In this article:
A skin boil, also called a furuncle, refers to the formation of small, red nodules in the skin pores. These boils may either be present in the hair follicle or oil gland as a painful nodular structure.
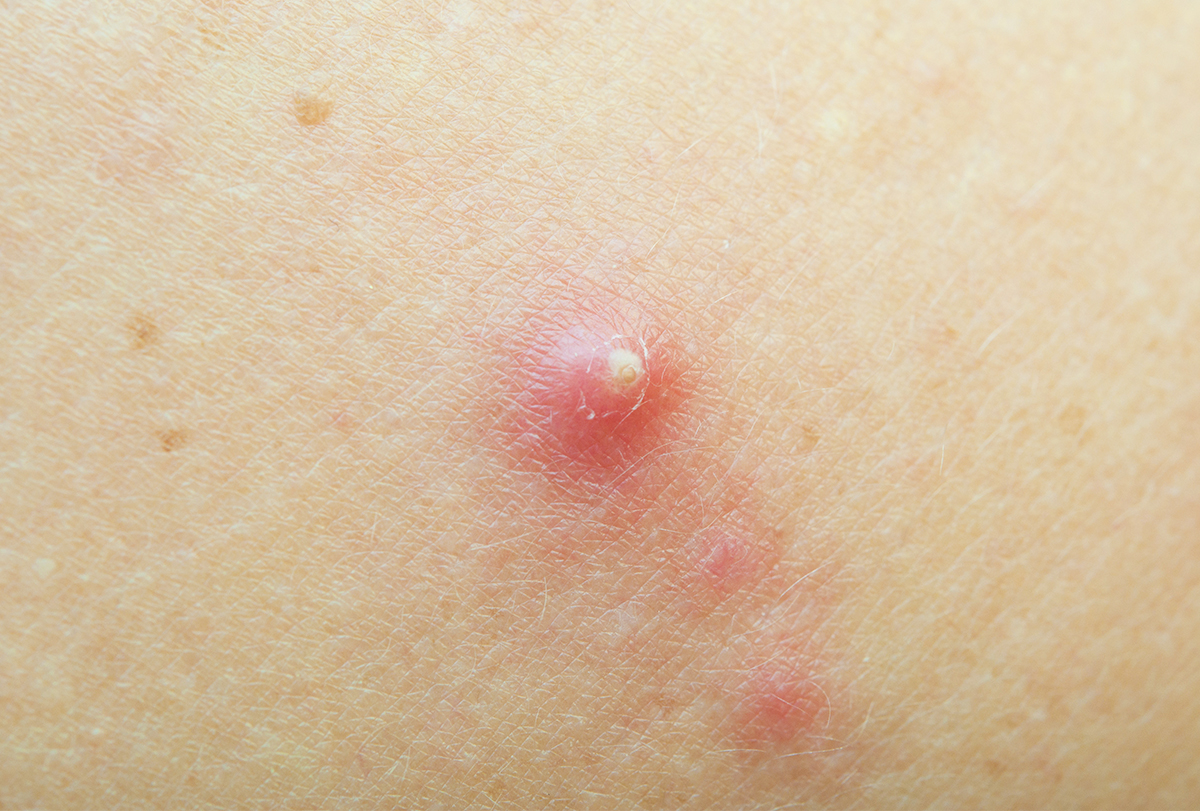
Boils generally develop in exposed skin areas such as the arms, hands, neck, and face. However, they can also spread to the shoulders and back. Boils can even occur on the eyelids and the condition is called a stye.
Boils are accompanied by inflammation and pus accumulation. They are smaller than an abscess, but if left untreated, boils can develop into a larger abscess eventually.
Cause of Boils and Abscesses
The most common cause of boils and abscess is skin infection due to bacteria such as: (1)
- Staphylococcus
- Streptococcus
- Chlamydia (in case of vaginal boils)
These bacteria are a part of the normal microbial flora present on the skin surface, such as armpits, nostrils, and upper thigh junction.
However, a cut in the skin can provide a path for the bacteria to enter the hair follicles and oil glands, wherein the body’s immune system is not as strong. This causes inflammation in the hair follicles known as folliculitis.
Once inside the skin pores, the bacteria cause an infection, which persists for around 10 days. Within this period, the body’s immune system assigns white blood cells to the site of infection.
The WBCs, along with cell debris, can collect in the wound, leading to the formation of pus and thus resulting in a painful abscess.
Symptoms Associated With Boils and Abscesses
Boils appear as red, elevated bumps, often with a yellowish-white top due to the accumulation of pus. Abscesses, on the other hand, have a distinctive pinpoint at the center of the bump from where the pus can ooze out.
Additionally, boils and abscesses may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Erythema
- Nausea
- Swollen lymph nodes
Medical Treatment for Boils and Abscesses

The treatment for boils and abscesses depends on their severity. The various treatment options include: (2)
1. Topical antibiotics
Topical antibiotics may be given if there are severe and large boils that are painful. You may be prescribed to apply 2% fusidic acid cream or 2% mupirocin 2% cream twice a day. These are generally used in combination with other treatments.
Boils, folliculitis, or abscesses may recur if the bacteria causing them become resistant to antibiotic treatment. In such cases, the doctor may prescribe clindamycin, which is another topical medication mainly used for targeting antibiotic-resistant staphylococcus bacteria or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
2. Oral antibiotics
The doctor may also suggest the use of oral antibiotics if there are several boils or abscesses.
3. Topical antiseptics
These are available in the form of creams containing benzoyl peroxide, soaps, and hypochlorite solutions. For recurrent infections, antibiotics are used in adjunction with topical antiseptics.
4. Pain medication
Drugs such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen may be given to help manage the pain.
5. Surgery
This involves making a cut on larger abscesses to help drain out the pus. This procedure is also known as a surgical incision or lancing the boil. Gauze may be used to help keep the abscess open for continued drainage.
Diagnosing the Cause of Boils and Abscesses
While boils and abscesses can be identified based on their appearance alone, the doctor may take a closer look to find the source of the problem. The physical exam includes looking for ingrown hair or injury.
Further, the doctor may order a culture of the skin cells to identify the presence of infection-causing bacteria. For recurrent boils and abscesses, you may require blood and stool tests.
Risk Factors for Boils and Abscesses
The following factors can predispose you to bacterial infections and, thus, developing boils and abscesses by weakening or damaging the protective skin barrier:
- Diabetes (3)
- Endocarditis
- Skin problems such as eczema
- Kidney failure (4)
- Obesity (5)
- Weak immune system
- Poor nutrition
- Iron deficiency
- Lack of hygiene
- Chemotherapy
- Contact with harsh chemicals
- Medications such as antibiotics and cortisone
- Contact with a staph-infected person
- Hormonal imbalance during puberty
- Smoking (6)
- History of boil or abscess (5)
- Chlorinated swimming water
- Young age or childhood
Complications of Untreated Boils or Abscesses

If left untreated, the infection causing boils and abscesses can give rise to the following complications:
- Tooth abscess
- Cellulitis
- Fatigue
- Permanent scarring
- Redness around the eye or infected area
- Infection in the bones, spinal cord, or even brain
- Sepsis
When to See a Doctor
Boils generally resolve on their own or with proper self-care, but they can be troublesome in severe cases.
It is best to consult a doctor if:
- The boils appear in clusters, known as a carbuncle.
- Persistent boils and abscesses that don’t heal within 2 weeks.
- The boils are spreading.
- The lymph nodes are swollen.
Final Word
A boil or abscess is a pus-filled red bump on the skin and causes pain, especially when touched.
While generally not a severe problem, the bacterial infection that causes boils may spread and cause complications. Therefore, it is best to consult a doctor if the boil or abscess doesn’t resolve on its own within a week or two.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


