In this article:
It is common for people to experience sudden stuffiness in their ears, which is often short-lived. More often than not, you may experience this stuffiness along with diminished hearing, pain, and imbalance, on account of a clogged ear or Eustachian tube dysfunction. (1)

Almost anyone can suffer from a clogged ear, but it affects children more frequently than adults, especially during a common cold or nasal allergy. (2)
Causes of Clogged Ears
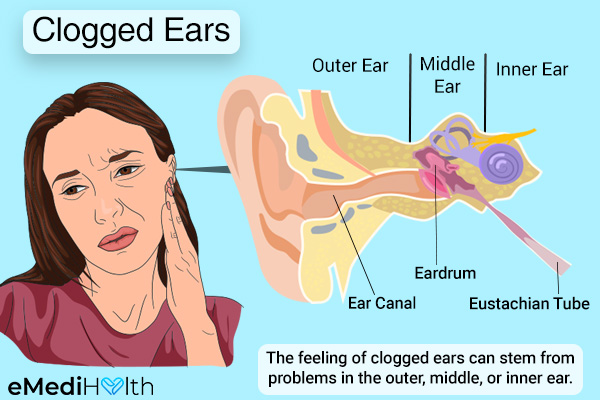
A number of rather innocuous factors can lead to clogged ears (1) such as:
1. Pressure differences
Because your ears are connected to your nose, nasal congestion can cause partial swelling or closing of the Eustachian tube. This can lead to pressure changes within the ear causing a feeling of fullness, dizziness, and even a mild earache.
2. Common cold
Viral infections such as the common cold cause increased mucous secretion and swelling, which often move up to the ear blocking the ear tube (Eustachian tube).
3. Middle ear infections
Even after a cold has cleared, the ear tube may remain swollen, hindering the drainage of the infected fluid. The trapped fluid acts as a breeding ground for microbes, often giving rise to a middle ear infection known as “otitis media,” (3) which may be the result of your swollen ear tube being completely shut for several days.
4. Earwax impaction
The accumulation of excessive earwax inside the outer ear canal (outside of the eardrum) can lead to clogged ears.
5. Blowing the nose
Exerting a great deal of force in blowing your nose can push sinus secretions into the ear tube.
6. Changes in altitude
A sudden increase in air pressure due to a change in altitude, as experienced when your flight makes a landing or during mountain driving, can cause clogged ears.
7. Foreign bodies trapped in the ear
Occasionally, small objects get lodged inside the outer ear canal and often this can be your own doing.
8. Swimmer’s ear
This condition is so named as it is most prevalent among swimmers. People who spend a lot of time in the water tend to get water trapped in their outer ear canal, which can result in an infection of the outer ear canal skin, causing swelling and a feeling of ear blockage.
Signs and Symptoms of Clogged Ears
A case of clogged ears is usually characterized by the following symptoms:
- Mild pain in the ears
- Increased pressure in the ears, like you are underwater
- A feeling of fullness in the ears
- Ringing, clicking, or popping noises in the ears
- Hearing problems, such as sounds may seem muffled
- Feeling a little dizzy
- Moderate to severe hearing loss
- A sense of disequilibrium in the body, which makes it difficult for you to keep your balance
Medical Treatment for Clogged Ears

The clogging of your Eustachian tubes is an uncomfortable yet harmless condition that usually resolves on its own. If required, treatment will depend on the cause:
- If you experience an earache along with the blockage, the doctor may recommend an over-the-counter pain medicine to manage the pain.
- If the blockage is due to earwax buildup, your doctor may use a curet or rubber bulb syringe to remove it.
- Anti-inflammatory medicines in the form of nasal sprays are usually recommended if the ear clogging is due to allergies.
- If the problem is traced to an infection in the outer ear canal, antibiotic eardrops may be necessary.
- If the infection is behind the eardrum in the middle ear, you may need a prescription of oral antibiotics.
- Oral decongestants or nasal decongestant sprays may be helpful for the treatment of clogged ears but should be used only briefly due to risks of side effects.
Diagnosing Clogged Ears
To pin down the exact reason behind your ear blockage and to get a better understanding of your condition, your doctor will first inquire about your symptoms, any aggravating or mitigating factors, and home treatments you have tried.
This will be followed by a closer examination of your ear using a special tool called an otoscope, which is inserted into the outer ear canal. It is important to determine the site of the problem, whether it is arising from the middle ear behind the eardrum or from the outer ear outside of the eardrum.
Risk Factors Associated With Clogged Ears
The following factors can increase your likelihood of developing clogged ears:
1. Age
Ear infections are more prevalent among children than adults. This is primarily because children have shorter and straighter ear tubes than adults, allowing easier and quicker entry for germs into the middle ear. (4) The structure of their Eustachian tube is such that any backflow of fluid tends to become trapped there.
2. Smoking
People who smoke have a greater likelihood of suffering from clogged ears. Smoking tends to damage the cilia lining the middle ear and Eustachian tube and thereby reduces the movement of the mucus, leading to the accumulation of mucus within the ear tubes.
3. Excessive weight
Overweight or obese people can have fatty deposits around the Eustachian tubes, which can lead to abnormalities in their function.
4. Sleep disorders
People with sleep apnea have altered pressures when breathing during sleep; such alteration is thought to change the Eustachian tube function.
5. Pharmacological drugs
Many medications, especially diuretics, anxiety medications, sleeping medications, and some antihistamines, have a negative effect on the cilia and also increase the stickiness of the mucus made in the middle ear, nose, and sinuses. This can also result in an increased risk of accumulation of middle ear pressure and middle ear fluid.
When to See a Doctor

You may have to schedule a visit to your doctor, preferably an ENT specialist (otolaryngologist) if the blockage in your ear persists despite appropriate self-care and primary home treatment.
A visit to the doctor is also warranted if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Moderate to severe pain in the affected ear that gradually worsens
- Severe pain in your head or face
- Pus or bloody discharge from the affected ear
- Ringing in the affected ear
- Loss of hearing/changes in hearing
- Severe dizziness
- Running a fever higher than 101°F, especially in adults
Expert Answers (Q&A)
Answered by Dr. Mike Dilkes, MBBS (Otolaryngologist)
Repeated swallowing can help ease ear pressure and blockage symptoms as the action of swallowing causes the involved muscles to pull on the Eustachian tube. This allows pressure to be equalized, thus relieving blockage.
This is why airlines used to give their passengers hard candy when landing. The sweets make you salivate and, consequently, swallow.
Blocked or clogged ears can be related to many medical conditions, particularly glue ear, wax impaction, foreign body in the ear canal, chronic middle ear infection, tumors of the middle ear, and postnasal space.
Clogged ears can last for a few minutes, such as when landing in an airplane, or many months. It can last even years when due to glue ear, wax impaction, or tumors.
Earwax is best dissolved using specifically designed ear drops. Many formulations can be bought over the counter. The better ones contain a chemical called sodium bicarbonate.
Ears naturally clear themselves through the migration of the ear canal lining. This is how natural wax from the ear canals is cleared without resorting to cotton buds. Some causes of ear clogging can, therefore, clear themselves if given enough time.
A sinus infection is commonly related to clogged ears as swelling and discharge from the sinuses interact with the Eustachian tubes at the back of the nose.
This causes blockage of the Eustachian tubes, so fluid and pressure build up in the middle part of the ear.
Wax buildup is the foremost cause of clogged ears. Try not to use cotton buds to clear earwax as this often forces the wax deep into the ear canal where it jams in place. Instead, it is best to let your ears clear naturally.
Going swimming can often help as the earwax is quite easily washed out by swimming or showering, in tiny amounts that you do not even see.
Final Word
Colds, sinus infections, and allergies can cause swelling in the Eustachian tube, preventing their opening. This results in pressure changes in the ear, often leading to pain and fluid accumulation.
Therefore, it is best to manage colds and allergies to prevent clogging of ears. Visit your doctor if the condition persists or your child experiences Eustachian tube dysfunction.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


