In this article:
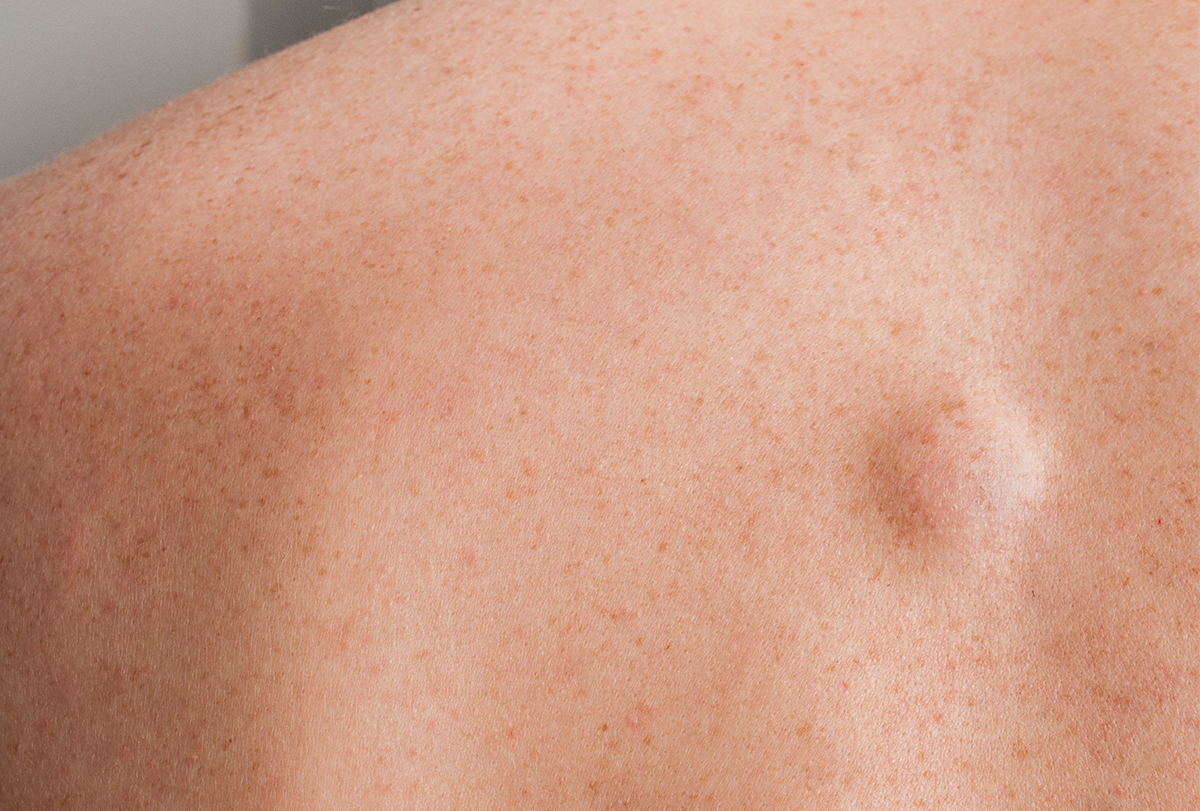
Lipoma is a painless lump of fat that forms just underneath the skin – in the subcutaneous tissue that lies between the skin and the underlying muscle. One can even develop multiple lipomas over the course of one’s life, but this is not very common.
Lipomatosis affects people of all ages but is more prevalent among those aged between 40 and 60 years. Plus, men are slightly more susceptible to it than women.
Lipoma is pretty common as it affects nearly 1 in every 100 people. The good thing is it is noncancerous and does not hurt, so you can easily go without treatment.
However, this benign growth can look odd and cause discomfort if located on a tricky spot. In such cases, you may get it surgically removed. But if you are apprehensive about going under the knife, you can try some natural remedies that can slowly but surely dissolve the fatty lump over time.
Natural Remedies for Lipoma
The only way to completely remove lipoma is through surgery, but a number of natural remedies can help shrink it.
However, bear in mind that these remedies tend to work slowly and have to be used consistently for months to get the desired results. So, be patient.
Also, experiment with different remedies. If one doesn’t seem to work for you, try another.
1. A mixture of frankincense oil and castor oil

Frankincense oil contains boswellic acid, which exhibits antitumor properties (1) that may help shrink the lipoma. It is also an anti-inflammatory agent that can help bring down the swelling associated with such lumps.
Castor oil is credited with skin-healing properties and can be safely used in pharmaceutical applications. (2) Its main component is ricinoleic acid, which shows anti-tumor effects.
Since castor oil penetrates deeply into the skin quite readily, mixing it with other active ingredients such as frankincense oil will enhance their absorption as well. Thus, the combination of these two oils may be more effective in curbing lump formation. (3)
How to use:
Mix frankincense oil with either coconut oil or castor oil and massage it into the affected area.
2. A mixture of neem oil and flaxseed oil/tea base ointment

Studies have shown that neem exhibits anti-tumor activity, (4) which can be utilized for treating lipoma. Plus, it has anti-obesity effects, (5) so it helps reduce fat deposition inside the body, which is associated with lipoma formation.
Flaxseed oil is loaded with essential fatty acids (EFAs) that curb inflammation and promote wound healing. This ingredient is also credited with antitumor effects. (6)
How to use:
- Mix 1 teaspoon of flaxseed in 2–3 tablespoons of neem oil or flaxseed oil.
- Apply the mixture to the lipoma.
Another remedy using flaxseed is mixing it with green tea. Green tea is full of antioxidants that provide anti-inflammatory and skin-healing effects. Additionally, it is known to have anti-obesity effects as it inhibits fat deposition inside the body, (7) which is a major contributor to lipoma development.
How to use:
- Mix 1 teaspoon of flaxseed in 1–2 tablespoons of chilled green tea to make a paste, and apply it to the lipoma.
- You can also consume green tea to prevent further fat deposition. (7)
3. Turmeric paste

Turmeric is renowned for its multiple healing properties, most of which can be traced back to its main component called curcumin.
Curcumin has successfully been used for addressing inflammatory, tumorous, and infectious skin conditions. (8) This goes to show that it can be a useful aid in the treatment of lipomatosis as well.
How to use:
- Mix a few drops of olive oil with 1 teaspoon of turmeric to make a soft paste.
- Apply the paste to the lipoma.
- Cover it with a bandage to avoid turmeric stains.
4. A mixture of dried sage and neem oil

Sage is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and anti-obesity effects, (9) all of which can help reduce the size and occurrence of lipomas.
It inhibits fat deposition inside the body to deter lipoma formation and growth, especially if you suffer from high cholesterol levels.
How to use:
- Put ½–1 teaspoon of dried sage in a bowl and mix in 2–3 tablespoons of neem oil or flaxseed oil to make a paste.
- Apply the paste to the lipoma.
5. Eastern white cedar/northern white cedar/Arborvitae red cedar

Thuja occidentalis, also known as eastern white cedar, is known to possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. (10) This explains why it is widely used in homeopathic medicine.
Thuja is occasionally used for treating abnormal growths on the skin such as warts and spongy tumors, and it may prove helpful in dissolving fatty lumps such as lipoma.
How to use:
- Mix thuja extract in some water to make a paste.
- Apply the paste to the lipoma three times every day until the lump dissolves.
Other Natural Interventions
Essential oils are potent liquids derived from various medicinal plants and credited with different healing properties.
Some that may prove helpful in treating lipomatosis are ginger essential oil, (11) clove essential oil, (12) grapefruit essential oil, cumin essential oil, cinnamon essential oil, and sweet orange essential oil, (13) among others.
All these oils have the ability to fight body fat as well as tumor cells. Thus, they help reduce lipoma lumps and keep them from turning cancerous.
Belladonna is a herbal plant with several medicinal benefits that have been widely used in homeopathy. (14) It may help in dissolving the fat cells inside the lipoma, shrinking its size and possibly making it disappear completely.
According to one case study, this homeopathic medicinal herb was very helpful in treating giant lipomas. (15) Note that belladonna as it is an extremely poisonous perennial herb and should be used with caution. (16)
Causes of Lipoma
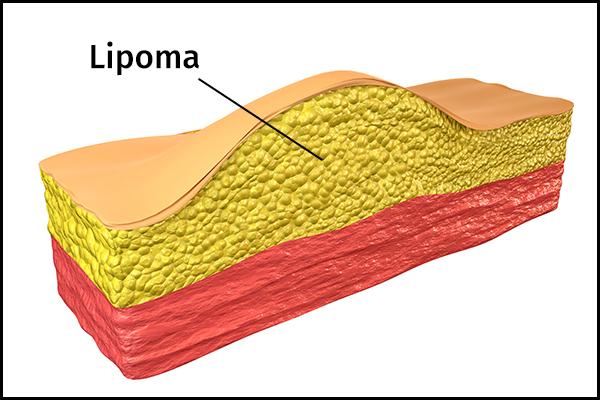
The exact cause of lipomatosis is still unknown, but genetics may play a role.
Some people suffer from a rare condition called familial multiple lipomatosis, wherein they inherit a faulty gene that triggers the growth of multiple lipomas on the body.
Another possible cause is physical trauma to the skin.
Symptoms of Lipoma
Here are a few characteristic symptoms of lipoma:
- Lipoma usually forms on the neck, head, shoulders, or back but can sometimes develop elsewhere on the body such as the thighs or on internal organs such as the stomach and bowels.
- It tends to grow slowly, typically up to the size of 1–2 cm. If it grows rapidly, it’s best to get it checked by a doctor to rule out the risk of cancer or any other serious underlying cause.
- It is composed entirely of fat cells, which is why it feels soft like dough. (17)
- It moves easily when pressed lightly.
- It generally does not cause any pain and is not tender to the touch, but it can be discomforting if it develops on your joints or grows too big and can even restrict your movement.
Treatment for Lipoma
Lipoma is a benign, painless tumor made up of fat that can be left untreated if it does not bother you. However, if you do want to get rid of it, there are two clinical procedures that serve that purpose:
- A minor surgery can excise all the fatty tissue and is the only way to completely remove the lipoma
- Liposuction involves using a needle and large syringe to suck out the fatty tissue. (18)
- Both procedures leave behind scars. In some cases, the lipoma may develop again near its original spot.
Diagnosis of Lipoma
- In order to diagnose lipoma, the doctor will first physically examine the lump for its appearance, size, texture, and mobility.
- They will also observe the skin covering the mass for any abnormalities or changes.
- This is followed by a round of imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans (computerized tomography), and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to get an inside view of the lump.
- Finally, the doctor may order a biopsy if a cancer risk is suspected.
Risk Factors
The following factors can make you more prone to lipomas:
- Obesity
- Alcoholism
- Liver disease
- Glucose intolerance (19)
Dietary Interventions for People With Lipoma

Since excessive body fat and obesity are prime culprits behind lipoma formation, you can do well by implementing some dietary control to manage a healthy weight. The main aim is to follow a low-fat but nutritious diet. (20)
Here are a few recommendations:
- Increase your intake of vegetables and fruits to leave less room for fatty foods.
- Eat more fish, which is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, (21) or take omega-3 supplements.
- Minimize your intake of deep-fried, junk foods.
- Consume foods that contain L-carnitine such as red meat, poultry, and fish, or take it in supplement form. (22)
Note: Always consult your doctor before starting any supplement.
Can Lipoma Be Cured With Exercise?
Exercise helps you burn fat, but lipoma is composed of different types of fat cells that do not respond to exercise. Thus, exercise cannot shrink lipoma, but it does help reduce excess body weight and fight obesity, which is a major risk factor for lipoma.
Simply put, exercising may help prevent lipoma formation but cannot cure it once it is formed.
It is important to remember that the above-listed tips and remedies may or may not work for everyone, and it needs many months of continuous usage to see some benefits.
Final Word
Lipoma is essentially a noncancerous mass of fatty tissue that does not hurt or pose any risk to your life. However, it can be a cosmetic concern for some people, especially if you develop more than one.
Moreover, if the lump forms on the joints, it can impede your movement and cause discomfort. These are the main reasons people choose to get lipomas removed, or else they can easily go without treatment. However, this decision can only be taken once you are completely certain that the lump is indeed lipoma and not a cancerous tumor.
So if you do notice any new growth on the body, get it checked out by a doctor to make sure it’s benign. And even if you do choose to leave it untreated, keep an eye on it for any changes in color, shape, or size. In fact, you must get it medically evaluated by a doctor at regular intervals to make sure it hasn’t turned cancerous.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


