In this article:
Morning sickness is a common problem that every pregnant woman is bound to face through the gestation period. However, mild morning sickness is not a very serious problem and can be easily dealt with.

Home Remedies for Morning Sickness
You can manage nausea and vomiting with these simple remedies.
1. Get enough vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
Consuming vitamin B6 in appropriate amounts can help resolve the symptoms of morning sickness in pregnant women.
The findings of a randomized controlled trial suggested that the combination of doxylamine and vitamin B6 may help alleviate the queasy and nauseous feeling during pregnancy. (1)(2)
One study found vitamin B6 to be more effective than ginger in treating pregnancy-induced nausea and vomiting, (3) while another compared its effectiveness to the commonly prescribed antiemetic drug dimenhydrinate. (4)
How to use:
- Consume foods rich in vitamin B6 such as kidney beans, lentils, seeds and nuts, sweet potato, soybeans, and lean meats.
- Start taking prenatal vitamins at least 1 month before pregnancy to decrease the risk of severe nausea. Vitamin B6 supplements have also been found to be a safe option for the mother and the fetus, but you must consult your doctor about the correct dosage before starting.
Vitamin B6 is found to be effective in the treatment of morning sickness. Consult your doctor for the supplement.
2. Soothe your nausea with ginger

A systematic review and meta-analysis found that using ginger helped improve the symptoms of nausea without any risks of drowsiness, heartburn, or miscarriage. (5) However, more studies are needed to determine the dose and preparations of ginger to be used for this purpose. (6)(7)
Note: Ginger must be eaten in minute quantities as excessive use during pregnancy can increase the risk of a miscarriage. A study found that consuming less than 1,500 mg of ginger daily did not increase the risks of heartburn, miscarriage, or drowsiness. (5)
How to use:
- Use ginger in your daily cooking.
- Consume ginger tea when feeling nauseous.
- Ask your doctor about starting you on a supplement if suitable.
Ginger root contains compounds called gingerols and shogaols that may help provide relief from nausea and vomiting. (7)
3. Calm your senses with aromatherapy
a. Peppermint
The refreshing smell of peppermint has been greatly utilized in aromatherapy for relaxing the mind and body. This intervention can also help relieve morning sickness by calming your gastric muscles and gag reflex.
One study demonstrated the positive effect of peppermint aromatherapy in managing pregnancy-related nausea and vomiting, but much of this was due to psychological conditioning rather than any actual physiological impact of peppermint oil aromatherapy on symptom relief. (8)
Another study found that peppermint inhalation had no effects on reducing nausea and vomiting in pregnant women. (9)
Given these conflicting results, more research is needed to confirm the actual effectiveness of peppermint oil aromatherapy.
Inhaling the therapeutic vapors of peppermint oil can help relax your stomach muscles for better digestion and thereby reduce the tendency to throw up.
b. Use lemon essential oil
One study reported that 40% of the pregnant female participants successfully used lemon essential oil aromatherapy to get comfort from nausea and vomiting. (10)
Although anecdotal evidence has encouraged several women to use lemon essential oil aromatherapy, further in-depth research is required to validate its antiemetic properties.
Note: Essential oils can be too harsh in their original potency and, therefore must be diluted in a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil, before using.
Lemon essential oil exudes a soothing smell that can help ease your digestive distress and mitigate the intensity and frequency of morning sickness.
4. Consume fennel seeds

Fennel seeds have been extensively used as digestive aids and antiemetic agents. (11) Both these properties justify their use in the management of morning sickness.
How to use:
- Simply chew 1 teaspoon of fennel seeds after meals to facilitate better digestion.
- Prepare fennel tea by boiling 1 cup of water and then steeping 1 teaspoon of crushed fennel seeds in it after turning off the heat. Strain the liquid after a few minutes, and add a bit of honey and lemon juice in it for better taste. Drink this soothing beverage whenever you feel queasy or nauseous.
Note: Consult your doctor before trying any herbal tea to rule out any health risks and determine the appropriate dosage.
5. Drink raspberry tea
Raspberry leaf tea is typically recommended in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy to relieve the symptoms of nausea and vomiting. (12)
How to use:
Steep 1–2 teaspoons of the raspberry herb in 1 cup of boiled water for about 10 minutes, and then strain the liquid in a cup. Drink 1 cup of this therapeutic tea a day to get through a spell of morning sickness with less discomfort.
Note: Consult your doctor before trying any herbal tea to avoid any health risks and determine the appropriate dosage.
Alternative Treatment
You can also try these complementary therapies along with your standard medications and self-care measures, but only after consulting your ob-gyn:
1. Acupressure
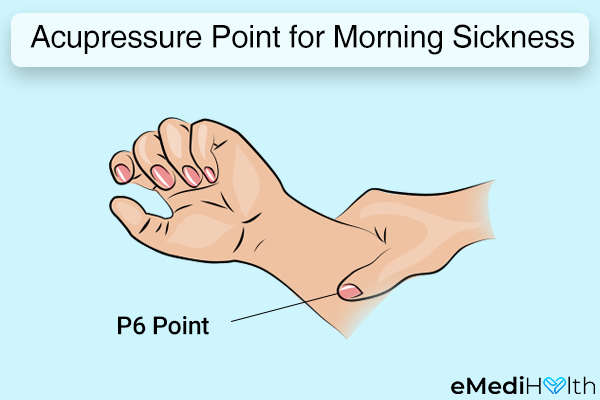
Acupressure involves applying gentle but firm pressure on specific points of the body with your fingers or a spatula to stimulate blood circulation and the release of chemicals that can help relieve several illnesses.
Pressing a point called P6 on the inner side of your wrist is known to reduce the symptoms of morning sickness, but there isn’t enough scientific evidence to conclusively establish this claim. (13)
2. Acupuncture
Acupuncture works through the same mechanism as acupressure but involves the insertion of specially designed needles to activate the pressure points.
A 2016 systematic review that pooled the results of 20 trials found that acupressure therapy was effective in reducing the symptoms of morning sickness. Although the therapy was effective, some participants experienced pain, swelling, and numbness in their hands. Further research is required in this area. (12)
Note: Acupressure therapy must be performed under expert supervision, and acupuncture must only be performed by a practicing acupuncturist.
Tips to Avoid Mild Morning Sickness
If you have been experiencing mild bouts of morning sickness, your doctor is likely to advise the following:
- Get adequate rest; fatigue can worsen nausea and vomiting.
- Avoid foods that have a smell that irritates your senses.
- Do not skip your breakfast. An empty stomach can lead to nausea and vomiting. Eat a bland breakfast, such as dry toast or crackers.
- Try the BRAT diet, which includes bland foods such as bananas, rice, applesauce, and tea.
- Avoid spicy and fatty foods.
- Take small meals high in carbs and low in fat at frequent intervals. These include rice, bread, and pasta.
- High-protein meals in the morning help with nausea.
- Prefer cold foods.
- Do not rush out of your bed in the morning. Instead, pull yourself slowly when getting up to avoid morning sickness.
- Avoid smoking. Restrict exposure to passive smoke.
- Expose yourself to fresh and airy environments.
- Practice light and relaxation exercises and techniques.
- Drink adequate amounts of water and stay well hydrated. Adequate hydration is needed in pregnancy to help combat constipation, dehydration, preterm contractions, and many other things, so water should be part of your daily regimen. You can choose to eat plenty of watery fruits and vegetables, such as melons, grapes, apples, pears, squash, and oranges, carrots, tomatoes, and celery.
Most-Asked Questions About Morning Sickness

What is considered as a severe case of morning sickness, and how is it treated?
A serious form of morning sickness known as hyperemesis gravidarum is known to trigger particularly intense and prolonged episodes of vomiting and nausea.
This kind of severe morning sickness affects approximately 1–3 in every 100 pregnant women and makes it impossible for them to stomach any food or fluid without being sick.
Since you throw up anything you consume, your body may become deprived of water and sufficient nutrition over time.
What’s worse is that this condition is usually unresponsive to the standard anti-sickness medications and requires hospitalization so that nutrition and fluids can be administered intravenously. (14)
Thus, the continued dehydration and malnourishment can make you lose as much as 5% of your pre-pregnancy weight. To keep that from happening, you must seek prompt medical assistance the minute you feel that your morning sickness is becoming unmanageable. (15)
The following symptoms should warn you about a possible risk of dehydration:
- Your mouth feels increasingly “dry.”
- You feel unusually thirsty all the time.
- Your urine output is reduced.
- You experience frequent headaches, dizziness, and confusion.
- Your vision turns blurry or distorted.
- Your urine turns unusually dark in color.
- You experience constant lethargy or drowsiness.
- You feel generally unwell.
- Your muscles begin to cramp more than usual.
Is morning sickness limited to the early hours of the morning?
No. For most women, the symptoms of morning sickness tend to come and go throughout the day but are most pronounced in the morning.
But in some cases, the feeling of sickness may persist for the entire day, which can hamper your energy levels and can disrupt your day-to-day life, but it is unlikely to jeopardize the health of your baby.
Can nausea and vomiting associated with morning sickness harm the unborn child?
No. Morning sickness does not pose a threat to your unborn child unless it takes a severe form where the mother may be at risk of losing a considerable amount of weight as well as fluids from the body.
Is severe morning sickness associated with having twins or triplets?
Yes. Although pregnancy itself can cause morning sickness, bearing multiple children may increase the risk of experiencing the condition.
Final Word
A persistent case of morning sickness that continues after the first trimester or lasts throughout the pregnancy is a serious cause for concern. This may be a severe case of morning sickness called hyperemesis gravidarum. Consult with your doctor for professional help.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


