiting, lasting from 1 to 3 weeks. (2) Chronic bronchitis generally lasts for years.
Common Causes of Chronic Bronchitis
Smoking is, by far the most common cause of chronic bronchitis.
Other causes include:
- Prolonged exposure to environmental and occupational irritants, such as air particles from indoor wood stoves, industrial vapors, and chemical fumes, can cause chronic bronchitis.
- Asthma and tuberculosis can eventually lead to chronic bronchitis/COPD.
- A propensity to contract viral and bacterial infections frequently can trigger the onset of chronic bronchitis.
Symptoms of Chronic Bronchitis

The most common symptoms of chronic bronchitis include:
- Shortness of breath
- Cough with or without phlegm production
- Wheezing, which refers to a whistling or squeaky sound produced while breathing
- Chest tightness
- Frequent respiratory infections such as colds and the flu
In severe cases, the patient may experience:
- Sudden weight loss
- Weakness in the lower muscles
- Swelling in the ankles, feet, or legs
Can Chronic Bronchitis Be Cured?
Chronic bronchitis cannot be cured but could be controlled with medication and smoking cessation. (3)
Treatment for Chronic Bronchitis

Treatment mainly involves inhalers and some medications. Patients who have COPD may require a rescue inhaler along with multiple maintenance inhalers depending on the severity of the disease.
Breathing exercises and certain cough assist devices may also help in clearing your lungs of excess mucus. Please discuss with your healthcare provider regarding specific modalities.
Lifestyle Changes to Ease Chronic Bronchitis
Patients with chronic bronchitis who implement lifestyle modifications can control and slow the progression of the disease. The most important lifestyle change to modify disease progression is smoking cessation.
Physical activity and avoidance of occupational and environmental exposure may also slow down the progression of chronic bronchitis.
Foods Recommended for Chronic Bronchitis Patients
Patients with chronic bronchitis can suffer from malnutrition as the lungs have to use more energy to breathe. It is important to eat a nutrition-rich diet to maintain good body weight and avoid being underweight or overweight. (4)
Night-Time Aggravation of Chronic Bronchitis

Sleep is crucial in keeping your mind and body healthy. You go through different sleep stages, from light to deep sleep.
As the body passes through the various stages of sleep, your lung capacity decreases, with less effort being put in by the breathing muscles and gradual narrowing of the airway.
People who have underlying lung disease are not able to cope with the resultant loss of breathing reserve and therefore have more symptoms at night. Please discuss with your healthcare provider if you are experiencing worsening of symptoms at night, as you may require a change in the management plan.
How Serious Is Chronic Bronchitis?
Yes. Like many other chronic diseases, chronic bronchitis requires lifestyle modification, including smoking cessation and medication management.
Patients can live for many decades with the disease if adequately controlled. If it is not well controlled, it can lead to serious breathing issues, decreased quality of life, and hospitalization, among other things.
Can Chronic Bronchitis Turn Into Pneumonia?
Patients with chronic bronchitis are at much higher risk of getting lung infections, including pneumonia. Chronic bronchitis does not per se turn into pneumonia. (5)
Can Chronic Bronchitis Lead to Permanent Lung Damage?
Smoking and other above-mentioned causes can lead to permanent lung damage, especially damage to the bronchial tubes. This damage leads to chronic cough, which is described as chronic bronchitis.
Is Chronic Bronchitis Reversible?
No. It is similar to diabetes or hypertension where you cannot cure it but can control it with medications.
Is Chronic Bronchitis Contagious?
No. People who have chronic bronchitis are not contagious unless they are suffering from flare-ups, where they can catch lung infections and can transmit viruses/bacteria to someone else.
Can Chronic Bronchitis Lead to Lung Cancer?
No. People with chronic bronchitis have higher chances of developing lung cancer due to smoking, but lung cancer is not directly related to chronic bronchitis.
Final Word
Chronic bronchitis, as the name suggests, is usually a lifelong struggle that can be managed but not cured. This condition has to be taken seriously since it affects perhaps the most basic but essential body function – breathing.
It is important for you as well as your caretakers or family members to educate yourselves about the problem and the ways to manage attacks at home. You must stick with your medication but also be prepared for any emergency. Since the slightest irritant can trigger an episode, you must always carry an inhaler with you.
The doctor-prescribed treatment has to be coupled with proper diet, lifestyle changes, and other self-care measures to reduce the intensity and frequency of attacks.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


