In this article:
Dermatitis refers to a group of skin conditions that commonly cause itching, dryness, redness. Depending on the type of dermatitis, these symptoms may be accompanied by cracks, scales, and bleeding.

Dermatitis most commonly affects the forearms and head, but it can also develop on the face, mouth, inside of the throat, neck, and chest.
It is essential to treat dermatitis, as constant itching can interfere with daily life. Moreover, continually scratching the skin can damage it severely.
Home Remedies for Dermatitis
The following at-home therapies may be useful in the treatment of dermatitis.
Disclaimer: Only use the remedies if you are not allergic to any of the ingredients. Conduct a patch test first to ensure that the remedy is suitable for your skin type and will not worsen the problem.
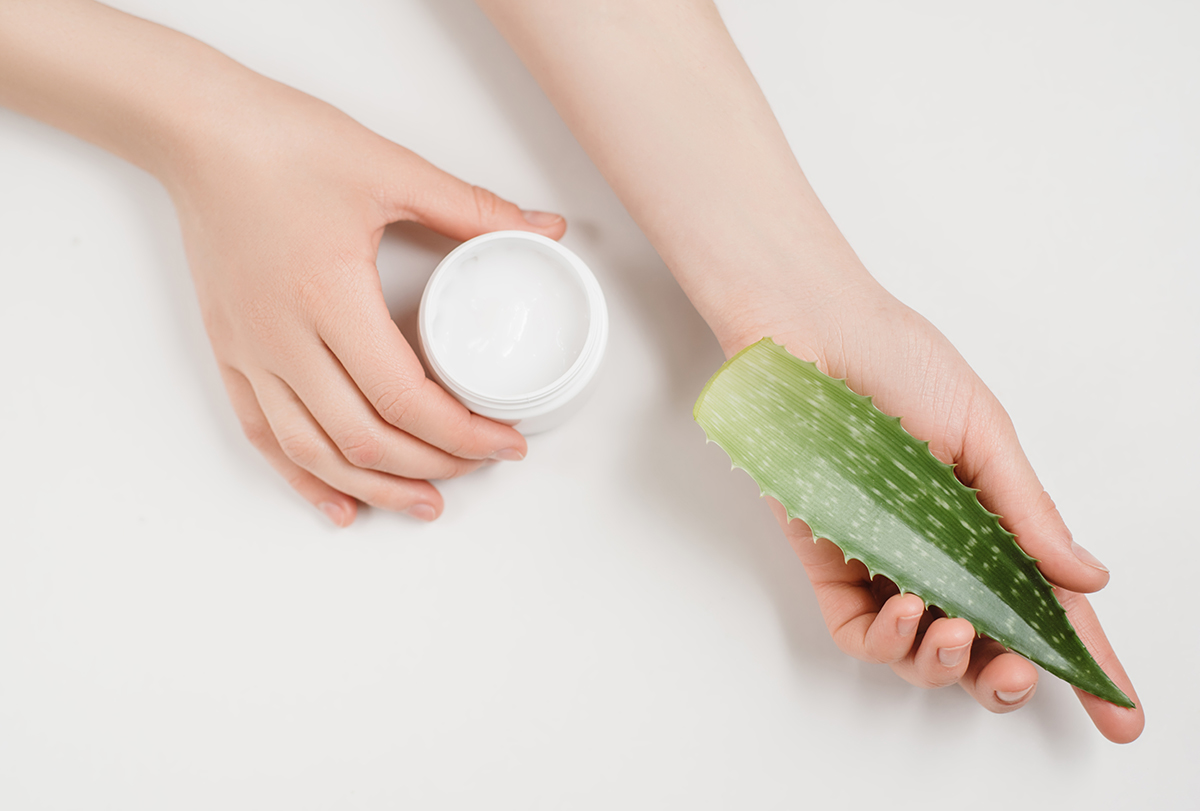
1. Apply aloe vera gel

Aloe vera possesses potent moisturizing and antibacterial properties, which make it useful in treating inflammatory conditions such as dermatitis. (1)(2) Moreover, the application of aloe vera gel helps restore skin pH, which may relieve skin irritation and itching.
How to use:
- Extract fresh aloe vera gel from a leaf and apply it to the affected areas a few times a day until you see improvement.
- Consume aloe vera juice to help improve your skin health.
2. Take a colloidal oatmeal bath
Soaking yourself in a colloidal oatmeal bath can help relieve the itching, irritation, and rashes, while cleaning and moisturizing the skin at the same time. (3)(4)
How to use:
- Mix 1 cup of powdered oatmeal in lukewarm bathwater and soak in it for 15–20 minutes. Repeat this treatment every day for 1 month.
- Apply over-the-counter oatmeal creams to help treat mild atopic dermatitis in children. (5)
3. Use coconut oil
Coconut oil is a natural moisturizer and antimicrobial agent that can be useful in providing relief from dermatitis. (6)(7) Applying coconut oil to the affected area can effectively reduce the scaling, dryness, and redness.
How to use:
Warm some coconut oil and apply it to the affected area. It is best to leave it overnight for maximum effect.
4. Use honey ointment

Honey possesses anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antiseptic properties and is therefore beneficial in the treatment of dermatitis. (8) The topical use of manuka honey, twice a day, helps to improve radiation-induced dermatitis.
How to use:
- Mix manuka honey with olive oil and beeswax.
- Heat this mixture in a double boiler to make an ointment and allow it to cool.
- Apply the ointment to your skin daily for a few weeks.
5. Apply apple cider vinegar
The topical use of apple cider vinegar (ACV) can help manage the itching and irritation associated with dermatitis. (9) It also moisturizes the skin and helps maintain its pH.
How to use:
- Dilute ACV with equal parts water. Using a clean cotton ball, apply the solution to the affected area daily. Clean with a damp cloth after 30 minutes of application.
- Consume 2 teaspoons of ACV with a glass of water 2–3 times a day.
6. Dab vitamin E oil
Vitamin E oil helps by promoting skin healing. It also helps improve the inflammation and itching associated with dermatitis. (10)
How to use:
- Directly apply vitamin E oil to the skin, preferably at bedtime.
- Use vitamin E-based creams and lotions.
- Increase your consumption of vitamin E-rich foods, such as wheat germ oil, corn, peanut butter, and sunflower seeds, to prevent dermatitis. (11)
7. Take vitamins and supplements
People with dermatitis or eczema can turn to vitamins and nutritional supplements to help manage inflammation and boost the immune system.
These supplements and vitamins include:
Note: It is important to note that the need and efficacy of such supplements differ in different patients with their conditions. Always consult your doctor before taking any supplements, as they may interact with each other or have side effects.
Alternative Treatments
The body produces inflammation under stress, which can ultimately trigger eczema flare-ups. The following stress management techniques can help in managing eczema:
- Perform yoga and meditation. Yoga is a popular meditation and mindfulness technique that involves the use of controlled breathing and physical poses. It helps manage stress and anxiety and improves sleep and overall health, all of which can help manage dermatitis.
- Acupressure and massage. Acupressure involves applying slight pressure to pressure points in the body to release stress. Massaging uses slight pressure-based movement on the whole body to help relax the muscles. It is a must to contact a professional for acupressure or massage treatments.
Self-Care and Management for Dermatitis
The following self-care measures can help manage and prevent dermatitis:
1. Drink plenty of water

Dermatitis commonly results from dehydrated or dry skin. Therefore, it is important to consume enough water to keep yourself and your skin hydrated.
2. Avoid scratching your skin
Excessive scratching of the skin can cause cuts and breaks, which act as entry points for infection-causing microbes.
If you cannot resist the urge to itch, gently rub the area with your fingertips rather than your nails. Moreover, keep your nails trimmed and wear gloves at night.
3. Do not use products that end with -caine
Anesthetic medications such as benzocaine can aggravate eczema.
4. Use OTC creams and medications
You can apply anti-inflammatory and anti-itch OTC creams such as calamine lotion and hydrocortisone cream to relieve the symptoms. You can also use nonprescription oral antihistamines for severe itching.
5. Apply cool compresses
The application of a cold, wet compress soothes the skin.
6. Limit your bath time
Do not shower or bath for more than 10 minutes. Also, avoid using hot water. Adding bath oils to your bathwater may also help.
7. Use a gentle cleanser
Use a mild, gentle, nonsoap cleanser to wash yourself. Gently pat your body dry after bathing instead of rubbing with a harsh towel. Using syndet bars may reduce the problem of dermatitis, improve your skin condition, and maintain the hydration of the skin.
8. Moisturize
It is best to moisturize your skin while it is slightly damp. You can use oils, lotions, or creams to moisturize your skin. Choose unscented and effective products that are suitable for you.
A study showed that the use of protective moisturizers in high-risk infants helped reduce the cases by around 50%. (16)
9. Modify your diet
It is recommended to consume anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, fish, lentils, beans, fruits, turmeric, and cinnamon to help manage eczema flare-ups.
Additionally, consuming probiotic foods such as kombucha, milk kefir, and yogurt helps restore probiotics in the body, helping improve eczema. Moreover, avoid inflammation-causing foods such as wheat, dairy, eggs, and soy.
10. Protect itch-prone areas
Cover the affected areas with a dressing to prevent scratching them. Always wear protective clothing when working near irritants or chemicals.
11. Use OTC shampoos for seborrheic dermatitis
Using shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, coal tar, salicylic acid, and selenium sulfide may be useful.
Most-Asked Questions About Dermatitis

Can dermatitis be cured?
Dermatitis is a life-long condition that cannot be cured completely. However, proper treatment helps manage the symptoms to a large extent and prevent flare-ups.
How is psoriasis different from dermatitis?
Psoriasis is commonly mistaken for seborrheic dermatitis as both conditions produce symptoms such as redness and flaky skin.
However, the scales associated with psoriasis are thicker and more uniform edged than those in dermatitis. It is possible to be affected with both conditions at once, known as sebopsoriasis.
Does dermatitis cause pain?
Some cases of dermatitis may produce pain, depending on the type and severity of the condition.
Does dermatitis cause a burning sensation?
A few people suffering from dermatitis feel a burn under their skin along with the itchiness. The symptoms of dermatitis are different in different people.
Final Word
Dermatitis is a common condition that causes a strong urge to scratch the skin. However, the more you scratch the skin, the more it is irritated and the higher the chances of infection.
It is best to consult a doctor to help determine the cause and type of your dermatitis. You can try home remedies and self-care measures along with the prescribed treatment to better manage the condition.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


