In this article:
Many women suffer from excessive hair growth on areas such as the face, back, thighs, and pubic areas. The condition in women characterized by dark coarse hair in male-like pattern is medically known as hirsutism.

Hirsutism is a common presentation in dermatological settings mainly for cosmetic reasons. It often causes emotional stress, anxiety, and depression in women as it is an unwanted cosmetic issue.
Hirsutism is the most prevalent endocrine disorder among women in the United States and affects around 10% women in most populations. (1)
Hirsutism and Testosterone
The most common reason of hirsutism in women is increased testosterone levels, which may result from problems in the ovaries or adrenals, the glands that secrete the majority of testosterone in women. (2)
Increased levels of active testosterone, known as dihydrotestosterone, lead to the production of longer, thicker, coarser hair, different from the normal female hair.
Causes of Unwanted Facial Hair (Hirsutism)
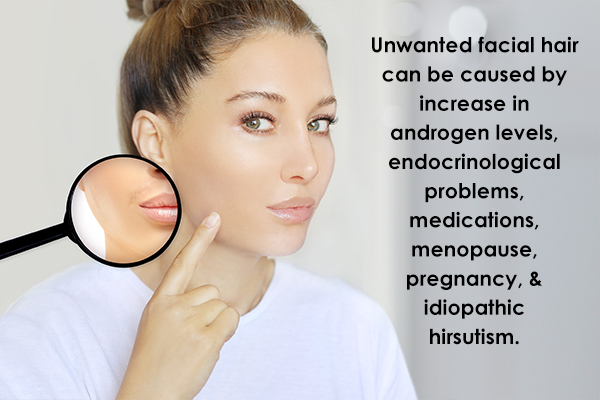
Hirsutism can be a result of various reasons, including:
1. Increase in androgen levels
The most common cause of hirsutism is the increased production of androgens, which may result from:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Tumors in the ovary or adrenal glands
- Non-classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia
2. Endocrinological problems
While not very common, endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, hyperprolactinemia, and acromegaly can cause hirsutism, among other symptoms.
3. Medications
Hirsutism is a common side effect of estrogen antagonists, cyclosporine, diazoxide, androgens, danazol, interferon, and phenytoin. (2)
However, in many cases, these drugs may cause hypertrichosis, which results in excessive hair growth in patches or all over the body in both men and women, as opposed to hirsutism, which is male-pattern hair growth in females.
4. Menopause
Discontinuation of ovarian estrogen production post menopause can result in mild hirsutism. (3)
5. Pregnancy
Prolactin secretion during pregnancy can also cause mild hirsutism. (4)
6. Idiopathic hirsutism
Idiopathic hirsutism refers to cases with an unknown cause. Idiopathic causes make up to 10% of the total cases of hirsutism.
Symptoms That May Accompany Hirsutism
Hirsutism is most commonly characterized by hair growth on the upper lip, upper back, chin, sides of the face, shoulders, upper abdomen, and sternum. However, depending on the cause, it may be accompanied by other symptoms, including:
- Dyslipidemia
- Acne
- Obesity
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Oligomenorrhea
- Cancer
- Deepened voice
- Alopecia
- Decreased breast size
- Infertility
- Increased muscle mass
- Abdominal discomfort
- Amenorrhea
Medical Treatment for Unwanted Facial Hair (Hirsutism)
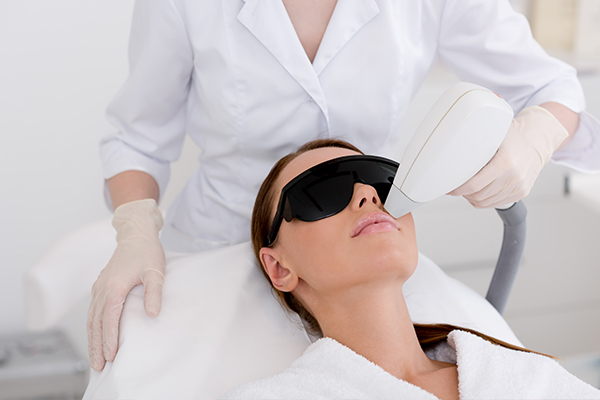
Most cases of hirsutism can be managed with medical treatment, including: (5)
- Anti-androgens: These medications help prevent the production of hormones and include spironolactone, finasteride, and flutamide. Anti-androgens should only be taken upon consulting your doctor.
- Electrolysis: Electrical current is used to damage hair follicles, thus preventing hair growth. However, it is an expensive treatment that may cause redness, swelling, and scarring of skin.
- Birth control pills: These medications help reduce the concentration of androgens. Consult your doctor on the use of birth control pills for hirsutism as combination oral contraceptives are disproved by the FDA.
- Depilatory creams: These may be effective in controlling hair growth but may cause irritation.
- Prescription creams: Creams such as eflornithine help retard facial hair growth but may produce side effects such as stinging or skin rash.
- Laser and intense pulsed light (IPL): These treatments help destroy hair roots, thus preventing hair growth.
- Insulin sensitizers: These are helpful for women who are affected by hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and hirsutism. (5)
- Cancer treatment: Hirsutism caused by tumors may be improved with the use of radiation therapy or surgery.
Diagnosing Hirsutism
To determine the cause of hirsutism, the doctor will study your medical history and perform a physical exam. Furthermore, you may be required to undergo tests such as:
- Serum androgen level
- Serum DHEA-sulfate test
- ACTH stimulation test
- Pelvic ultrasound
- 17-hydroxyprogesterone blood test
- CT scan or MRI
The degree of hirsutism can be determined using the Ferriman-Gallwey scale. (6) Besides the physical presentations, it is also important to understand the mental impact of hirsutism in a woman for a wholesome treatment, as this disorder can affect a person’s self-image.
Risk Factors Associated With Unwanted Facial Hair
The following factors can predispose you to hirsutism:
Complications of Untreated Hirsutism
When left untreated, the underlying problem can cause following complications:
- Infertility
- Cancer
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Social isolation
- Osteoporosis
- Obesity
When to See a Doctor

It is essential to consult a doctor if you suspect hirsutism, especially when accompanied by:
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Receding scalp line
- Male-pattern hair
- Darkening of the neck, groin, and armpits
- Enlarged clitoris
- Breast milk leakage when not breastfeeding
- Deepened voice
Final Word
Women develop very fine hair on the lips, chin, chest abdomen, or back. However, some women may grow darker, coarser hair in these areas, which is more common among men.
This condition is known as hirsutism, which generally results from excessive androgens in the body. Medical treatment and cosmetic attention can help manage most cases of hirsutism over time.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


