In this article:
Climbing stairs is a daily function most people do without a thought. It is a common physical activity that can be useful for weight loss and mobility improvement as well.

However, despite the advantages, several disadvantages are also associated with climbing stairs that people should be aware of. These disadvantages can range from physical injuries to psychological stress, which may have long-term effects on an individual’s health.
What Are the Potential Disadvantages of Climbing Stairs?
If done excessively and without care, climbing stairs can lead to some disadvantages.
1. Physical disadvantages
One of the most significant disadvantages of climbing stairs is the potential for physical injury. Climbing stairs requires significant physical exertion, and if done improperly, it can result in various injuries.
Difficult for people with joint problems
Individuals who climb stairs frequently may experience joint pain, muscle strains, and sprains. In addition, those with preexisting conditions such as arthritis and osteoporosis may experience increased pain and discomfort when climbing stairs, making the activity difficult and potentially dangerous. (1)(2)
A potential risk factor for falling, especially in older adults
Falls are a significant problem for older adults, with a high risk of occurrence while climbing stairs.
According to research, around one-third of community-dwelling adults aged 65 years and over experience at least one fall per year, and up to 50% of these individuals experience multiple falls.
The risk of falls increases with age, with an annual fall rate of about 50% among those aged 85 years and over.
Falls often result in injuries, ranging from minor bruises to severe hip fractures, with approximately 25% of falls resulting in injuries. Hip fractures, in particular, are severe consequences of falls, with a 1-year mortality rate of about 25% following a hip fracture. (3)
The researchers concluded that while climbing stairs is an excellent form of physical activity, individuals should be aware of the potential risks associated with the activity, particularly if they have preexisting medical conditions.
2. Cardiovascular disadvantages
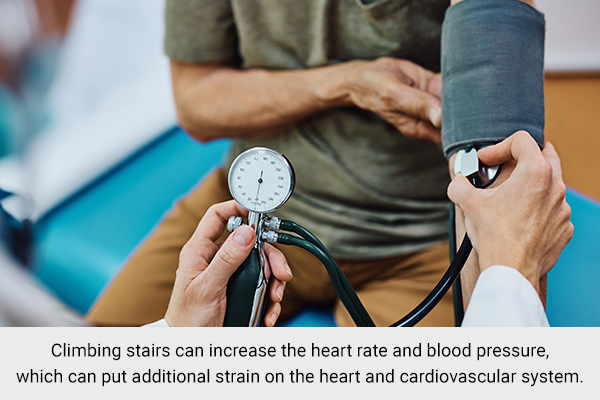
While climbing stairs is an excellent way to improve cardiovascular health, it can also have potential disadvantages. For individuals with preexisting cardiovascular conditions, such as hypertension and coronary artery disease, stair climbing may not be recommended by many experts.
According to a study, people with problems going up the stairs had elevated blood pressure. (2)
Moreover, climbing stairs can increase the heart rate and blood pressure, which can put additional strain on the heart and cardiovascular system.
According to a research study, wearing a face mask, as many did during COVID-19, during stair climbing can put a strain on the heart. Additionally, wearing a face mask during stair climbing significantly increased the pulse rate and systolic blood pressure, indicating an increased cardiovascular workload. (4)
3. Muscular disadvantages
Excessive/strenuous stair climbing can sometimes lead to muscle soreness.
A study examined participants who performed a challenging stair-climb session and found out that muscle soreness remained significantly elevated above the baseline even after 72 hours, and no interventions such as hot/cold water immersion or static stretching were helpful in combating the muscle soreness. (5)
Experts explain that this could be because climbing stairs requires a lot of muscle activity in the legs and buttocks.
4. Psychological disadvantages
In addition to physical disadvantages, climbing stairs can also have psychological disadvantages.
Falling and hip fractures due to climbing stairs have significant consequences, leading to a loss of independence and quality of life and contributing to admissions to long-term nursing and residential home care.
Even noninjurious falls from stairs have severe consequences, including a fear of falling, decreased mobility, social isolation, depression, and reduced quality of life.
Research consistently links fall incidences in older people to problems with step or stair negotiation, which could lead to injuries. (3)(6)
Moreover, a study found that while stair use is a moderate-to-vigorous physical activity that can contribute to physical health, there is limited evidence to suggest that it is beneficial for psychological health.
The evidence from studies using self-report measures indicated that perceived difficulty using stairs was positively associated with increased symptoms of anxiety and depression.
The evidence suggested that climbing stairs can be challenging and stressful for some individuals, which can lead to negative psychological outcomes. (6)
The idea that climbing stairs can be bad for mental and psychological health may seem counterintuitive, but that may indeed be the case.
5. Respiratory disadvantages

Respiratory issues are not uncommon when climbing stairs.
Breathlessness/shortness of breath, especially in people with respiratory problems
Climbing stairs can be stressful for your lungs if you suffer from a respiratory issue.
In a study that included patients with COPD, climbing stairs can worsen breathing difficulties. This is because stair climbing increases the production of a substance called blood lactate and causes the lungs to stay inflated for longer periods, both of which can cause shortness of breath or breathlessness in people with respiratory conditions. (8)
Therefore, you should take into account respiratory conditions before taking up stair climbing as an exercise. (8)
Exposure to pollution if the stairs are outside the building
Climbing stairs can also have disadvantages due to poor environmental conditions.
For example, individuals who climb stairs frequently may be exposed to poor air quality, particularly if the stairs are located near busy roads or in areas with high levels of pollution. They can inhale pollutants such as cigarette smoke, which is not good for the lungs or overall health.
How to Correctly Climb Stairs?
Observing the proper technique for climbing stairs can help prevent falls and injuries. Here are some tips to follow to correctly climb stairs: (7)(9)
- Focus on the stairs and avoid any distractions.
- Avoid rushing and take one step at a time to maintain your balance.
- Use the handrail for support.
- Ensure that your entire foot is on the step, and not just the toes or the heels.
- Use your leg muscles to lift your body up each step.
- Breathe in and out regularly while climbing the stairs to maintain your oxygen levels and prevent fatigue.
- Avoid carrying heavy objects.
By following these tips, you can correctly climb stairs and reduce the risk of falls and injuries.
What Increases the Risk of Falling While Climbing Stairs in Older Adults?

The risk of falls while climbing stairs increases with age. The reasons for this include age-related physiological changes, such as loss of muscle mass and strength, decreased mobility, vision problems, and changes in balance and gait.
These factors make it challenging for older adults to maintain balance and negotiate steps or stairs effectively. Older adults may also have underlying health conditions that increase their risk of falls, such as osteoporosis, Parkinson’s disease, and dementia. (3)
Most-Asked Questions About Climbing Stairs
Can stair climbing help improve balance and coordination?
Yes, stair climbing can help improve balance and coordination as it requires proper coordination of various muscles and movements.
How many calories can one burn by climbing stairs?
The number of calories burned while climbing stairs depends on several factors such as body weight, intensity, and duration. On average, one can burn around 8 kilocalories per 20 steps of stair climbing. (10)
Final Word
While climbing stairs is an excellent form of physical activity that has numerous health benefits, it can also have potential disadvantages. These disadvantages can range from physical injuries to psychological stress, and individuals should be aware of the potential risks associated with the activity.
By taking precautions, such as consulting with a healthcare provider and being aware of their surroundings, individuals can engage in stair climbing safely and reap the benefits of this excellent form of physical activity.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


