In this article:
Your hair is in a constant state of growth, loss, and regeneration, known as the hair growth cycle. Each individual hair on your head is in a different phase of this cycle and hence, it is normal to lose a few hairs every day and grow new ones. (1)

Hair loss occurs when this cycle is disturbed – hair starts to fall out at a higher rate than normal or the growth of new hair slows down.
Since this problem affects millions of people around the world, a lot of research is going on in the pharmaceutical industry to find effective treatments for hair loss. As of now, the two most useful hair growth medications are Redensyl and minoxidil. (2)
Minoxidil has been the go-to treatment for alopecia for a long time. It helps increase blood circulation to the scalp, consequently delivering more oxygen and nutrients to the hair follicles. This influx of nourishment stimulates the hair follicles to produce better-quality hair at a faster speed. (3)
Redensyl, by contrast, is still a relatively new drug but it has been shown to be incredibly effective in promoting hair growth. (4) In fact, it is touted as an alternative for hair transplantation.
Redensyl vs. Minoxidil
Here are the key differences between these two hair growth medications:
- Redensyl does not have any negative impact on your hair growth even if you stop using it abruptly. Minoxidil is a stronger medicine that should not be discontinued without the approval of your doctor as it may cause rebound hair loss.
- Redensyl is available over the counter and is used in many serums, oils, and hair packs. Minoxidil oral is a prescription-grade medication in the US (5) that should not be used unless advised by a doctor. However Minoxidil topical is available without prescription in the US.
Hair Growth Cycle
The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases: (6)
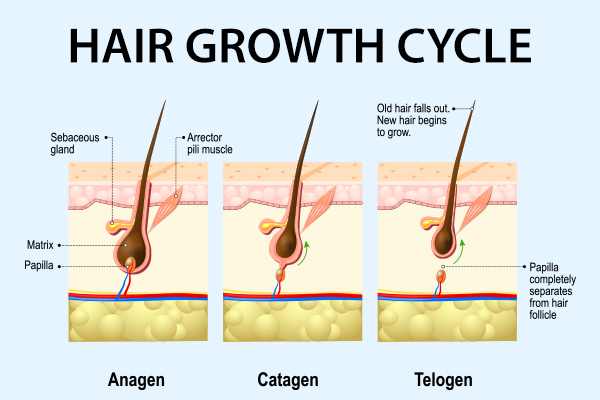
- Anagen phase: The anagen phase, also known as the growth phase, is the first stage of the hair growth cycle. In this phase, your hair follicle builds new hair, which keeps growing for 2–6 years until it reaches its maximum length. Most of the hair on the scalp is in this stage. (1)
- Catagen phase: In this second stage of the hair growth cycle, your hair stops growing. The hair stays attached to the scalp but the lower part of the hair follicle shrinks. The hair root separates from the follicle and becomes clubbed. The catagen phase lasts for a short time, only about 10 days before the hair enters the telogen phase. (1)
- Telogen phase: The telogen phase, also referred to as the resting phase, is the final stage of the hair growth cycle. It lasts for 3–4 months, after which the hair that was separated from the follicle falls out and a new hair shaft starts growing in its place. (1)
What Is Redensyl and What Are Its Benefits?
Redensyl is an active cosmetic medication developed by Induchem Group. (7) It contains an active ingredient called dihydroquercetin-glucoside (DHQG).

DHQG helps prolong the anagen phase, which is marked by active hair growth, and thereby delay the telogen phase of the hair growth cycle. This allows a longer period for your hair to grow before it falls out of the follicle.
It does so by stimulating the stem cells, or outer root sheath cells (ORSCs), inside the hair follicles to divide more rapidly. (7) These stem cells push the hair follicles into the growth phase such that they start building hair. (8) Thus, Redensyl directly induces hair growth on the scalp.
Apart from DHQG, Redensyl also contains epigallocatechin gallate-glucoside (EGCG2), zinc chloride, meta-bisulfite, zinc chloride, glycerine, glycine, and water, all of which help improve hair health. (4)
Redensyl is a regenerative medication with no side effects. It promotes cell growth without affecting your hormone levels, unlike most other hair growth medicines.
What Is Minoxidil?
Minoxidil is the most popular hair growth medication in the world. (9) Topical minoxidil has been proven to be an effective treatment for androgenetic alopecia. It helps promote new hair growth, increases the thickness of hair, and curbs hair loss. (10)
Minoxidil also induces cell division and DNA synthesis (9) and stimulates blood flow to the scalp, (11) all of which are conducive to hair growth.
Minoxidil triggers shedding of hair in the resting phase and promotes growth of new, thicker hair in its place. (12) It also prolongs the anagen phase of the hair cycle, resulting in increased hair growth. (13)
Is Redensyl Approved by the FDA?

Minoxidil and finasteride are the only hair growth medications that have been granted FDA approval. (14)
As of now, Redensyl has not been approved by the FDA. However, it is a relatively new medication that has been shown to be effective in inducing hair growth and seems to have a promising future.
Final Word
Both Redensyl and minoxidil are effective treatments for hair loss. Redensyl is a fairly new product and can be an effective remedy for earlier stages of hair loss.
Minoxidil remains the number one treatment for more severe forms of alopecia. Although Redensyl is available over the counter, it is best to consult your dermatologist before starting any new medication.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


