In this article:
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) refers to an ovarian problem characterized by increased production of androgen in women. PCOS manifests physical symptoms such as hair growth, acne, and weight gain.
Dietary Modifications for PCOS
Diet plays a critical role in the management of PCOS symptoms.
Your diet should include at least 5 portions of fruits and vegetables daily, lean meats such as fish and chicken, and whole foods such as brown rice, wholegrain cereals, and wholemeal bread. (1)
Caution: Speak with your ob-gyn before trying or adopting any new dietary interventions for PCOS to avoid any complications.
Adding the following items to your diet can help manage PCOS better.
1. Turmeric
Turmeric owes much of its medicinal potency to curcumin, which acts as a natural estrogen source. Thus, it can be beneficial for menstrual regulation and fertility.
Animal studies have highlighted the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin, which may help in managing PCOS symptoms. However, there is still a need for direct human trials to conclusively establish these claims. (2)(3)
How to use: Add turmeric powder to water or use it as a spice. However, it is best to consume turmeric milk daily.
2. Omega-3
Foods that are rich in omega-3 are particularly suitable for women with PCOS as they are helpful in decreasing bad cholesterol levels while increasing good cholesterol levels, reducing waist circumference, and decreasing the interval between menstrual periods. (4)(5)
You can include the following omega-3 rich foods in your diet:
- Fish oil: This helps enhance insulin sensitivity and thereby reduce androgen secretion. (6)
- Flaxseeds: While there is some scientific support for the use of flaxseeds for PCOS management, further research is needed to establish its efficacy. (7)
- Tuna
- Salmon
- Walnuts
- Soybeans
Note: To avoid complications, it is best to speak with your doctor about the appropriate and safe dosage of these foods that will help your condition. Also, you may ask your doctor about taking omega-3 supplements, as it may improve the quality of eggs produced from the ovaries and, thereby, your fertility.
3. Vitamin D and calcium
Women with PCOS generally run low on vitamin D. (8) The primary role of vitamin D is to help your body effectively absorb calcium from food.
Additionally, this vital nutrient plays a key physiologic role in reproduction, including ovarian follicular development. (9) Therefore, vitamin D deficiency can cause poor bone mineralization and worsen PCOS symptoms. (10)
Women with PCOS who are deficient in these nutrients can benefit from taking vitamin D and calcium supplements upon their doctor’s recommendation. (11)
4. Magnesium
Insulin resistance and/or type 2 diabetes are associated with increased excretion of higher-than-normal amounts of magnesium in the urine.
The continued loss of heavy amounts of magnesium can render one deficient. This is why experts believe there may be an association between magnesium deficiency and the development of insulin resistance. (12)
Some of the best food sources to meet your daily magnesium needs include green leafy vegetables, nuts, whole grains, legumes, dairy foods, and meat.
5. B vitamins
Foods that contain B vitamins alleviate PCOS symptoms by promoting the healthy functioning of the hormonal system while reducing androgen levels in the body. (13)
One of the predominant symptoms reported among women with PCOS is an overwhelming sense of fatigue. Consume more of whole grains, nuts, and skim milk, all of which are brimming with B vitamins and can help you deal with symptomatic fatigue. (14)
Lifestyle and Self-Care
Many PCOS symptoms improve with positive lifestyle choices. Here are things you can do to help manage your condition.

1. Maintain a healthy weight
PCOS symptoms tend to be more pronounced in women who are on the heavier side. Strict weight management is the only way to ensure that your ovaries function normally.
If you are overweight, shedding only 5% of the extra pounds may register significant relief from PCOS symptoms. (15)(16) Healthy weight management can help reduce the risk of other long-term health issues that usually develop in association with PCOS.
2. Have regular health checks
PCOS can pave the way for other chronic medical conditions. Thus, you have to work closely with your doctor to monitor your overall health.
Regular health checkups can help your doctor detect the early signs of other PCOS-related conditions so that they can be treated right at its onset before it becomes serious.
3. Keep your stress in check with yoga and meditation
The therapeutic effects of yoga are not limited to your physical body alone but encompass the mind and soul as well.
Certain yoga exercises relieve abdominal compression, restore gastrointestinal balance, and improve digestive functioning by gently massaging the internal organs. These asanas facilitate improved blood flow in the body, help open up the pelvic area, and make you feel relaxed. (17)
Meditation is another fundamental aspect of yoga that helps you center your mind and tune out the stress of the world by focusing your energies inward. (18)
Doing a bit of yoga regularly can also help you lose weight and keep your metabolism rate high.
4. Exercise to re-energize (for cramps)
Most of the discomforting complications associated with PCOS can be adequately managed by improving insulin resistance in the body. Regular exercise is extremely effective in this regard, even if it does not result in any noticeable change in weight or body fat measurement. (19)(20)
Women with PCOS are usually recommended to take up a multipronged exercise routine that focuses on building both cardiac health and muscle strength.
5. Quit smoking
A lot has been said about the damaging consequences of smoking on both cardiovascular and respiratory health, but not a lot of people know that smoking can also spike the level of male hormones in the body.
The study found that women with PCOS who smoke are more likely to develop diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and other cardiovascular problems than women with PCOS who do not smoke. (21)
6. Try a ketogenic diet

A ketogenic diet aims to supplement your body’s energy needs through foods that are low in carbs and high in fat. Sticking to this diet may help trigger faster weight loss as your carb intake is greatly reduced while your body uses up the fat reserves for energy.
According to a small-sized study, a ketogenic diet helped lose an average of 12% of total body weight, accompanied by nearly a 54% reduction in fasting insulin levels and considerable improvements in the levels of PCOS hormones. (22)(23)
7. Limit junk food and added sugars
Maintaining healthy body weight is an absolute must for women with PCOS if they wish to avoid ovulation problems and loss of fertility.
Some common foods to avoid include: (24)
- Candy
- Muesli bars
- Milk chocolate
- Potato chips
- Ice cream
- Fruit juice
- Soft drinks
Most-Asked Questions About PCOS
Will my symptoms go at menopause?
PCOS is brought on by an overproduction of androgens in the female body and this hormonal imbalance does not resolve with age or menopause.
You can only hope to manage or reduce the symptomatic discomfort caused by PCOS. Although the hormonal imbalance does not worsen with age, you become more vulnerable to other PCOS-related health problems as you get older. For instance, PCOS can predispose you to diabetes, stroke, and heart attack. The risk only increases with advancing age.
Is PCOS in lean women a myth?
While PCOS is commonly associated with excess body weight, it is not limited to women who are on the heavier side. Nearly 5% of lean women are diagnosed with PCOS, which accounts for 20%–30% of all PCOS cases. Women of average weight are less prone to insulin resistance, which is recognized as an underlying cause of PCOS.
Medical experts debate the possibility that thin women with PCOS may not suffer from the same level of insulin resistance as heavier patients. (25)
Can one conceive with PCOS?
A lot of people are under the misguided impression that women with PCOS are infertile, which is anything but true.
Some women with PCOS may face no trouble at all in getting pregnant, whereas others may require special fertility treatments to help the process along. These treatments are usually multifaceted.
What is the difference between PCOS and ovarian cyst?
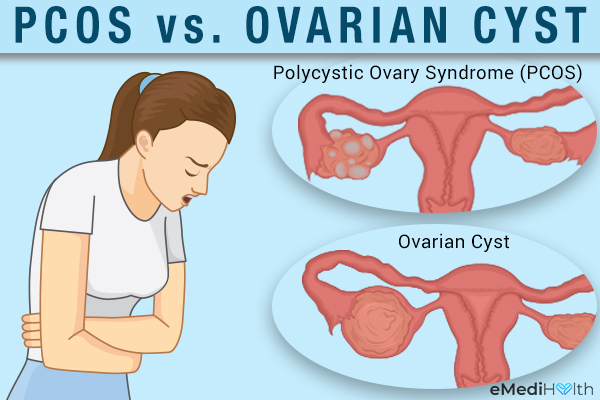
Having ovarian cysts does not necessarily mean that you have PCOS. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on one or both the ovaries, usually as a result of a normal menstrual cycle.
Most women get these harmless cysts at some point in their lives, which often disappear on their own without any medical intervention. Unlike normal ovarian cysts that are functional in nature, PCOS is brought on by a substantial hormonal imbalance in the female body.
Final Word
While PCOS cannot be cured, taking healthy measures such as losing weight and modifying your diet can help prevent the development of associated health conditions, including diabetes and hypertension. It is best to consult a dietitian for an exercise and food regimen suitable for you.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


