In this article:
Glutathione is a crucial molecule in many cellular processes and plays an important role in maintaining the overall health of an organism. It acts as a powerful antioxidant by neutralizing harmful free radicals and reactive oxygen species that can damage cells and cause a variety of health problems, including aging, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.

In addition to having antioxidant properties, glutathione is involved in a wide range of cellular functions. For example, it is important for the metabolism of nutrients, such as amino acids, vitamins, and minerals.
Glutathione is also involved in the regulation of gene expression, DNA and protein synthesis, cell proliferation and apoptosis, and immune function. It can also modulate the activity of enzymes and other proteins. (1)
In summary, glutathione is an essential molecule that plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular health and function. Its antioxidant properties, along with its involvement in a range of cellular processes, make it an important target for therapeutic interventions aimed at improving health and promoting skin well-being.
Take a look at the benefits and side effects of glutathione on the skin.
Beneficial Effects of Glutathione on the Skin
Glutathione has been shown to have beneficial effects on the skin due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Here are some of them.
1. Provides antiaging effects
Glutathione deficiency contributes to oxidative stress and, therefore, may play a key role in aging. Therefore, the use of glutathione can help fight aging signs on the skin. (1)
Glutathione has been studied for its potential in antiaging. Several studies have suggested that it can help reduce the signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines, by neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress.
In a research trial, subjects who received glutathione exhibited a substantial decrease in wrinkles in comparison with those taking placebo. An inclination toward improved skin elasticity was also observed in the glutathione-treated group compared with the placebo group.
Overall, glutathione has potential as a therapeutic agent for skin health and aging. (2)
2. Helps fight hyperpigmentation

Glutathione has been shown to have a skin-lightening effect by inhibiting the production of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. This effect is thought to be due to glutathione’s ability to inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in the production of melanin.
Many doctors assume it to be a wonder drug for skin lightening and hyperpigmentation treatment, especially in people who have darker skin tones. (2)
3. Protects the skin from UVB damage
Studies have suggested that increasing the level of endogenous glutathione (GSH) in the skin may help protect against skin damage caused by UVB irradiation. (3)
UVB radiation can cause oxidative stress and damage to skin cells, leading to inflammation, DNA damage, and premature aging.
GSH, as an antioxidant, plays an important role in protecting skin cells from oxidative stress and reducing inflammation.
4. Brightens and whitens the skin
Glutathione has been commonly used in Asia as a dietary supplement to lighten skin color. Some studies suggest that glutathione may have a potential effect on skin color.
Research has found that both oral and topical forms of glutathione could brighten skin color in sun-exposed areas. However, further research is needed to determine the true effects of glutathione on skin whitening. (4)
Side Effects of Glutathione
Some side effects have been reported with the use of glutathione, (2) including:
- Pruritus (itching)
- Macular erythema (redness and inflammation of the skin)
- Transient minute red spots on the skin
- Tiredness
However, it is important to note that the incidence and severity of side effects may vary depending on the individual and the dose and duration of treatment.
How to Incorporate Glutathione Serum into Your Skin Care Routine
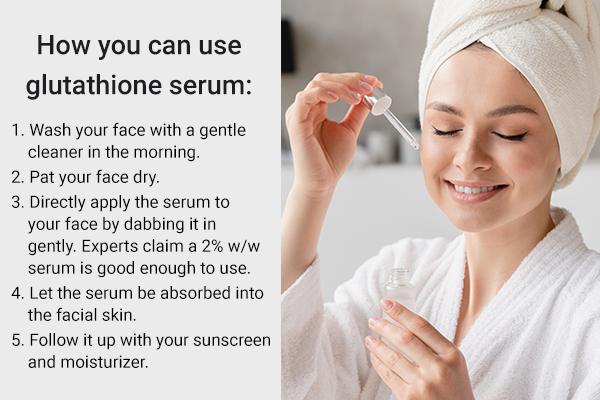
Here’s how you can use glutathione serum:
- Wash your face with a gentle cleaner in the morning.
- Pat your face dry.
- Directly apply the serum to your face by dabbing it in gently. Experts claim a 2% w/w serum is good enough to use.
- Let the serum be absorbed into the facial skin.
- Follow it up with your sunscreen and moisturizer.
Can Glutathione Be Taken Orally?
Glutathione is generally considered safe when used as a dietary supplement in appropriate doses. Topical and oral forms are deemed to be safe, while the safety and efficacy of intravenous forms have not yet been confirmed to date.
Research has shown that glutathione has a high lethal dose and no serious adverse reactions have been observed in many clinical trials. Oral toxicity occurs at more than 5 g/kg, indicating that glutathione is nontoxic.
Glutathione 250 mg/day is enough to bring about positive changes in skin properties. (2)
Which Is More Beneficial for the Skin: Topical or Oral Glutathione?

According to experts, topical glutathione is more beneficial for the skin compared to oral glutathione. Topical application allows glutathione to directly target the skin cells, providing localized benefits.
Experts also claim that using both topical and oral glutathione can provide additional benefits for the body, with topical application targeting the skin directly and oral supplementation supporting overall health. However, it’s best you consult a professional for better and more personalized advice.
Generally, it may take several weeks to months of regular use of either topical or oral dose before noticeable improvements in skin health and overall well-being are observed.
Research on glutathione use in dermatology found that glutathione injections can also be beneficial, but due to limited evidence, there’s no proven efficacy and they may have adverse effects. (5)
Most-Asked Questions About Glutathione Serum for Skin
Can I apply my glutathione serum after my moisturizer?
Experts recommend putting on a serum before a moisturizer to allow its proper absorption.
How often should I use glutathione serum in a day?
Experts say that you can apply glutathione serum safely twice a day.
Can I get glutathione from food?
Glutathione is naturally present in various foods, but its absorption from dietary sources is limited.
The body relies on the synthesis of glutathione from amino acids such as cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine. Foods rich in these amino acids, such as fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and legumes, can support the production of glutathione in the body.
Final Word
Glutathione has been shown to have several benefits for skin health and is becoming an increasingly popular ingredient in skin care products.
As an antioxidant, glutathione can help protect skin cells from oxidative damage and reduce inflammation, both of which can contribute to visible signs of aging such as fine lines, wrinkles, and loss of elasticity.
In addition, glutathione has been shown to have a skin-lightening effect and may help reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation and age spots. Therefore, incorporating glutathione into your skin care routine can be a beneficial way to support skin health.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


