In this article:
Different sorts of exercises fulfill different objectives, and an ideal workout program should include a good mix of all of them. You have to customize your workout routine to meet your individual goals with exercises. Some people are in it for losing weight, or building stamina, muscle building, or disease management.

While cardio exercises are considered good for the heart, numerous weight lifting exercises to train and strengthen your muscles. They basically target specific muscle sets to give you a sculpted physique.
The muscles use up a lot of energy while carrying the heavy equipment, which helps burn the fat and replace it with more bulging muscles.
Best Form of Exercise: Lifting Weights, Cardio, or Aerobics?
Everybody is out there trying to find the fastest and most convenient way to lose weight, but there is no ONE correct way to do that.
In order to live a healthy lifestyle by improving your body composition and decreasing your body fat percentage, you must incorporate a combination of weight lifting, cardio training, and aerobic exercises.
Strength training or weight lifting exercises are movements that provide resistance to the muscle, causing small tears in the muscle fibers. After this controlled microtrauma caused during exercise, the muscle goes through a series of repair and remodeling to heal and grow. (1)
Common Strength Training Exercises
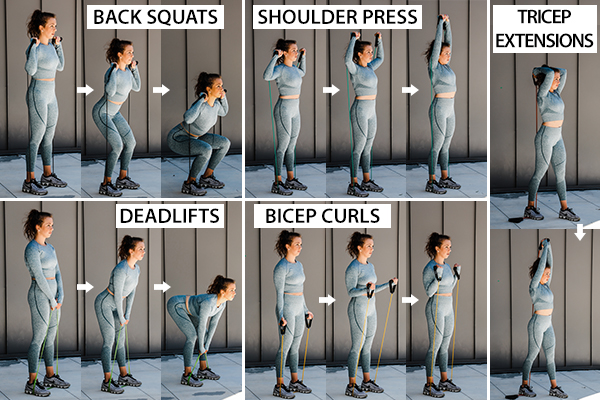
Weight lifting takes many shapes and forms. There are numerous movements for every muscle group in the body that, with some added weight/resistance, allow you to incorporate strength training into your fitness regime.
A few of the essential moves include:
- Back squats
- Deadlifts
- Shoulder press
- Bicep curls
- Tricep extensions
Health Benefits of Lifting Weights
We know that cardio training, such as running or biking, is great for getting your heart pumping and improving your cardiorespiratory system. But weight lifting comes with its own set of health benefits, such as:
- Improving tendon and ligament strength surrounding your joints
- Increasing bone density (2)
- Increasing your resting metabolic rate (3)
Incorporating weight lifting into your fitness regimen can even decrease your cholesterol, (4) reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, (5) and improve your overall body composition. These effects, in turn, help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Lifting weights and resistance training has also been reported to lower the risk of colon cancer, among other positive effects. (6)
Can Lifting Weights Improve the Quality of Sleep and Reduce Depression?
Weight lifting is also linked to reduced sleep latency and the need for sleep-aid medication, helping you fall asleep fast and naturally. (7)
Resistance training plays a positive role in day-to-day mental health as well, through the release of endorphins. Much like during cardio or aerobic workout, this hormone is released to deal with the physical stress you are putting on your body.
At the same time, resistance training increases your serotonin levels, (8) which provide that magnificent sense of well-being and happiness that helps keep depression at bay. Plus, that feeling of strength and pride after accomplishing that last heavy set is a nice added bonus.
Importance of Weight Training for Women

Because of weight lifting’s positive effect on bone density, women, in particular, should focus on incorporating it into their fitness regimen.
As women get older, they tend to lose more bone density as compared to men. This side effect of hormonal imbalances from menopause leads to bones becoming more fragile and prone to developing osteoporosis or arthritis. (9)
Lifting weights can not only reduce the risk of osteoporosis, but it can also decrease the pain from existing osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis and even improve bone health in patients with breast cancer. (10)
Drawbacks of Weight Lifting for Women
It is so important for everyone to lift weights, but many women continue to overlook it because of misconceptions and social pressures.
One big problem that holds women back from lifting weights is this myth that they will become bulky and build muscles that are “too big.” That is simply not true.
First off, not every woman has the capacity to build “big bulky muscles,” and that comes down to genetics. Generally, women have less muscle mass and lower testosterone levels, which make it almost impossible for them to develop an unusually large, muscular physique, or “bulk.”
Another cause of hesitation in women is the perception of bulk in strength training. In the first few weeks of lifting weights, people will notice a difference in their bodies. They may feel like they are “thicker” or “bulkier.” The misconception here is that women think that feeling will last forever.
Within the first few weeks of weight lifting, muscles swell from the amount of strain and pressure they go through, thus the perception of “bulk.” Once that swelling subsides, the strong lean muscles start to show!
Weight Lifting Exercises for Weight Loss
Weight lifting helps increase your resting metabolic rate (RMR) by increasing muscle mass in the body. “The microtrauma-repair-muscle remodeling processes require increased energy for at least 72 hours following a challenging strength training session.” (11)
During the initial stages of weight lifting, about the first 10 weeks, people who incorporate at least 2–3 strength training sessions per week can improve their resting metabolic rate by about 8%–9% and increase their lean muscle mass by about 3 pounds.
This helps the body burn more calories during and in between workout sessions, leading to an increase in fat burn. This is because muscles require energy (calories) to maintain, whereas fat does not.
Is It Bad to Lift Weights Every Day?

If you are considering adding weight lifting into your fitness routine, it’s best to start by strength training 2–3 days a week. Allowing your body that time to rest is crucial when weight lifting. It takes time for our bodies to repair and remodel the muscles.
If you are serious about weight lifting, you could work for a certain muscle group every third day. For example, if you train your pulling muscle groups (biceps and back) on Monday, you wouldn’t train them again until Thursday.
Your pushing muscle groups (triceps and chest) would be Tuesday and Friday, and legs and glutes would be Wednesday and Saturday.
Another thing to consider when performing weight lifting movements is to incorporate at least 30 seconds of rest in between each set, depending on the weight and quantity of the set.
If you are trying to achieve greater muscular endurance, you would perform 2–3 sets of no more than 12 reps and no more than 30 seconds of rest in between each set.
If you are trying to gain more muscular strength, you would perform 2–6 sets of no more than 6 reps with at least 2 minutes of rest in between each set. (12)
Are There Any Harmful Effects of Weight Training?
Everyone can and should incorporate weight lifting into their workout routines. People who are overweight or suffering from obesity should also incorporate weight lifting into their cardio and aerobics program.
Always consult your doctor before you start weight lifting, especially if you have any existing health problems or injuries. The only ill effect of weight lifting is improper form and adding too much weight too soon. Be patient and take things one step at a time.
Final Word
In closing, before you start any new movement, practice the movement without any added weight. Make sure that you can safely and properly perform the movement with your own body weight first, before adding even an extra 5 pounds.
To make sure you have proper form and technique for weight-bearing movements, it’s important to warm up and cool down with some good stretching movements before and after your workout. Remember to take it one pound at a time, and if any of this sounds like a bit too much to handle in the beginning, professional personal trainers are always available to help!
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


