In this article:
Skin cancer that is caused by the formation of malignant cells in the skin tissue is the most common cancer type. It can be triggered by UV light exposure or smoking. Thus, it is essential to avoid such factors for prevention.
The Onset of Skin Cancer
The majority of skin cancers stem from unrepaired DNA damage in the skin cells, caused by the ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and indoor tanning. Thus, these cancers often develop on sun-damaged skin.
MCC is also caused by the Merkel cell polyomavirus. (1)
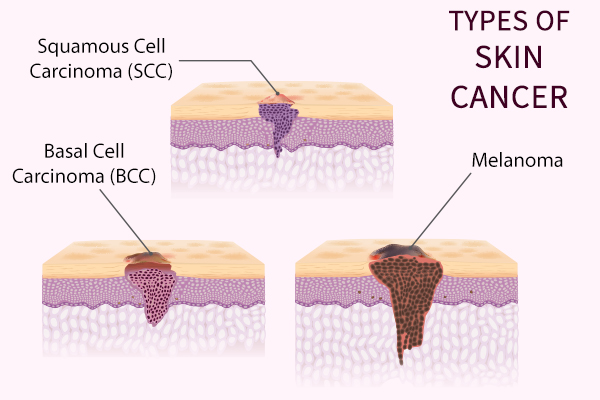
Different Types of Skin Cancer
The three main types of skin cancer are:
1. Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
It is the most common type, with an incidence of over 4.3 million per year in the United States. (2) It affects the epidermal keratinocyte cells of the skin.
2. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
It is the second most common type, affecting 1 million people every year. (3) Similar to BCC, SCC arises from abnormal keratinocytes.
3. Melanoma
Over 45 thousand melanomas were diagnosed annually, with a rate of 19 cases per 100,000 persons. (4) This cancer type starts in the melanocytes, which are cells that produce the skin pigment.
There are several other types of skin cancer, such as the rare and aggressive Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC), but they occur much less often.
The incidence of Merkel cell carcinoma is approximately 3,000 cases per year. (5) It was originally thought to arise from the Merkel cells, which are involved in touch sensation, but it is now thought to possibly derive from skin stem cells. (6)
If caught early, the cure rate of most skin cancers is excellent. However, delayed diagnosis can potentially be fatal.
Difference Between a Normal and Malignant Skin Spot
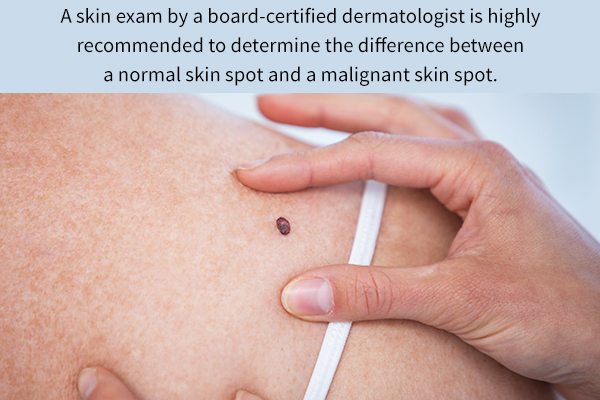
Normal skin lesions and malignant ones can sometimes be difficult to differentiate. Some clues that a lesion may be malignant are:
- Non-healing
- Bleeding
- Ulcerated
- Scaling
Some benign lesions may not have these qualities usually because they have become inflamed with chronic irritation.
A skin exam by a board-certified dermatologist is highly recommended to determine the difference between the two. The ABCDEs (asymmetry, border, color, diameter, and evolving) are often used to evaluate a pigmented lesion. (13)
Most moles are homogeneous (all one color, usually brown) with smooth borders. However, melanomas can be asymmetrical, have irregular borders, and have many colors. (14)
They can be larger than the size of a pencil eraser and are evolving with time. As early detection is key, a lesion with any of these qualities should be evaluated by a dermatologist. (14)
Different Stages of Skin Cancer
Skin cancers often start small and are more easily treated if detected early.
Patients with BCC and SCC often state having an enlarging, non-healing lesion on the skin and can report symptoms of bleeding or pruritus (itching) or no symptoms at all.
1. BCC
The most common type of BCC is the pink-pearly (sometimes pink-brown) nodular BCC, which makes up about 60%–80% of the reported cases. (7)
- The second most common type of BCC is superficial BCC, which is confined to the top layer of skin. It is usually a pink and scaling thin plaque.
- BCCs are typically slow-growing but can ulcerate and invade surrounding structures if left untreated.
- Metastatic BCC (spreading to lymph nodes and/or internal organs) is rare, occurring in about 0.0028%–0.005% of tumors. (8)
2. SCC
SCC is more aggressive than BCC and is the second most common skin cancer, accounting for about 20% of the cases. (9)
- SCC comes in different forms, ranging from the slow-growing, indolent keratoacanthomas to the more aggressive, poorly differentiated form (meaning little resemblance to the original keratinocyte). (10)
- SCC on the lips and ears are considered more high risk and can be fatal if not treated early.
- More aggressive squamous cells can spread to the lymph nodes and internal organs with a reported rate of approximately 5,604–12,572 patients per year developing nodal metastases.
- The staging of SCC is dependent upon the presence of high-risk factors, such as perineural involvement (PNI) or location on the lips/ears, and the spread of the disease to nodes and distant organs.
3. Melanoma
Melanoma is considered the most dangerous of the three most common skin cancers. (11) The staging for melanoma is based upon the quality of the lesion (i.e., ulcerated), the depth of the lesion, and any involvement of lymph nodes or internal organs.
Major Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Each type of skin cancer manifests different symptoms. However, most skin cancers, including the three most common types, do present the following symptoms:
- Non-healing lesions
- Pruritus
- Bleeding
Moreover, BCC clinically can look like a pearly nodule, a scaling ulcerated plaque, or a waxy scar. SCC can resemble a crusty wart, scaly red patch, or elevated ulcerated nodule.
Melanoma can be flat or raised and is most often dark with multiple colors and irregular borders. (12)
Survival Rate of Different Types of Skin Cancer
A skin cancer survival rate is dependent upon the type of skin cancer as well as the stage. Early detection is key. All of the three main skin cancers have a less aggressive course if diagnosed early.
BCC has a 5-year survival rate of 100%. (15) SCC has a variable survival rate based upon the stage and aggressive qualities of cancer.
Cutaneous SCC has an excellent cure rate, while advanced cutaneous SCC (metastases to lymph nodes or internal organs) is associated with much higher morbidity and mortality. (16)
Melanoma is similar in that a less advanced cancer will have a higher survivability rate. For a thin melanoma (stage I), the 5-year survival rate is 99%, while a more advanced stage with distant metastases has a rate of 25%. (17)
Final Word
Early detection of skin cancers is essential for proper, timely treatment. This helps avoid surgery or other complications such as disfigurement or even death. It is recommended to consult your doctor to assess your risk level and undergo diagnostic tests for early detection if required.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


