In this article:
Scarring is the final result of the wound-healing function of your body, which has evolved to quickly restore injuries.
Scar tissue is a familiar aesthetic concern for many people. As the name suggests, it is a type of scar that appears on the skin in place of your normal skin as a result of a skin wound or injury.
Scar tissue is not known to cause pain, but it is surely a beauty concern, so it is normal for you to look for ways to get free of it. (1)
Continue reading to learn more things about it.
What Does Scar Tissue Look Like?
Scar tissue consists of a tough fibrous tissue called collagen and is formed after a skin injury. It generally appears:
- Red
- Raised
- Hard
Experts explain that, with time, scar tissue fades as it softens and flattens out.
What Causes Scar Tissue Formation?
Scar tissue formation can be triggered by multiple reasons such as: (1)
- Minor burns
- Cuts
- Acne
- Infection
- Bites
- Surgery
How Is Scar Tissue Formed?
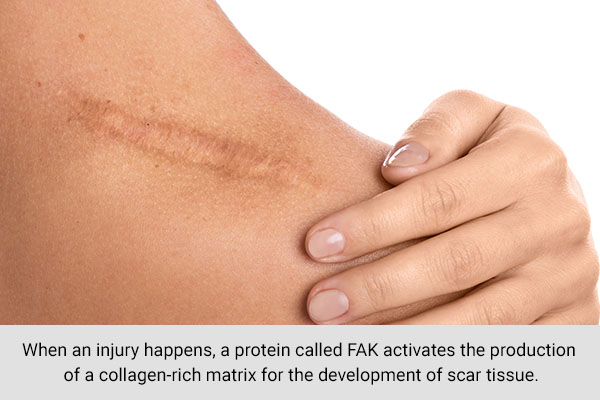
As humans evolved, their bodies developed a mechanism to close wounds as soon as possible to control the bleeding after an injury and prevent infection, and this led to the creation of scar tissue.
Scientists explain that, when an injury happens, a protein called FAK activates the production of a collagen-rich matrix for the development of scar tissue. When a wound starts to close, skin cells form collagen, which creates the building blocks of a scar. (1)
What Are the Different Types of Scars?
There are multiple different types of scars, and the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery describes them as follows:
- Keloid scars – These scars stretch beyond the site of the injury and may hinder movement. They are more commonly seen in people with dark skin.
- Contracture scars – These scars are formed from burn injuries and can hinder movement when they tighten. Based on how severely the skin was burned, these types of scars may also impact the muscle and tissues below the skin.
- Hypertrophic scars – These are thick and, in some cases, raised scars that remain within the boundary of the injury or within the area of the wound. These can be itchy and tender.
- Acne scars – These scars are formed during the healing process of acne and can range from small blemishes to deeper scars.
Treatments for Scarring
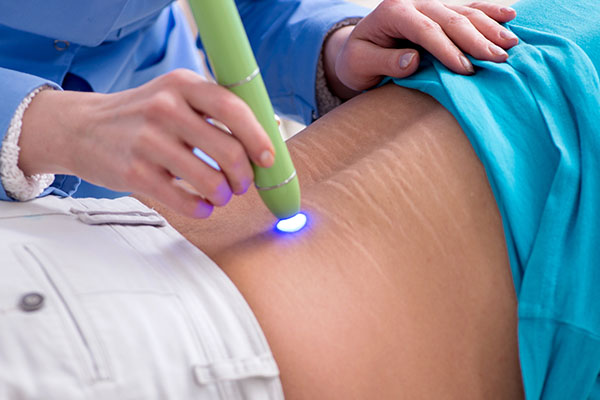
Several treatment options are available for scars, but they may not be effective for everyone. Doctors must clarify the limited success rate of these treatments to their patients. Some of these treatments also have side effects. (2)
Treatment options for scars include:
- Injectable steroids
- Cryotherapy using liquid nitrogen
- Radiotherapy
- Laser therapy
- Silicone treatments
What Are Some Side Effects of Scarring?

According to the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, some side effects of scarring may include:
- Itching
- Tenderness
- Pain
- Sleep disruptions
- Anxiety
- Disturbance in daily activities
How Is Scar Tissue Different From Normal Skin?
In normal skin, collagen organizes itself like a net, but when a wound opposes staying shut, the tension causes the collagen in the scar tissue to align itself like a bundle of ropes, producing what is known as scar tissue.
Thus, scar tissue is much stronger and less flexible than normal skin. (1) Also, a scar will not support any outgrowths such as hair or oil glands. (1)
Complications From Scarring
Scar tissue is pretty rigid and inflexible, so increased collagen production can result in scarring that can inhibit movement and facial expressions when a scar covers a joint or the face, respectively. (1)
When to See a Doctor
If your scar is very old and is not improving in appearance, you may have to go to your doctor for professional treatments, which can include laser therapy and chemical peels.
Also, if you observe itchiness or redness in your scar, seek medical attention.
Final Word
Scarring is part of the body’s natural defense mechanism, but it can be worrisome for some people as it is a beauty concern. So, for aesthetic reasons, people get scars removed.
Doctors have numerous choices to select from when treating scar tissue, but some treatments are more useful for particular types of scars. Nonetheless, decisions for scar treatment should only be made after addressing the psychological effects and movement constraints that scars can cause in some people.
 Continue Reading7 Home Remedies to Manage Scar Tissue
Continue Reading7 Home Remedies to Manage Scar Tissue
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


