In this article:
Lymph nodes or lymph glands are present everywhere in the body. They are an irreplaceable part of the immune system because they enable the body’s defense mechanism to fight germs by recognizing them as foreign bodies.
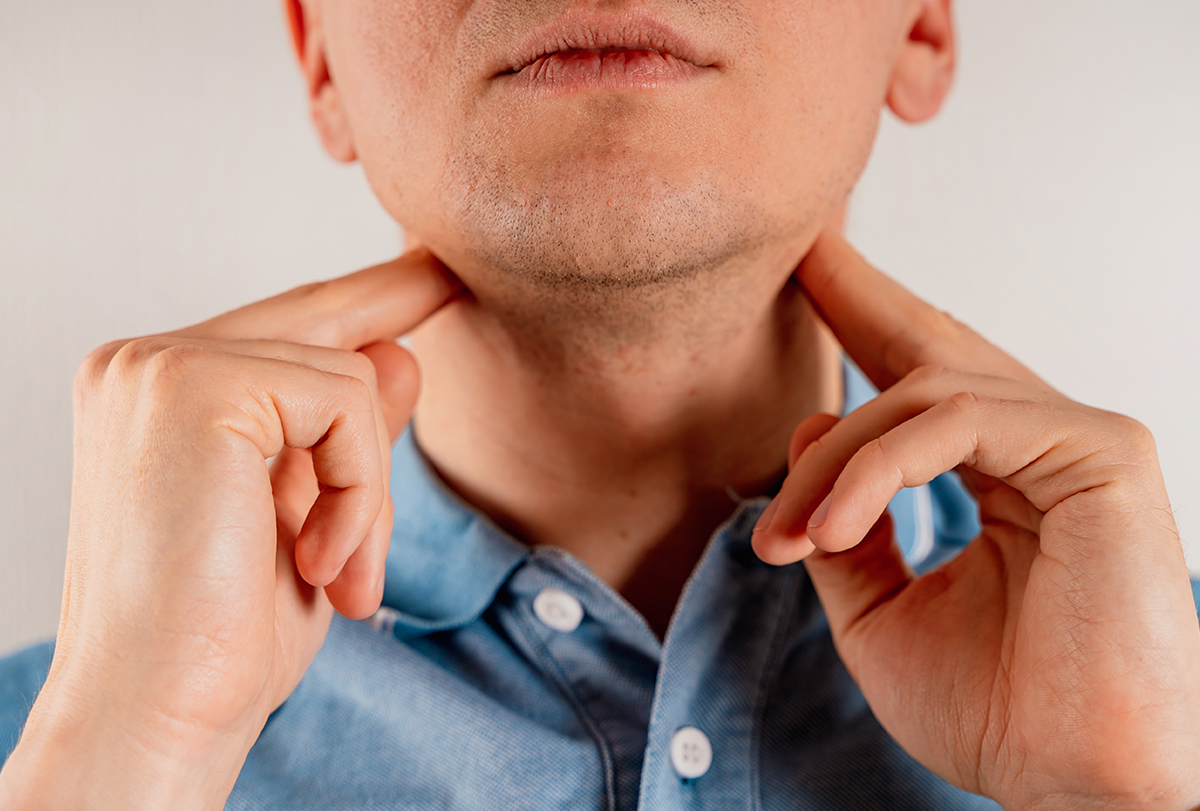

Lymph nodes are filled with white blood cells (WBCs) that help your body fight infections. When lymph nodes become infected, it’s usually because an infection started somewhere else in your body.
About 600 lymph nodes are present in the body, but normal lymph nodes may only be felt below your jaw, under the arms, and in the groin.
The parts of the body where lymph nodes are found very commonly include:
- Neck
- Jaw
- Head
- Ears
- Groin
- Armpits
Although they’re very important, they can be problematic if they get swollen, which is a condition known as lymphadenopathy or lymphadenitis.
The size of the swelling can vary from person to person and case to case. The swollen lymph nodes can be as big as an egg or as tiny as a pea. (1)
The good news is that there are remedies and some ways you can manage the symptoms associated with lymphadenitis at home.
Home Remedies to Manage Swollen Lymph Nodes
Here’s how you can improve swollen lymph nodes at home.
1. Massage the affected area

Massage is well known for increasing the flow of blood to the massaged area. Similarly, massaging can be an effective remedy to manage swollen lymph nodes in the case of lymphadenitis.
Massaging the affected area will help stimulate your lymph nodes to function properly and will also aid in decreasing the swelling and any accumulation of impurities in the area.
You can gently massage a swollen lymph node for a few minutes using your fingers twice daily. Getting a professional massage to drain your lymph can also be a helpful way to deal with lymphadenitis. (2)
2. Use garlic
Garlic is famously known for its anti-inflammatory properties, which can reduce inflammation symptoms including swelling, which is the chief problem in lymphadenitis. It also has good antibiotic properties; thus, it is effective in cleansing your system while promoting healing.
All you need to do is include garlic in your diet by eating raw garlic cloves to get these benefits. You can also apply garlic oil topically to the affected area. Do note that applying it to sensitive skin may cause some burning sensation, (3) and, due to its odor, it may cause nausea.
You can also talk to a medical professional about taking garlic supplements. (4)
3. Try honey
Honey has been a famous anti-inflammatory agent since time immemorial. It helps treat inflammation and related symptoms such as swelling and pain, which are usually associated with swollen lymph nodes.
Like garlic, honey also has antibacterial properties and will thereby help fight any infection that may be the underlying cause of your swollen lymph nodes.
Consume honey by mixing it in a warm cup of water with a few drops of lemon juice. Drink this two times a day for at least a week.
Topical application of raw honey to the affected area may also be a good way of dealing with lymphadenitis. Let it sit for a few minutes before you rinse it off with warm water. Do this at least twice daily to see the effects. (5)
4. Use turmeric
Turmeric is a natural anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agent. This means that it will not only alleviate any discomfort that may arise from pain and inflammation, but it will also bring down any swelling associated with lymphadenitis.
These properties of turmeric are due to its chemical compound called curcumin.
To apply turmeric to the affected area, make a paste by mixing it with coconut oil. Other than topical application, you can also consume turmeric milk to promote healing. (6)
5. Consume apple cider vinegar

Apple cider vinegar has antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties; thus, it can be used to treat infections that can be the underlying cause of swollen lymph nodes. It can also balance the pH levels in the body.
However, remember to use apple cider vinegar with caution and report any side effects to the doctor immediately.
How to use:
Mix 2 teaspoons of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water, and drink the mixture at least twice a day. (7)
6. Apply a warm compress
Applying a warm compress promotes blood circulation to the area and is an effective way to promote healing. A warm compress can also reduce infection by fighting bacteria and can soothe the inflammation in and around the swollen lymph nodes.
To use a warm compress on the affected area, all you have to do is soak a clean towel in warm water and hold it close to the affected area for a few minutes. Do this at least twice a day until you see the fluid start to drain.
Make sure that the compress is not too hot, especially when applied to the vaginal area as it is very sensitive and delicate. (8)
7. Make use of herbs

Chamomile tea is a good treat for those who wish to reduce the swelling and other symptoms associated with swollen lymph nodes due to its anti-inflammatory properties. It can also ease the pain.
You can make chamomile tea by steeping chamomile tea bags or fresh chamomile flowers. (9)
Other herbs good for swollen lymph nodes are:
- Pot marigold
- Dandelion
- Figwort
- Cleavers
- Ashwagandha
8. Perform skin brushing
Skin brushing, also known as dry brushing, is a good technique to increase the flow of lymph and reduce swelling. It is done by gently brushing over your skin in the direction of lymph flow, which is upward from the feet toward your collarbones.
The best time to do skin brushing is when your skin is dry, that is, before you take a bath in the morning.
Causes of Swollen Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes are the body’s way of telling you that something is wrong such as an infection. The common causes can include: (1)
- Ear infections
- Measles
- Common cold
- Mononucleosis
- Gingivitis
- Skin infections
- Measles
- Tonsillitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
In some cases, those who suffer from cancer or HIV can also experience swollen lymph nodes. Certain medications can also cause lymphadenitis as a side effect.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips to Manage Swollen Lymph Nodes
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Take over-the-counter painkillers to relieve the pain related to swollen lymph nodes.
- Give your body enough time to recover by taking proper rest.
- Drink cinnamon tea with basil every day.
- Make sure you wash your hands frequently to avoid infections that may cause swollen lymph nodes.
- Treat infections that can cause swollen lymph nodes, such as fungal infections, skin infections, sinus infections, common cold, and others. Do consult your healthcare provider for the proper treatment.
When to See a Doctor
Immediately seek medical help if your swollen lymph nodes occur for no underlying reason. If your lymph nodes continue to grow and enlarge or have been there for more than a few weeks, you may require professional assistance.
Also, if your swollen lymph nodes start to feel harder than before or do not move when pushed, you must take them seriously and seek medical help.
Most-Asked Questions About Swollen Lymph Nodes
What are some common symptoms of swollen lymph nodes?
Lymphadenitis is mainly characterized by swelling of the lymph nodes, which can also accompany other symptoms such as: (1)
- Pain
- Soreness in the throat
- Fever
- Cough
- Swelling in the limbs
- Sweating at night
- Weakness/lethargy
- Runny nose
Are swollen lymph nodes related to cancer?
Swollen lymph nodes are always not an indication of cancer. In fact, the most common reason for lymph node swelling is infections that can include a cold, sore throat, and ear infection. However, it is always a good option to check with your doctor to rule out cancer.
How can swollen lymph nodes be prevented?
Here’s how you can prevent lymphadenitis: (8)
- Maintain proper hygiene.
- Wash your hands frequently.
- Do not touch your nose or face too often.
- Maintain distance from those who suffer from communicable infections.
- Clean your house with disinfectants.
- Get good sleep.
- Practice physical exercise daily.
- Consume a healthy diet.
How are swollen lymph nodes diagnosed?
Your doctor may do the following to diagnose swollen lymph nodes:
- Order a blood test such as a complete blood count (CBC) to check for an infection
- Take fluid from the lymph node for culture and testing to see what type of germs are present in the lymph node and treatments can be done to stop the infection.
- Take a small sample of tissue or fluid from the lymph node for testing under a microscope to rule out malignancies.
Final Word
Treating lymphadenitis would mean treating the underlying cause of the swelling. Usually, the swelling will go away with time without much intervention. Using a few remedies can be helpful in managing the condition.
However, if the swelling lasts for more than a few weeks, it may be a sign of something serious, and you should seek immediate medical help.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


