In this article:
Pimples, a common symptomatic lesion of acne vulgaris, refer to small, red bumps that form due to blockage in the oil glands. The occurrence of pimples is highly common among teenagers and women during their periods.

Pimples are more commonly seen in areas rich in oil glands, including the chest, face, shoulders, upper back, and neck.
While usually a mild problem, acne can leave scars, which may be a source of concern for many. This article discusses the different causes, treatment options, and complications associated with pimples.
How Common Are Pimples?
Acne vulgaris is the eighth most common skin disease, with a 9.38% estimated global prevalence among people of all ages, according to the Global Burden of Disease Study. (1)
How Pimples Develop
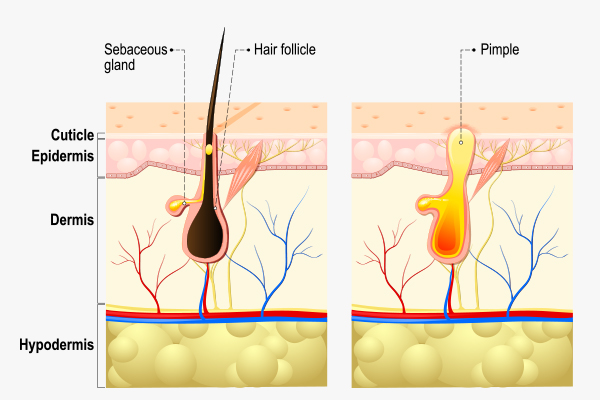
The skin has pores or hair follicles that contain sebaceous glands. These oil glands release sebum to lubricate the skin and hair. As you age, the body releases hormones that stimulate increased sebum production.
However, excessive sebum, along with dead skin cells, can accumulate in the pores and block them. This may be accompanied by the entrapment and multiplication of bacteria within the pores.
Such bacterial infections cause inflammation (2) and papule formation (pimples without pus) within the tissues. As the infection persists, the body releases white blood cells (WBCs) to fight the infection. The WBCs leave behind cellular debris in the pores, resulting in the formation of pus-filled pimples.
Medical Treatment for Pimples
The treatment for pimples is based on the severity of the condition, your age, and the cause. It usually focuses on preventing acne scars and minimizing pimples with the use of topical and/or oral medications. (3)
Here are the common treatment options for pimples:
- Benzoyl peroxide ointment – This controls the bacterial infection and reduces inflammatory pimples.
- Retinoids – Retinoids such as tretinoin prevent further development of pimples and also boost skin repair.
- Antibiotics – Erythromycin, clindamycin, or other antibiotics may be given in the form of topical creams or oral pills to control bacterial growth and inflammation.
- Topical creams – These include azelaic acid, tazarotene, salicylic acid, and dapsone.
- Phototherapy – Also known as blue light therapy, phototherapy uses radiation to kill bacteria.
- Pulsed light and heat energy (LHE) therapy – This is used for severe cases of pimples and works by killing bacteria and shrinking the pores.
- Birth control pills – Some women may need birth control pills or patches if they have a persistent menstruation-associated problem of pimples. Women suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome are usually prescribed these pills to prevent symptoms such as acne.
Treatment Options for Pimple Scars
Consult a dermatologist if you are bothered by the appearance of scars caused by pimples. The dermatologist may suggest one of the following treatments:
- Dermal fillers – These are collagen injections that help push up depressed scars, thus helping smoothen the skin.
- Dermabrasion – Electric devices are used to remove the upper layer of damaged skin.
- Chemical peeling – Chemicals such as glycolic acid are employed to remove the upper layer of dead skin cells, revealing newer skin.
- Punch grafts – Small skin grafts are used to replace the scarred skin.
- Autologous fat transfer – Fat from your body is injected beneath the skin surface to help lift depressed scars.
Diagnosing the Cause of Pimples
Pimples can be diagnosed with a physical exam and medical history.
The doctor will make note of the type of pimples and the areas they appear. He may also conduct a skin biopsy to help determine the cause behind the pimples.
It is essential to consult a doctor as you may mistake some other medical conditions, such as hidradenitis suppurativa, for pimples or acne.
Risk Factors for Pimples
The following factors increase the chances of developing pimples and acne:
- Medications such as corticosteroids, anabolic steroids, or contraceptives (4)
- Endocrine disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome, Cushing’s disease, or congenital adrenal hyperplasia (5)
- Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, and menstruation
- Foods such as white bread, sugary drinks, and rice (6)
- Pressure on the skin from equipment such as helmets, tight clothes, and backpacks
- Irritants, including high humidity and environmental pollution
- Heavy cosmetics that block the skin pores
- Picking (squeezing or popping) the acne, which can increase the risk of acne scars and even exacerbate the condition
Complications of Untreated Pimples

Pimples can be generally managed with self-care and preventive steps. However, when left ignored, the problem may become severe, commonly causing scars. Also, persistent infection can result in cyst formation.
The appearance of pimples and scars also causes aesthetic concerns, which may be associated with depression, anxiety, and social withdrawal in some cases.
When to See a Doctor
It is recommended to visit a doctor if you experience:
- Sudden acne breakout
- Rapid increase in the number of pimples
- Scar formation
- Emotional distress due to the appearance of pimples
Final Word
Acne is a highly prevalent skin problem all over the world. It is more commonly seen among teenagers and women on their periods.
While self-care can help control mild acne, it is suggested to consult a doctor to prevent exacerbation of the problem. This helps avoid the development of scars and other associated complications. The treatment for pimples requires daily care, medications, and patience for effective results.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


