In this article:
Hives, or urticaria, are rashes that develop on the skin as a reaction to irritants, allergens, or other causes. They appear as small reddish bumps that are very common in people with sensitive skin, although they can happen to anyone. They can cause itching and irritation.
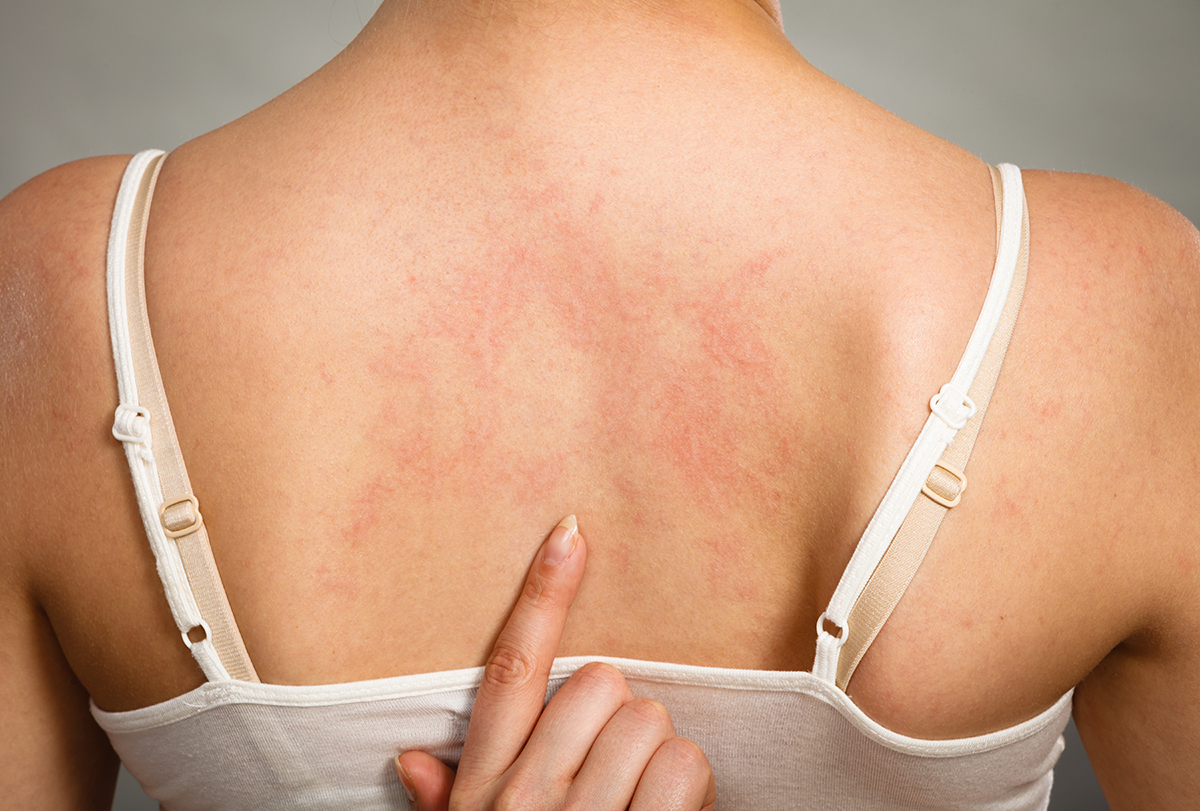

What Are Hives?
Hives can be caused by an allergic reaction to certain substances or sometimes can occur without any trigger. (1)(2) They are red or skin-colored bumps that are itchy and sometimes swollen.
Hives can develop on any part of the body and appear as separate bumps or clusters. Scratching the rash and stress can make them worse. (3)
Most cases of hives resolve on their own in a few days. However, hives that appear along with significant swelling or breathing difficulties may require immediate medical attention. (4)
Types of Hives
Hives can be of three types:
1. Acute hives
Acute cases of hives occur due to a reaction to insect bites, allergens, or an infection. These are temporary and usually do not cause any serious complications. Acute cases of hives resolve on their own within a day or two.
2. Chronic hives
Chronic cases of hives continue for a long time – sometimes years. It can be difficult to identify the cause behind chronic hives.
Chronic hives whose causes cannot be determined are medically called chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). CSU needs to be evaluated and treated by a dermatologist. (5)
3. Inducible hives
When hives occur due to something that comes in direct contact with the skin, it is known as inducible hives. Examples include copper jewelry (a common cause of induced hives), some fabrics such as leather, and even sweat.
What Causes Hives?

Hives occur when the immune system mistakenly takes any harmless, everyday substance or object as a threat. This prompts the cells to release a chemical called histamine, which leads to allergies, inflammation, and rashes.
There can be many different causes of hives, the most common ones being:
1. Allergic reactions
Hives can be triggered when your body has an allergic reaction to some substances such as:
- Medications: Certain medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics such as penicillin, and birth control medicines can cause an allergic reaction an hour or two after taking the medicine or in a few days.
- Foods: Certain foods such as dairy products, nuts, seafood, and mushrooms can cause an allergic reaction in some people. Processed food products containing preservatives and artificial flavors can also cause allergies in rare cases.
- Respiratory allergens: Inhaling mites, pet hair, pollen, etc., may also cause allergies in certain people. Cigarettes are a common source of respiratory allergies.
- Contact urticaria: Allergies can be caused by coming in direct contact with something such as leather.
- Insect bites: Insect bites can lead to allergic reactions, especially in small children.
2. Overreaction to heat, sweat, or cold/due to pressure on the skin (physical causes)
Certain physical factors such as heat or extreme cold, pressure from belts, or chafing can also lead to allergies.
3. Stress
When you are stressed, your body releases excess stress hormones in the body. This can cause allergic reactions in some people.
4. Sunlight
Excess exposure to sunlight is a rare factor for allergies.
5. Systemic diseases such as thyroid diseases and rheumatic diseases
Certain conditions such as thyroid disorders and diabetes can lead to chronic allergies.
6. Idiopathic urticaria
Allergies that occur without any identifiable cause are known as idiopathic urticaria.
7. Infections
Many different kinds of infections including parasitic infections, urinary tract infections, respiratory infections such as bronchitis, and skin infections can cause allergies in people.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Hives?

Some characteristic symptoms of hives are as follows:
- Raised itchy bumps, either red or skin colored: Hives appear as raised, itchy bumps on the skin. Their color can be pinkish or red on lighter skin and somewhat darker on brown skin.
- Blanching (when pressed, the center of a red hive turns white): Blanching, or paling, of the bumps may occur when you press on it.
- Itching, burning, stinging, and warm to the touch: Bumps that itch or sting (sometimes severely) are a sign of hives.
- Covering large areas of skin: Hives can occur in a couple of spots, in a single place, or over huge patches of skin.
- Distinct raised spots or patches: Hives can appear in the form of small raised bumps or large patches of itchy raised skin (called plaque).
- Swelling (angioedema) on the lower lip: Hives can cause swelling and inflammation in the mucous membranes of the body. This may lead to swelling of the lips. The medical term for this condition is angioedema. (6)
Where Do Hives Develop on the Body?
Hives most commonly appear on the following spots (although they may occur anywhere):
- Stomach or abdomen
- Legs
- Arms
- Thighs
Hives can also cause swelling on the lips, nose, etc.
Treatment for Hives
The best treatment for hives is to avoid the allergen that is causing them. However, it is not possible to determine the cause or allergen, as is the case with CSU. (7)
Here are some treatment measures to control or treat hives:
General measures to treat hives
- Use an over-the-counter anti-itch lotion for temporary relief. It helps alleviate the skin irritation and soothe the area.
- Avoid the allergen if you can determine what is causing the hives. Learn to identify triggers by tracking your symptoms and their timing. (8) If you have hives that are stinging or burning, it may be better to avoid taking painkillers such as aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These medicines can worsen your symptoms in some cases.
- Do not stress over the hives as this may worsen them.
- Try to avoid common allergens such as dust, pollen, and seafood.
Treatments for acute cases of hives
Acute hives or temporary cases of hives are easily treatable with over-the-counter allergy medicines such as Benadryl, Zyrtec (cetirizine), and Allegra (fexofenadine).
Some medicines commonly used to treat acute cases of hives include:
1. Antihistamines
Antihistamines are medications that stop the release of histamines into the body. This provides relief from the hives and swelling.
2. Combination of antihistamines
A combination of antihistamines may be more effective for acute urticaria than antihistamines alone. Antihistamines help provide lasting relief from hives for most people.
Non-drowsy antihistamine formulas are sometimes prescribed for the daytime and a sedating antihistamine for nighttime. This combination helps more people take the medication easily without feeling drowsy or lethargic.
Treatment for chronic hives
Chronic hives are hives that persist for weeks and do not seem to resolve on their own. Such cases may require medical attention from a dermatologist. Your doctor may prescribe a drug such as cyclosporine or omalizumab.
Some common treatments prescribed for chronic cases of hives include:
1. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are steroid medications that can help reduce inflammation and swelling. They are available in the form of creams that you can apply to the affected skin, tablets, or injectables.
Corticosteroids are prescribed by a doctor only when antihistamines fail to work and should only be used for a short while. Prednisone and betamethasone are corticosteroids commonly used to treat hives. (9)
2. Omalizumab
Omalizumab is a fairly new medicine that has been shown to be helpful in reducing allergies and hives in most cases. It is a prescription-only drug (10) and has helped in reducing hives in 83% of patients in one study. (9)(11)
3. Cyclosporine A
Cyclosporine A is an immunosuppressant used to treat chronic cases of hives and has shown significant improvement in many patients. It is also a prescription-only drug. (12)
4. Montelukast, zafirlukast
Montelukast and zafirlukast are leukotriene inhibitors that can help reduce chronic hives by suppressing inflammation. They should only be taken when prescribed by a dermatologist.
5. Methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil
Methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil are anti-inflammatory drugs that help reduce inflammation and skin irritation and thus relieve hives. Dermatologists prescribe them when antihistamines fail to work.
6. Dapsone
Dapsone (4,4’-diaminodiphenylsulfone) is an antibiotic often used in the treatment of inflammatory dermatological diseases. It has also been used in the treatment of urticaria, although evidence for its efficacy has been scarce.
Dapsone may be an alternative in the treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria, especially if treatment is combined with antihistamines.
Dapsone is an antibiotic and anti-inflammatory medicine that is prescribed when dermatologists suspect an underlying infection or when other treatments do not seem to reduce the symptoms
7. Auto-injector
Commonly known as the EpiPen, auto-injectors are an extremely useful and lifesaving medicine that should be used in severe allergic reactions. The EpiPen is a shot of epinephrine that helps suppress the immune response and reduce inflammations.
8. Light therapy
Phototherapy can help cure chronic cases of hives in some cases. It is a noninvasive procedure performed in a doctor’s office. Phototherapy may require several sessions over a few weeks or months to show improvement.
Treatment monitoring
When it comes to CSU, monitoring your symptoms and the effect of treatment is important in finding a long-term cure. Make sure to inform your doctor about your entire medical history and record your symptoms daily after starting your medications. (13)
How Are Hives Diagnosed?
The following tests can help diagnose the cause of hives:
1. Blood tests
Complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C reactive protein (CRP), and absolute eosinophil count help rule out the possibility of an underlying infection that may be causing your rash.
2. Allergy tests
The urticaria activity score helps keep track of your symptoms and timings to determine a cause. The autologous serum skin test helps to determine whether the hives are caused by an autoimmune disorder or condition.
3. Skin prick test
A skin prick test can help identify the cause of your allergy. It can test for multiple allergens such as pollen and dust, among many other things.
Important points in diagnosis:
- Diagnosing allergies or urticaria requires a detailed history of your symptoms, frequency and timings of breakouts, exposure to different substances and skin care products, any medicine you may have taken or are taking, and any medical condition you have, among others.
- Problems in allergy testing can occur. Skin prick testing results can vary based on whether you are taking allergy medications, whether your skin has raised bumps at the time of the test, and some other factors. (14)
- Serum IgE testing is a blood test used to measure the amount of IgE antibodies in your blood. This test is more reliable than skin prick tests. However, it is more expensive.
Most-Asked Questions About Hives
What is the latest treatment for hives?
Omalizumab is the most recent development in the treatment of hives and CSU. It has proven to be an effective treatment, and its use has caused significant improvement in a majority of patients.
Severe attacks of hives are rare but can happen to some people. Anybody who has severe allergies and is at risk of an anaphylactic shock should always carry an EpiPen with them. (14)
What is the most common cause of chronic hives?
Hives can be caused by several things including certain medicines such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs), common allergens like pollen, nuts, etc., or infections.
The most commonly reported causes of hives are infections (e.g., viral infections such as HIV and hepatitis or bacterial infections such as an H. pylori infection). (15)
Final Word
Hives, or urticaria, are a common skin condition and affect many people. Most episodes of urticaria are acute and resolve in a few weeks. However, some people may experience chronic urticaria, which may require medical intervention and lifestyle changes to avoid triggers. (14)

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


