In this article:
People with diabetes are at higher risk of developing skin ulcers and wounds on the feet and hands, and they are prone to developing wound infections. (1)
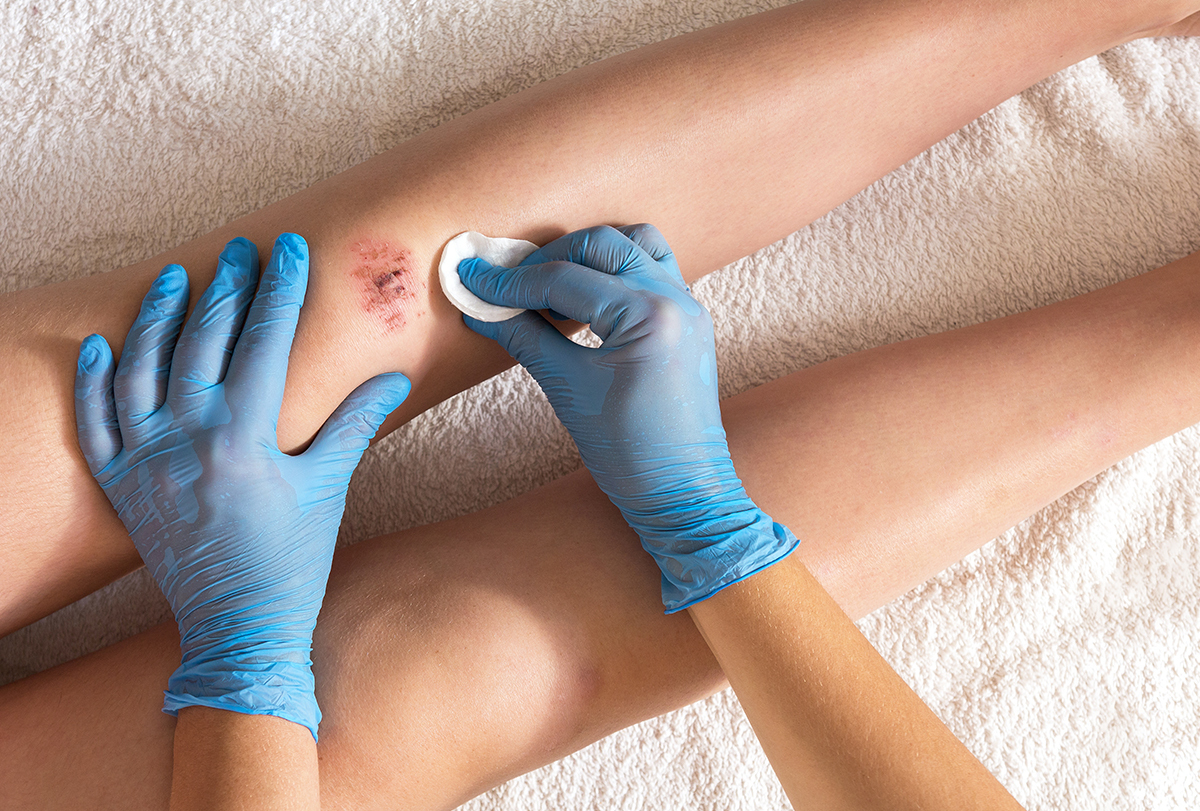
This is because diabetes is commonly associated with poor blood circulation, decreased immunity, and loss of sensation in the lower extremities (peripheral neuropathy).
If you or anyone you know have diabetes, it is important to know that even tiny cuts and injuries can develop into major wounds and proper care is necessary to avoid these problems. (2)(3)
Important Wound Care Tips
Here are some common wound care methods you should adopt to help wounds heal faster and prevent infections:
1. Self-examining your wound
It is necessary to regularly self-check your feet for any changes or injuries.
One easy way to do it is by incorporating a daily foot examination into your shower routine. Look for any cuts, scrapes, minor injuries, skin that seems cracked or dry, and hardened, numb, or blue skin that may not be getting proper blood supply. If you are unable to do it yourself, get someone close to you to do it.
Any changes or cuts should be shown to a doctor immediately. (4)
2. Preventing infection

If you have a wound, especially on the feet, you should be extra careful to maintain proper sanitation to avoid infections. Dress the wound properly and clean it using an antiseptic recommended by your doctor. (5)
3. Managing blood sugar levels
Controlling your blood sugar levels is the key to healing your wound. Higher blood glucose levels cause a decrease in white blood cell efficiency and make you prone to infections. (6)
Here are a few tips to manage your blood sugar levels:
- Consume a healthy diet: Make sure to eat a lot of greens and nonstarchy foods every day. Watch your carbohydrate intake and try to follow the “plate method” of eating. Try to eliminate all refined sugar and high-carb food from your diet. (7)
- Adopt an active lifestyle: Physical activity is an important factor in regulating blood sugar levels. Try to incorporate at least 20 minutes of exercise into your everyday routine. (7)
Note: Consult your diabetologist before making any changes to your diet or physical activity as combining them with diabetes medications may cause low blood sugar in some people.
4. Taking the pressure off the area
You may be asked to wear some special footwear to avoid putting extra pressure on the area of the wound, called “off-loading.” This helps heal ulcers faster. There are braces and shoes as well as certain dressings available for this. (8)
5. Using monitoring devices at home
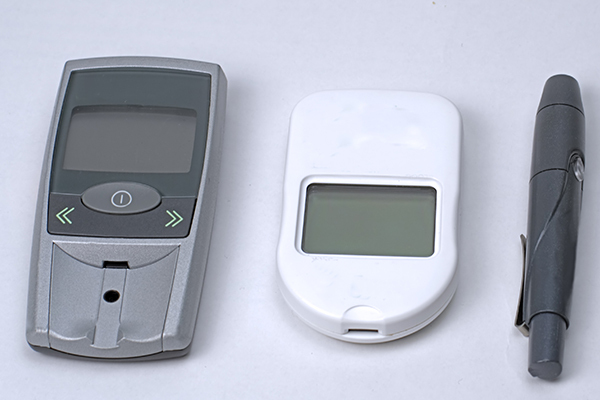

At-home monitoring can be considered for diabetic patients suffering from diabetic neuropathy.
There are smart insoles and socks that can detect extra pressure and temperature changes in the foot that may be a precursor to serious foot wounds. Some studies have shown that these devices help alert patients to any changes in their feet so they can get proper care on time. (9)
6. Removing dead skin and tissue
The removal of dead or damaged tissue is called debridement. Debridement can be done in a number of ways, and it is better to get this done in a hospital setting. (10)(11)
7. Applying honey dressings at home

Some studies have shown that applying honey to the wound can help in faster healing. Honey has several antioxidants and antiseptic properties. (12)(13)
Note: Do not apply this dressing without a doctor’s approval as improper care can put you at risk of secondary exposure infections.
How to use:
- Clean the wound area with warm water to get rid of dirt and germs.
- Rub honey on a wound dressing and wrap it around the affected area.
- Change the dressing 3–4 times a day.
Additional Prevention Tips
A few factors that can put you at risk for developing foot ulcers are:
- Having diabetic neuropathy or decreased sensation in the feet
- Poor blood circulation due to uncontrolled blood sugar levels
- Any feet deformity
- Not wearing the correct shoe size
- High blood sugar
- History of foot ulcers
- Smoking or excessive drinking
To prevent the formation of ulcers on your feet or other body parts.
- Never pick on a wound, scab, or wart on the feet.
- Avoid wearing tight socks or shoes when you have a wound on your feet.
When to See a Doctor
If you have diabetes, visit a doctor as soon as you notice any wound or cut on your feet. This can help prevent the development of foot ulcers and amputations.
Most-Asked Questions About Diabetic Wound Care
Can diabetics use liquid bandages?
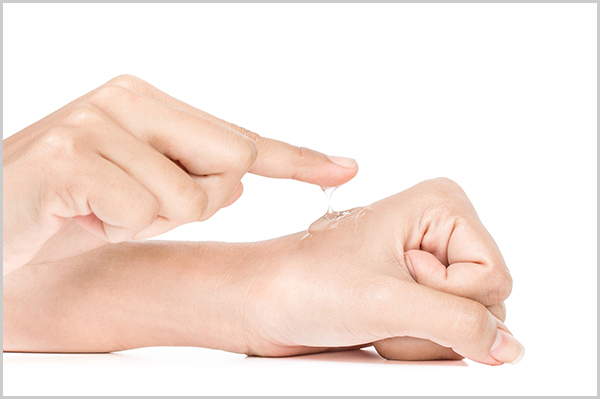
Yes, but gels are preferable according to most doctors.
What is the home remedy for a diabetic wound?
Clean the affected area with warm water daily and dry it properly. Apply an antiseptic to the wound.
What are the best ointments for diabetic ulcers?
Neomycin, gentamycin, metronidazole, etc., are common antibiotic formulations used for diabetic ulcers. (10)
What are the herbal treatments for diabetic ulcers?
Papaya leaves, custard apples, and rosemary are widely used as herbal medicine for diabetic ulcers. However, they may not be as effective as modern medicines in healing ulcers. (14)
Final Word
Amputations and sepsis are serious and common complications associated with diabetes. It is important to check your feet properly and prevent wound infections to protect yourself from these hazards. (15)
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


