In this article:
Melanin is a pigment compound that gives your skin, hair, and eyes their color. But that’s not its only function. It also protects the skin from harmful solar radiation. (1)

However, there is a flip side to this advantage: the extra melanin produced in the skin to ward off sun damage ends up making the exposed area darker. This kind of hyperpigmentation is generally termed sun-induced hyperpigmentation, which can make your skin look dull and uneven and rise to cosmetic concerns.
This article will discuss the various ways that can help reduce the excess melanin in the skin to restore your natural skin tone. (2)
Although melanin production cannot be stopped as it is a physiological process and a reduction in this process will lead to white patches, many things can be done to manage sun-induced hyperpigmentation (excess melanin production due to overexposure to the sun).
Role of Melanin in Sun Protection
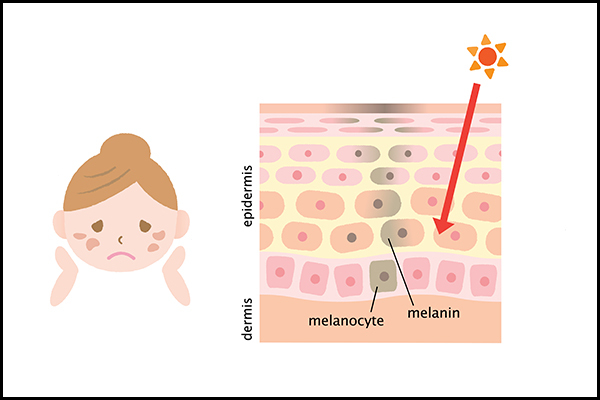
When sunlight falls on the skin, it triggers specialized cells called melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis to secrete melanin. (1) This melanin then absorbs the UV rays to prevent them from penetrating further and damaging the underlying cells and blood vessels. (3)
Thus, sun exposure increases melanin production in the skin. This is your skin’s natural defense mechanism against solar radiation. The increased melanin provides more sun protection, but it also makes your skin darker, which is known as tanning.
Other types of hyperpigmentation are also the result of increased melanin concentration in the skin. However, exposure to the sun’s UV rays is the primary cause of excess melanin synthesis. (4) Thus, people with naturally deep complexion are less vulnerable to sun damage than fairer individuals for the same reason, i.e., more melanin in the skin.
Ways to Reduce Excess Sun-Induced Hyperpigmentation
There are three different types of interventions that can help curb melanin synthesis in the skin, either directly or indirectly. You can consult your dermatologist to determine which one is best suited for your skin condition.
a. Topical medications
These ointments are effective in reducing melanin production and are often used for treating hyperpigmentation.
1. Kojic acid
Kojic acid when applied to the skin inhibits the activity of an enzyme called tyrosinase, which is a catalyst for melanin synthesis. Thus, kojic acid helps reduce melanin formation and thereby induce depigmentation through this mechanism.
Another plus point is it does not cause cellular damage unlike many other skin-lightening agents, which explains why it is so widely used in cosmetic and skin care products.
2. Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone has a strong inhibiting effect on tyrosinase activity, which ultimately leads to lower melanin production. However, when used in high concentrations, this bleaching agent can cause a lot of cellular damage, which is why it is banned in some countries. (5)
b. Clinical treatments
Dermatologists also recommend certain noninvasive skin procedures to help lighten hyperpigmentation. This includes laser skin lightening, (6) platelet-rich protein treatment (PRP), (7) and chemical peels.
However, these may cause the following side effects:
- Skin redness
- Itching
- Severe dryness
c. Natural remedies
You can also try the following natural interventions to reduce hyperpigmentation:
1. Vitamin C

Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that inhibits the activity of free radicals. Free radicals are unstable reactive molecules that release oxidative stress on healthy cells and cause damage.
Skin cells produce melanin to absorb and eliminate these free radicals. Vitamin C can help reduce this kind of melanin formation by neutralizing the free radicals themselves. (8)
2. Vitamin B3
Vitamin B3 (niacin) slows down melanin synthesis by impeding the interaction between melanocytes. (8)
3. Vitamin B5
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) interferes with the interaction between melanocytes to limit melanin production. (9)
4. Aloe vera extract
One study found that aloe vera contains active ingredients such as aloesin that help reduce melanin production. No wonder it is used in a variety of skin-lightening products. (10)
5. Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a group of polyphenolic compounds found in fruits and vegetables that exhibit strong antioxidant effects. These phytonutrients help counteract the oxidative effects of free radicals to inhibit excess melanin production. (11)
6. Green tea extract

Green tea extract contains natural compounds called polyphenols that work as strong antioxidants that deter free radical activity and thereby limit melanin formation.
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (ECGC) is the main active ingredient in green tea. (8)
7. Mulberry extract
The extract derived from the root bark of the mulberry tree is credited with skin-lightening properties, but more clinical trials are needed to confirm this claim. (8)
8. Soy
Soy (Glycine soja) is a safe and effective agent for reducing hyperpigmentation, but its effect is usually reversible. (8)
9. Turmeric
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, significantly inhibits melanin production in normal human melanocytes. It is often used as a whitening agent in cosmetics and hyperpigmentation treatments. (12)
10. Licorice extract

Licorice extract can help lighten skin pigmentation by limiting melanin formation and preventing its concentration in one place.
11. Milk
Milk contains certain proteins that work as strong antioxidants and help inhibit melanin production. (13)
12. Yogurt
Yogurt contains glycolic acid, lactic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, and citric acid, which help dissolve the dead cells settled on the surface of your skin so that they shed easily, revealing bright healthy skin underneath. (14)
However, this exfoliating effect is purely superficial and does not really influence melanin synthesis.
13. Honey
Honey may not affect melanin production, but it is a natural bleaching agent that helps fade hyperpigmentation and even out your overall skin tone. (8)
Daily Practices to Be Avoided
To reduce sun-induced hyperpigmentation, follow these measures:
- Avoid direct exposure to the sun.
- Don’t exfoliate or bleach frequently as it will render your skin ultra-sensitive to the sun’s UV radiation.
- Avoid any topical creams or homemade items with low pH such as lime or vinegar rinses.
Most-Asked Questions
Why is the production of melanin different among different races?
The amount of melanin differs by race as is evident from their basic skin color. This depends on the extent of sun exposure a particular race has had historically.
How does sun exposure damage the skin?
Sunlight contains UV rays that go deep into the skin and cause damage at the cellular level. This kind of sun damage breaks down the collagen in your skin. Collagen is the structural protein that keeps your skin tight, elastic, and supple.
The loss of collagen makes your skin loose and saggy, which paves the way for wrinkles, fine lines, and other signs of premature skin aging.
Prolonged sun damage can also cause genetic mutations in the skin cells that can make them cancerous, increasing the risk of melanoma. (15)
Can sunscreens fully block UV rays?
Sunscreen is the most important tool for protecting your skin from solar radiation, but it does not guarantee 100% sun protection. It forms a shield over the skin that blocks out or reflects the harmful UV rays of the sun so that they don’t penetrate into the skin and cause cellular damage.
Different sunscreens provide different degrees of sun protection depending on their formulation as well as strength, which is calculated in terms of sun protective factor (SPF). Skin experts recommend using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and preferably containing zinc.
But no matter how good the sunscreen, its effect wears off, and so it needs to be reapplied every 2–3 hours, especially after washing your skin or profusely sweating.
Final Word
Your natural complexion depends on the basic level of melanin in your skin which cannot be reduced, or else you will be left with depigmented white patches on the skin. The only thing you can control is the production of excess melanin in the skin which is mainly triggered by sun exposure.
The idea is to protect your skin from the sun to curb extra melanin synthesis in the exposed area. This uneven buildup of melanin will lead to dark patches and an uneven skin tone.
While you can’t avoid the sun altogether, proper preventive measures like wearing sunscreen and protective clothing/accessories before stepping out can help block it out. This along with the other measures mentioned in the article can help you avoid sun-induced hyperpigmentation, and even reverse it.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


