In this article:
Earaches refer to a sharp, dull, or burning pain sensation in one or both ears, and the pain may be constant or intermittent.
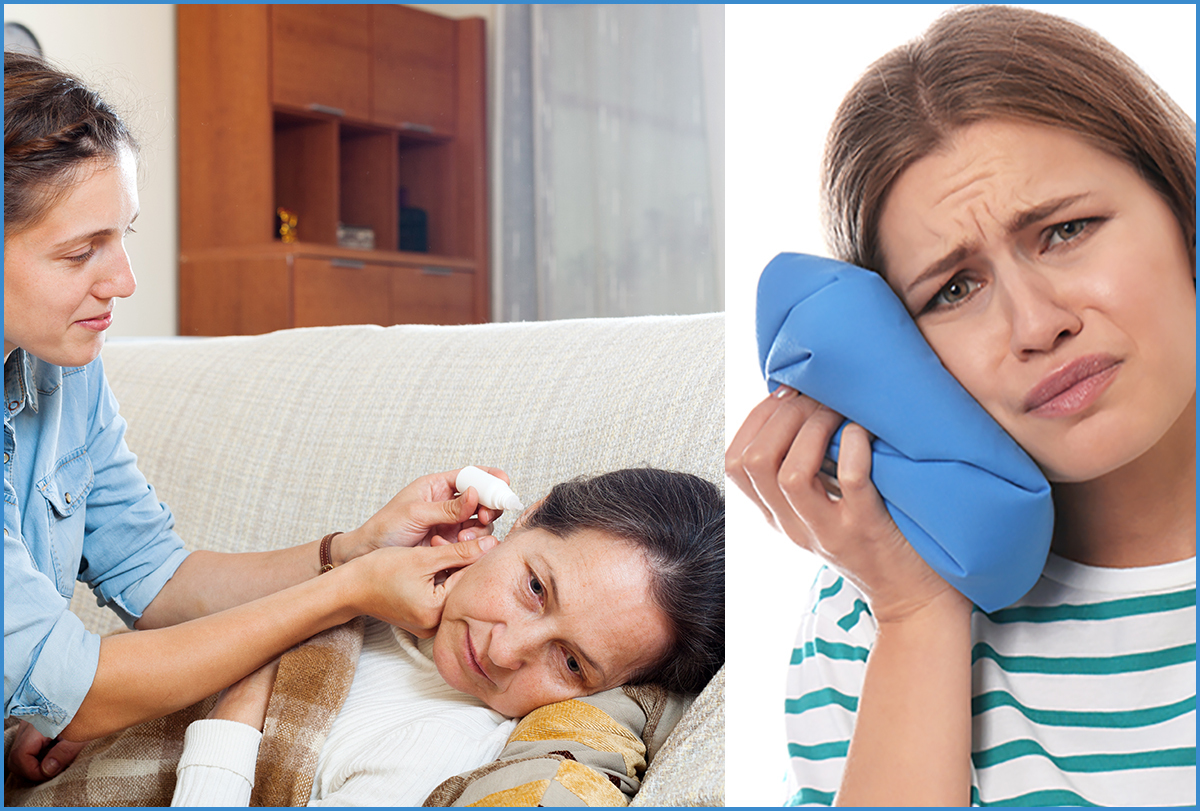

The condition is generally caused by problems in the ear or surrounding structures. The problem is common among children and may have various causes.
It is important to diagnose the causes of the pain as early as possible so that appropriate treatment can be started. Additionally, one can follow various preventive measures to avoid causing harm to the ear.
Home Remedies for Earache
You may try the following remedies to help relieve the ear pain at home.
1. Apply a warm compress

You may use a warm compress to help reduce the earache. (1) This easy-to-use remedy is safe for adults and children, provided it is done correctly.
It involves the application of gentle heat on the painful area to stimulate blood circulation, dilute any wax build-up, and relax any muscle tension. However, even low degree heat can give you burns when applied continuously to a specific spot for an extended period.
How to use:
There are many different types of warm compresses that you can make at home or buy from the market, but all of them may not prove convenient to be used on the ear. Here are two options that can get the job done:
a. Heating pad: You can hold a small heating pad over your ear for a few minutes, but make sure it’s not too hot before applying.
b. Warm rice sock:
- Put some rice into a clean tube sock until it’s halfway full and then tie its mouth to form a pouch.
- Sprinkle 1 tablespoon of water over the sock pouch and microwave it for about a minute.
- Check the temperature of the rice sock on your arm to make sure it’s not too hot.
- Place the rice sock over the ear for a few minutes repeatedly, until the pouch loses its heat.
2. Be mindful about your resting posture
It is recommended to sit in an upright position to reduce the pressure in the middle ear.
Try to sleep with your head elevated as lying down interferes with the function of the Eustachian tube (a tube that connects the nose and the ear) and may aggravate the pain associated with ear infections.
3. Yawn to relieve earache
Yawning stretches out the muscles that help open up the Eustachian tube. It is especially helpful for alleviating the ear discomfort induced by pressure changes during air travel.
This simple action can also help relieve the occasional earache you experience on waking up, probably due to an incorrect sleeping position.
4. Try chewing gum

Chewing gum works your entire jaw structure and can pull open your ear canal in the process. This is usually helpful when you are at a high altitude like on an airplane.
Avoid giving gum to young children as there is a risk of choking.
5. OTC drugs and drops
You can use ibuprofen or acetaminophen as directed on the label or by the physician to help ease the discomfort. Several ear drops are available over the counter to alleviate the pain.
Avoid using aspirin for earaches, especially for individuals below 18 years of age, as it is linked with the development of Reye’s syndrome, a condition that may cause brain and liver inflammation.
Note: Avoid the use of olive oil drops or most other OTC ear drops if the eardrum has burst. In serious cases, your doctor may prescribe an eardrop that can be used even when a perforation is present in the eardrum. For ear infections, refrain from getting water into the ear or putting objects such as cotton buds in the ear.
Self-Care Preventive Tips
Here are some measures you can take to prevent earache:
1. Get vaccinations
Consult your doctor to get your children vaccinated for the flu and pneumococcal infections to lower their risk of middle ear infections.
2. Breastfeed your infant
Breastfeeding children up to 6 months of age can help reduce the chances of ear infections.
3. Hold the baby in an upright position
To prevent the formula from flowing into the middle ear, it is essential to hold the baby’s head up while feeding. Avoid propping the bottle or feeding the child when lying flat.
4. Clean the outer ear
Use mild soap and a damp, soft washcloth to wash the external ear if there is discharge.
5. Take precautions when swimming
Cover your ears with a swimming cap or earplugs and swim on the surface of the water. Avoid swimming in dirty water.
6. Dry your ears
Make sure to gently dry out your ears after taking a bath or swimming. The safest way to do this is to use a blow dryer on a cool setting. Do not insert cotton swabs deep into the ear canal.
7. Keep the volume in check
Do not listen to extremely loud music, especially when using earbuds or earphones.
Additionally, it is important to keep the following tips in mind:
- Do not blow your nose forcefully or swim while having a bad cold or the flu, as this may increase the risk of having a middle ear infection.
- Avoid using cotton swabs or other objects to clean your ear. Allow the ear to clean itself naturally, dead skin cells and earwax migrate to the outer opening of the ear canal and are automatically sloughed off and out.
- Avoid smoking or secondhand smoke as it can increase the chances of an ear infection. (2)
- Maintain distance from anyone who has a cold or flu to avoid infections.
- Avoid allergens such as dust and pollen, treat your allergies more aggressively during allergy season.
- Prevent water from getting into the ear canal.
- Do not leave your baby unattended with a bottle.
Do Popular Internet Remedies Work?
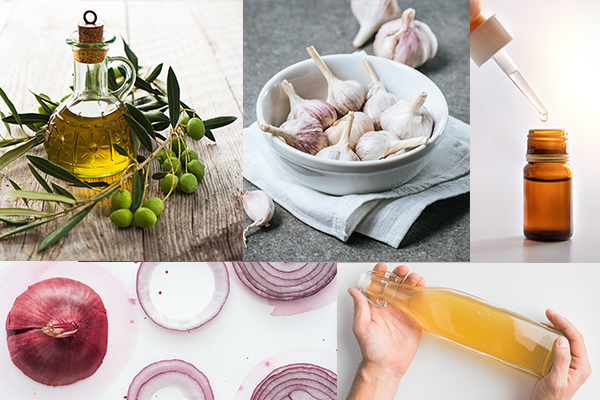

Various suggestions are available as home remedies for earache on all types of public media and the Internet. However, there is usually no scientific evidence to confirm their safety or effectiveness.
Some of the most commonly cited remedies on web forums include olive oil, garlic, herbal drops, onion, and vinegar, which may have worked for some users but are not guaranteed to work for everyone.
While garlic has certain antimicrobial properties, (3)(4) no research has evaluated its use for treating ear infections or pain. Similarly, deep cleaning your ears with invasive tools like cotton swabs or needles can irritate your sensitive ear lining and even puncture the eardrum. The same goes for using strong solutions like hydrogen peroxide to irrigate the ear canal which can do more damage than good.
This kind of aggressive cleaning can increase swelling in the ear canal, and thereby aggravate your pain. Thus, you shouldn’t be too experimental when it comes to your ears since they are extremely delicate and can suffer serious damage if a remedy goes wrong.
If you do consider using a remedy for your earache, always consult your doctor first to determine its safety.
Most-Asked Questions About Earache
Can earache impact a child’s hearing?
Temporary hearing loss caused by fluid buildup in the ear or middle ear infections is common among children. If the problem persists, it may affect the child’s language and speech skills. Therefore, it is essential to consult a doctor if your child has recurrent ear infections.
Why do people experience earache after they quit smoking?
Earache is a common withdrawal symptom of nicotine and other components of tobacco smoke. Therefore, it might be considered as a recovery symptom instead.
Final Word
It is vital to understand that earaches should be treated promptly, as a lack of treatment for an ear infection can cause significant damage. The infection may spread to surrounding structures and may even result in chronic or permanent hearing loss.
Therefore, it is essential to follow self-care and preventive measures for the treatment of ear problems and visit a doctor when necessary.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


