In this article:
Acne is a highly common skin problem that is found to affect approximately 90% of teenagers and 12%–14% of adults. (1) Acne can develop anywhere on the skin, especially on the face, back, chest, and shoulders.

Acne can present as blackheads, whiteheads, or pus-filled, inflamed, red lesions. The acne lesions initiate an inflammatory reaction in the body, wherein the body’s immune system sends different blood cells and collagen to the affected site.
These immune cells help prevent infection and repair the injured skin. However, the skin may not heal completely, leaving behind acne scars. This is more so common when you have severe acne, which re-flares before your skin can repair itself completely.
You can employ different medical and home treatments to fade acne scars, which will be discussed in this article.
Types of Acne Scars
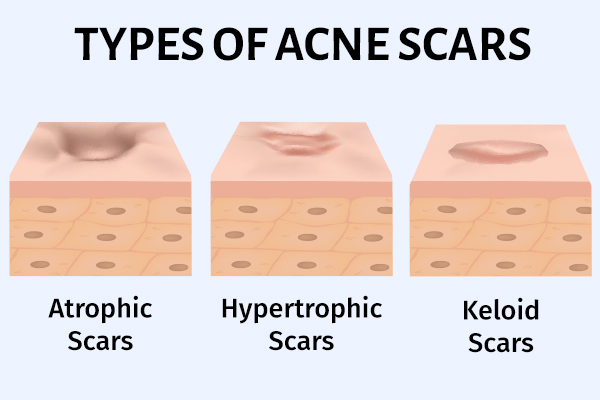
The treatment for acne scars can vary according to the type of scar. Acne scars are largely classified into the following:
- Atrophic scars: These scars present as depressions or indentations on the skin due to a lack of fibroblast production during skin healing. Atrophic scars can further be of two types – “icepick” scars that form as small holes in the skin and “boxcar” scars that are round indentations with steep sides, similar to chickenpox scars.
- Hypertrophic scars: This type of scar is characterized by raised bumps on the skin that develop due to an overproduction of collagen, even after healing has completed.
- Keloid scars: Similar to hypertrophic scars, keloid scars appear as raised bumps. However, these are thicker than the acne spot and are hyperpigmented. Keloid scars may also be accompanied by symptoms such as pain and itchiness.
Dermatological Treatment for Acne Scars
Acne scars, of both types, can be safely managed with different treatments. Consult your dermatologist for the treatment that suits your condition the best.
1. Dermal fillers
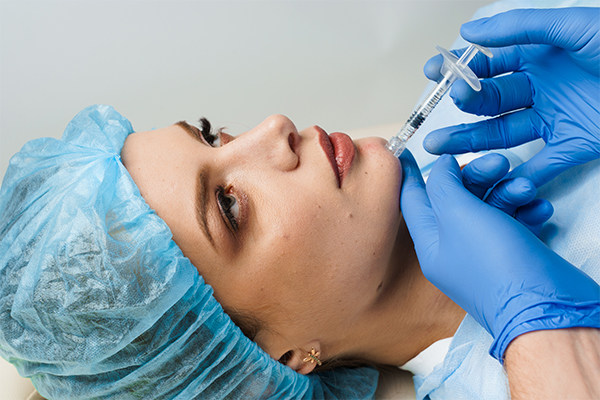
Dermal fillers are injections filled with collagen, hyaluronic acid, the patient’s own fat, or other substances, which are injected into the site of a depressed scar to plump the area and thus even out the skin.
2. Microneedling
Microneedling involves the use of minute needles to micropuncture the skin. This helps initiate skin healing, thereby stimulating an increase in the production of collagen and elastin. Microneedling may be combined with subcision for better results.
3. Microneedling RF
Microneedling RF is a skin-rejuvenation method that combines traditional microneedling technique and radio frequency (RF) energy.
In microneedling RF (MNRF), micropuncturing the skin enables the transfer of RF pulse into the inner layers of the skin. This, in turn, helps in tightening the skin and stimulating the production of elastin and collagen to help reduce acne scars.
4. Laser treatment
Mild lasers are used to remove the top, damaged layer of the skin. This procedure also tightens the middle layer, giving the skin a smoother appearance in 3–10 days, once the skin heals.
The doctor may recommend a pulsed dye laser (PDL) to help improve raised scars, hyperpigmentation, itching, and pain. Intense pulsed light (IPL) may be used if you have lighter skin. Commonly used lasers include CO2 lasers and Er:YAG lasers.
5. Sublative rejuvenation
Also known as eMatrix treatment, sublative rejuvenation involves the use of radiofrequency lasers to improve skin aging, texture, and scars.
Radiofrequency lasers can penetrate deep into the skin, thus initiating treatment in the inner layers by stimulating collagen production. This technique is less invasive and requires a shorter recovery time than other laser treatments.
6. Injections
Medications can be injected into the scars directly to soften and flatten thick scars. These injections may include corticosteroids and fluorouracil (5-FU). The dermatologist may recommend one or a combination of these injections once every few weeks.
7. Chemical peels
A chemical peel treatment involves the use of hydroxy acids to remove the top layer of skin. This promotes the production of new skin cells, thus aiding in the treatment of scars. (2)(3)
8. Mesotherapy
A noninvasive treatment method, mesotherapy includes multiple minor injections to the mesoderm. These injections contain peptides and growth factors that boost the production of collagen and skin cells. This treatment may be combined with hyaluronic acid injections to promote skin healing and regrowth.
9. Platelet-rich plasma therapy
In platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, plasma is injected into the affected areas to stimulate skin regeneration. The plasma, rich in growth factors, is extracted from the patient’s own blood. PRP therapy works best for rolling scars rather than boxcar or icepick scars. (4)
10. Dermabrasion
Dermabraders are motorized tools that have a small abrasive wheel that is used to deeply exfoliate the skin, removing the outer layer (epidermis) and part of the inner layer (dermis).
Dermabrasion, therefore, promotes the generation of new skin cells, thereby improving wrinkles and fading scars. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and can take 10–14 days to heal.
11. OTC topical creams

You can also consult your dermatologist on the use of OTC topical creams that contain ingredients such as retinoids, salicylic acid, lactic acids, and alpha hydroxy acids to improve acne pigments. These medications can also promote collagen production.
Make sure to conduct a patch test before using these creams to check for any sensitivity or allergic reaction.
12. Minor surgery
A minor surgical procedure, known as punch excision, may be performed to cut out individual scars, followed by stitches or skin grafts. Moreover, the doctor may insert needles under the scar to loosen the skin fibers, a technique known as subcision.
Natural Remedies to Help Fade Acne Scars
Many anecdotal remedies claim to help fade acne scars by improving the associated hyperpigmentation. However, these remedies are not supported by scientific evidence.
The most common natural ingredients that are said to improve acne scars include:
- Tea tree essential oil
- Coconut oil
- Aloe vera gel
- Turmeric
- Honey
- Rosehip oil
These ingredients may also prevent the formation of acne scars or acne in the first place.
Note: Always conduct a patch test before using a natural remedy to check for allergic reactions. Consult your doctor if you have severe acne or experience acne flare-ups after using a natural remedy.
Preventive Tips

The following tips may help reduce the risk of developing acne scars:
- Wash your face twice a day with a mild cleanser.
- Refrain from touching your face, especially the acne-affected area, to prevent the transfer of dirt and bacteria.
- Do not squeeze and pick your pimples.
- Do not scrub the acne-affected area as it can cause flare-ups, increasing the risk of permanent scars.
- Protect your sun from skin exposure as it can cause hyperpigmentation, making your scars more evident. Always wear a sunscreen with SPF 15 or higher before stepping outdoors.
- Consume plenty of water to flush out toxins from the body, thereby reducing acne breakouts.
- Consume a diet rich in minerals, vitamins, and essential fatty acids.
- Manage your stress as it can indirectly cause acne flare-ups.
- Get proper rest and sleep to allow your skin to repair itself and to boost collagen production.
- Avoid smoking.
Final Word
Acne usually causes scarring, giving the skin an uneven appearance. While acne-caused pigmentation may improve on its own, some scars might require treatment to fade them.
It is vital to treat acne scars timely for best results and to prevent permanent scarring, but only get treatment for acne scars after the inflammation has subsided. Consult your dermatologist for the best treatment option for your condition.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


