In this article:
Age spots are painless patches of pigmented skin that develop on sun-exposed areas. They go by different names, such as liver spots, senile freckles, sun spots, or solar lentigines and are a normal part of skin aging.

Age spots may appear cancerous, but they are mostly benign. However, age spots continue to be a pressing cosmetic concern for many. They blemish the face and make the complexion uneven.
Skin that is freckled with dark spots can be quite an eyesore, which is why people often choose to get them removed through topical or clinical procedures. This article discusses various reasons behind the development of age spots and the medical interventions available to deal with them.
The Connection Between Sunlight, Melanin, and Age Spots
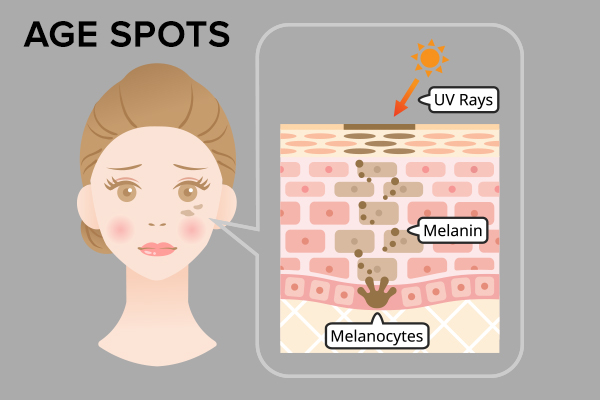
Sunlight contains UV rays that penetrate the skin to stimulate specialized cells called melanocytes to produce the skin pigment called melanin. (1)
Melanin not only gives your skin its color but also protects it from the harmful effects of UV radiation. It forms a barrier against UV rays to keep them from destroying the skin’s DNA and causing cancer.
Thus, the increase in melanin triggered by sun exposure is actually your skin’s built-in defense mechanism against UV-induced damage.
Characteristic Features of Age Spots
Age spots look like the following:
- Texture: Flat and even as the surrounding skin
- Shape: Circular or oval
- Size: Vary in size but generally have a small diameter
- Color: Darker than the surrounding skin, ranging from tan and brown to black
- Area of appearance: Sun-exposed parts of the skin, such as the face, especially the nose, neck, forearms, back of the hands, shoulders, top side of the feet, and upper back
Causes of Age Spots
Staying in the sun for too long or too often causes a uniform increase in melanin production in the exposed skin that makes it darker than the surrounding areas. This uniform darkening of the skin is known as tanning.
But age spots are different. They develop when the excess melanin concentrates in specific areas as opposed to being spread out all over the skin. The exact reason for this abnormal clumping of melanin is not clearly understood, but it typically occurs as one gets older, which explains the name “age spots.”
It can also be a result of dysfunctional melanocytes that overproduce melanin, which then is deposited in small areas that appear as hyperpigmented age spots. Repeated UV exposure can damage melanocytes and can trigger this kind of localized melanin buildup.
There are two major sources of UV damage that can trigger the formation of age spots: (2)
- Sun exposure
- Use of tanning beds and lamps
Symptoms Associated With Age Spots

Age spots do not cause any pain or discomfort and feel just like the adjoining skin. However, they are often accompanied by other signs of photoaging.
Photoaging is basically skin damage caused by extensive or frequent UV exposure, which makes your skin look older than it is. This early-onset skin aging may occur in the following ways: (3)
- Sagging of the skin
- Wrinkle formation
- Development of firm, crusty sores
- Loss of skin volume
- Solar elastosis
- Erythema
- Skin thinning
- Drying of the skin
- Broken blood vessels
Medical Treatment for Age Spots
Here are some standard medical treatments for reducing the appearance of age spots.
1. Topical creams and ointments
The doctor may prescribe gels or creams that contain retinoid, deoxyarbutin, alpha hydroxy acids, glycolic, kojic acid, and vitamin C. These compounds help lighten age spots by stimulating skin regeneration while slowing melanin production.
However, they can also render your skin increasingly sensitive to sunlight, which is why you must preferably apply them at night and always wear sunscreen during and after treatment. (4) These ointments may be available over the counter, but you must always consult your doctor before using them. Excessive or wrong application can greatly irritate your skin.
Another slightly controversial topical treatment for age spots is a compound called hydroquinone. It is found in many prescription bleaches that are used for lightening hyperpigmentation.
Hydroquinone works by reducing melanin synthesis in the targeted area. Repeated application over the dark spots gradually fades their color to match the normal skin around them. However, high doses of hydroquinone could prove cancerous, (5) which is why the FDA does not allow more than 4% hydroquinone in prescription skin products.
2. Laser therapy
Laser therapy involves shining a concentrated laser beam on the age spots to destroy the photodamaged melanocytes underneath them and thereby curb melanin production in the area. This helps lighten the spots without the risk of scarring.
3. Chemical peels
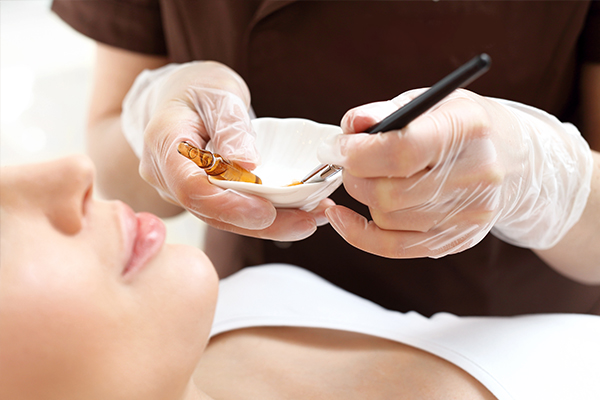
A chemical peel is a noninvasive skin procedure that is mainly used for treating superficial spots, preferably in a clinical setting.
The doctor applies a skin-peeling chemical, such as glycolic acid, all over the affected area to stimulate the shedding of the damaged upper layers of skin. As the spot-covered skin gradually sloughs off, new healthy skin forms in its place.
It can take multiple rounds of skin peeling to get smooth and spotless skin.
4. Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a standard treatment for sun-induced skin damage and precancerous skin lesions. It may prove useful in fading age spots as well.
5. Dermabrasion
Dermabrasion is a skin renewal technique that uses specialized tools such as a rotating brush to exfoliate the damaged surface layer of skin, which is then replaced by fresh new layers from underneath.
You may need to undergo multiple sessions to achieve the desired results. Moreover, dermabrasion is associated with some adverse skin reactions such as redness, swelling, irritation, and scabbing, but they will subside on their own after some time.
6. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion works on the same principle as dermabrasion, but on a smaller, less invasive scale. This procedure uses a diamond- or crystal-tipped brush to remove the damaged skin from the surface and promote the growth of new skin in its place.
7. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a relatively invasive technique that is used for removing large or prominent age spots. It involves freezing the pigmented skin by applying liquid nitrogen, which then sheds from the surface to make room for new healthy skin.
Diagnosing the Cause Behind Age Spots
Age spots are mostly harmless, but they can sometimes be a sign of severe photoaging and even skin cancer.
The doctor may use the following diagnostic techniques to understand the true nature of your age spot and to rule out the risk of other serious skin conditions or complications:
- Visual inspection, which is usually enough to diagnose age spots
- Skin biopsy, which involves scraping a small sample of the affected skin for lab testing (skin biopsy)
Risk Factors for Age Spots
People with the following risk factors are more prone to developing age spots:
- Older than 40 years
- Light skin color
- Caucasians
- History of frequent use of tanning beds
- Occupations that involve excessive or repeated sun exposure
- Genetics
Complications of Age Spots

As discussed earlier, melanin blocks the UV rays to prevent them from causing any real damage to the skin’s cellular structure.
Thus, tanning and age spots are actually signs that your skin is working well to protect itself from the harmful UV radiation, which otherwise has the potential to damage your skin’s DNA and pave the way for skin cancer.
However, intensive or repeated exposure to UV radiation can overwhelm the capacity of the melanocytes. Thus, people who spend a lot of time in the sun regularly are at a high risk of skin cancer.
In fact, what may start as harmless age spots may turn into precancerous lesions if you continue to expose your skin to UV radiation from the sun or other artificial sources.
Age spots that become bigger, change their color, or become raised or irregular can be early signs of cancer and therefore need to be tested and treated immediately.
When to See a Doctor
Age spots generally don’t pose a threat to your health, but they warrant medical attention if they:
- Change their size, shape, or color
- Grow darker even without sun exposure
- Start to itch
- Become red and tender
- Look shiny
- Feel waxy
Final Word
Age spots are usually not a cause for concern, but you must get prompt medical help if they change shape, size, or texture, which can be indicative of skin cancer. As for the benign marks, they may not compromise your health but they can certainly affect your appearance.
Fortunately, several standard treatment modalities can diminish the appearance of age spots, ranging from topical skin-peeling ointments and specialized exfoliation techniques to more invasive procedures such as laser therapy and cryotherapy.
Each of these interventions has its own side effects. So, it is important to have an in-depth discussion with your doctor about the pros and cons of all the available treatments to make an informed decision.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


