In this article:
Tension headaches, also known as stress headaches, are among the most common types of headaches experienced by adult populations across the world. Although this condition affects both genders, women tend to be more susceptible to tension headaches than men.

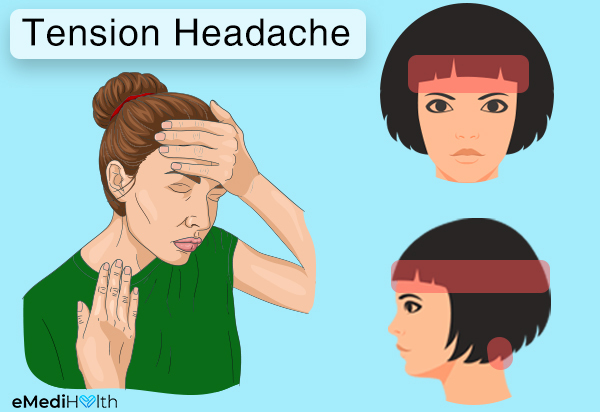
Tension headaches almost always give rise to a characteristic feeling of increased tightness or pressure across your forehead, on your temples, and at the back of your head.
Types of Tension Headache
Tension headaches fall under the following categories:
- Infrequent episodic tension headaches: Can occur less than 12 times in a year with each episode lasting from 30 minutes to 1 week.
- Frequent episodic tension headaches: May often occur, about 1–14 times a month, lasting for a period of 30 minutes to 1 week.
- Chronic tension headaches: May occur about 15 times a month lasting for hours. This type of headache may be accompanied by mild nausea.
Causes of Tension Headache
The jury is still out on what exactly causes these headaches, but the excessive contraction of the head and neck muscles may have a role to play.
Most cases of tension headaches are brought on by emotional triggers such as stress, anxiety, and depression, (1) which can make your facial, head, and neck muscles increasingly tense. They can also be the result of physical overexertion, but rarely so.
Other factors that may cause a tension headache include:
- Head injury
- Poor posture
- Impaired sleep
- Skipping meals
- Vision problems
- Eyestrain
- Excessive caffeine intake
- Teeth grinding or jaw clenching problems
- Sinus infection
- Alcohol
- Menstruation in rare cases
Signs and Symptoms of Tension Headache

The hallmark symptom of a tension headache is a feeling of a tight band clenched around your head, also termed as the “tight hatband” or “vise grip” sensation.
Your skull will feel heavy and compressed due to the clenching of the head and neck muscles. Tension headache is also described as a dull pain that radiates from the back of your head or top of your eyebrows to your entire skull and neck.
The pain may be mild to moderate and its duration depends on the type of tension headache. The characteristic pain may be accompanied by:
- Tenderness in neck, scalp, and shoulder muscles
- Trouble sleeping
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Inability to concentrate
- Heightened sensitivity to loud sounds and light
Standard Treatment for Tension Headache
The medical treatment for a tension headache depends on its symptoms, frequency, duration, and causative factors.
Infrequent tension headaches
Infrequent tension headaches can be treated per individual episode using analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or a combination of an analgesic and codeine.
Note: According to FDA guidelines, codeine is not considered safe for children or lactating women.
However, taking combination medications on a regular basis is not recommended, as it can trigger rebound headaches and can cause side effects on the kidneys, liver, and other body parts.
Medication overuse can also lead to addiction and can compromise your overall health. It is, therefore, in your best interest to consult a doctor for the appropriate dosage rather than to self-medicate.
Frequent/chronic tension headaches
Tricyclic antidepressants are the standard drug of choice for the treatment of chronic tension-type headache.
Individuals with a chronic or frequent tension headache may be prescribed amitriptyline to relieve the pain and advised to adopt some preventive strategies to stop an incoming headache.
Diagnosing Tension Headache
No diagnostic tests, as of now, can determine if your headache originates from tension. Your doctor is likely to review your case based on your medical history and family history after analyzing your symptoms.
Because tension-type headaches may mimic the symptoms of secondary headaches, there is a possibility of misdiagnosis if you do not convey your symptoms properly, such as the intensity or duration of the headache.
A CT scan or MRI of the head may be prescribed if your headache is accompanied by some unusual symptoms to rule out any underlying problem.
Risk Factors Associated With Tension Headache

It has been noted that tension headaches have a higher incidence in women than in men. The average age of occurrence in women lies between 30 and 39 years. However, with progression in age, the risk of getting a tension headache decreases in women.
Several other factors can increase your risk of getting a tension headache. These include:
- Sleep apnea or sleep disorders
- An injury or arthritis in the neck region
- Temporomandibular joint disease (TMJ)
- Certain medications
- Decreased physical activity
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Depression
- Hormonal changes in women during the premenstrual syndrome phase and menopause
Complications With Tension Headache
When not attended to, tension headaches can last for days or weeks. A tension headache can hamper your productivity and performance because of the pain and associated discomfort.
Although tension headaches are not the debilitating type, seek medical attention if you experience unusual symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- A headache that is accompanied by vomiting and fever
- A headache that brings loss of consciousness
- A headache right after an injury to your head
- A change in the pattern, frequency, or duration of the pain
- A headache not relieved by medications or taking medications more than 3 days a week
- A headache that worsens when lying down
Expert Answers (Q&A)
Answered by Dr. Martin M. Mortazavi, MD (Neurosurgeon)

The duration of a tension headache is variable and depends on the reason causing it, such as stress or too much work that leads to stress.
Yes, it is very normal.
The fastest way to get relief from a tension headache is to avoid the cause of stress. Temporarily, massage (2) and pain killers, as well as muscle relaxant medication, can help.
Tension headaches are usually caused by tension in the muscles attached to the skull, particularly those present at the back of the skull.
Care needs to be taken when performing a massage. Avoid pushing too much on the neck as excessive pressure can cause injury in the deep-seated arteries in the neck that bring blood to the brain. Any injury in these arteries can cause a stroke.
If you identify a certain cause such as work overload or familial stress, please make every effort to reduce them. Here’s how:
• Engage in running or swimming every day for almost an hour.
• Get a soft massage around your neck and shoulder.
• Read a book to learn how to deal with stress.
• In worse cases, take a mild pain killer or muscle relaxant prescribed by your doctor while you are practicing the above advice.
Final Word
Living with pain can be physically debilitating and emotionally distressing. Coping with persistent headaches can be made easier with professional assistance.
It is important to get professional help. There are neurologists that subspecialize headaches and are very well versed in nontraditional treatments.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


