In this article:
A ganglion cyst is a bump filled with fluid. It usually occurs near the joints or tendons and is painless.

Ganglion cysts are masses of soft tissue commonly found on the hands or wrists (although they can appear near the feet as well.) They can range from small (pea-sized) to as big as a lemon. (1)
Young women are more at risk of developing ganglion cysts than men. They are also frequently observed in gymnasts. (1)
The joints of the body contain “synovial” fluid, a body fluid that lubricates movements. Ganglion cysts are made of this fluid.
Although they are mostly harmless, they can cause pain or restrict movement of the joint at times. They tend to go away on their own after a while, but some may require additional treatment. (1)
Read on to take a deeper look at the causes and symptoms of ganglion cysts and the treatment for them.
What Are the Symptoms of Ganglion Cysts?
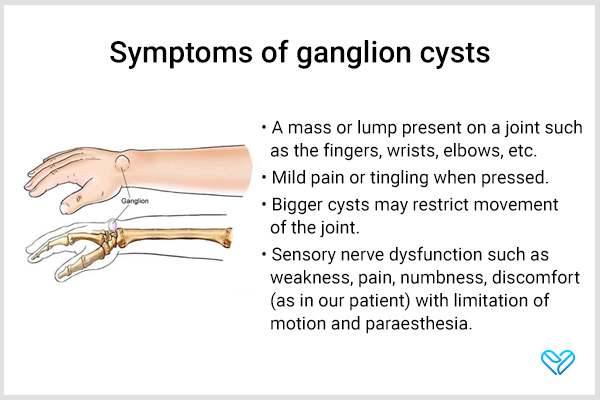
Some common symptoms of ganglion cysts are:
- A mass or lump on a joint such as the fingers, wrists, and elbows
- Mild pain or tingling when pressed
- Restriction of movement of the joint in bigger cysts (1)
- Sensory nerve dysfunction such as weakness, pain, numbness, and discomfort with limitation of motion and paresthesia (2)
What Is the Cause of Ganglion Cysts?
The specific cause of the development of ganglion cysts is still unknown. However, many doctors believe they may occur due to the overuse of a joint or leakage of synovial fluid from it. (3)
Synovial fluid from a joint may leak and accumulate in an area or “sac” to form a ganglion cyst.
What Are the Treatments for Ganglion Cysts?
Small or painless cysts that do not cause any harm may not require treatment at all. Some patients opt for treatment due to cosmetic reasons.
If your cyst is hurting you or causing difficulty in moving the joint, your doctor may suggest the following procedures:

- Immobilization – Your doctor may immobilize the joint by wrapping it in a brace or splint to prevent movement. This may cause the cyst to shrink.
- Aspiration – Aspiration involves draining fluid from the cyst using a needle or other methods. This method can shrink the cyst, but it may still recur.
- Surgery – If other treatment methods are not working, the doctor may recommend surgery to remove the cyst. (4)
- Nonsurgical methods – Some cysts may be treated nonsurgically depending on the location.
What Are the Diagnostic Tests for Ganglion Cysts?
Your doctor can diagnose a ganglion cyst based on its appearance and by physical examination. They may ask you to undergo some diagnostic tests such as:
- X-ray (this may be an unreliable method to diagnose a ganglion cyst)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Biopsy
- Ultrasound – To help identify a cyst and rule out other vascular conditions. It also helps provide a clear view during needle aspiration of the cyst to prevent injury to arteries.
When to See a Doctor
You can consult a doctor immediately if you notice:
- The cyst growing rapidly
- Pain in the cyst
- Restricted movement in the joint
- Redness or warmth in the area around the cyst
- Numbness or a tingling sensation
Final Word
Ganglion cysts are common and are usually not a cause for worry. They are painless lumps that tend to go away on their own or can be treated with some home remedies or by visiting a doctor’s office.
 Continue Reading8 Simple Home Remedies for Ganglion Cysts and How to Use Them
Continue Reading8 Simple Home Remedies for Ganglion Cysts and How to Use Them
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


