In this article:
Boils or furuncles are red, pus-filled lumps on the skin caused by an infection in the hair follicles. (1) The lesions are often painful and keep growing until they rupture and drain.
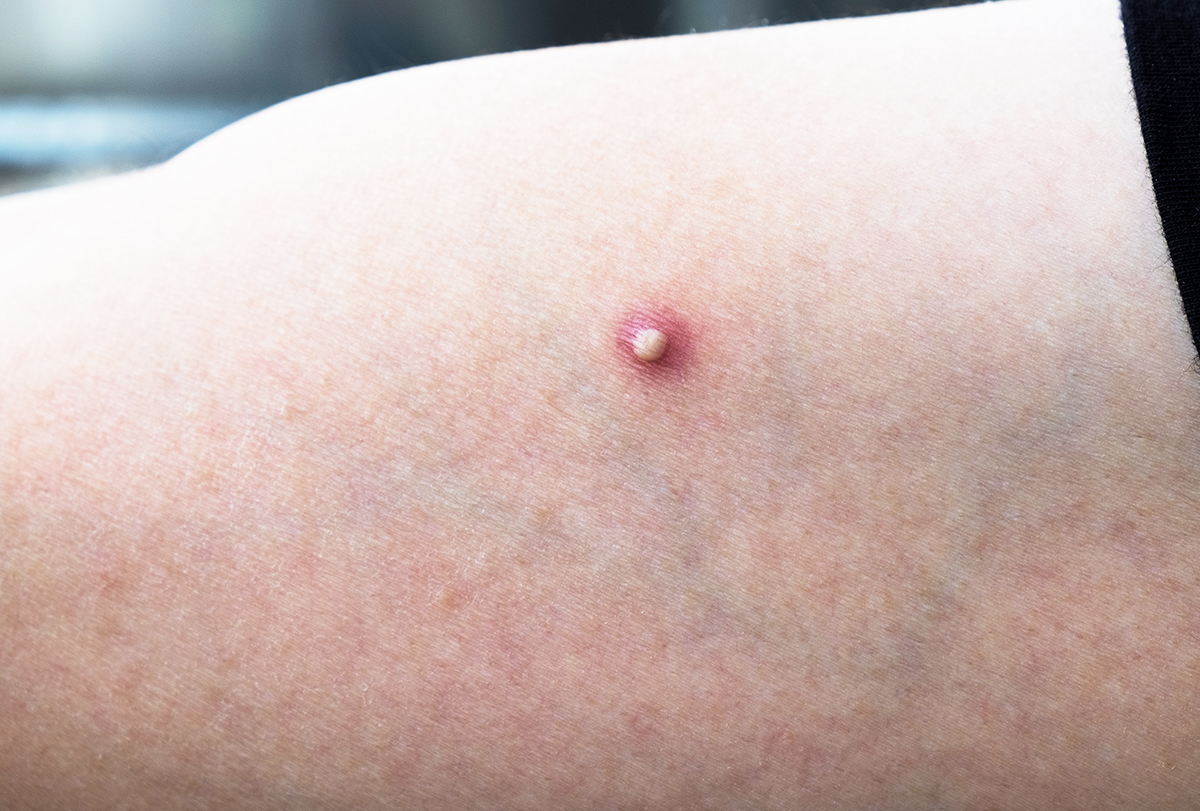
Boils can develop on the eye, known as a stye, or may occur in clusters on different parts of the body such as the trunk, armpit, and buttocks, known as carbuncles.
It is common for boils to develop on the inner thighs as the friction and sweat increase the chance of infection in the hair follicles in these areas.
Most cases of boils disappear on their own, but medical treatment and home remedies aid in the recovery and prevention of complications.
Causes of Boils
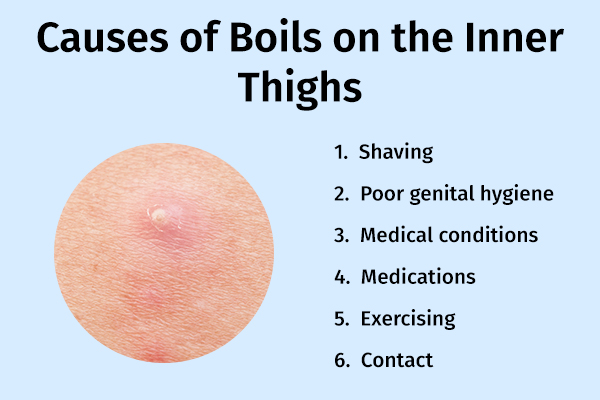
Boils occur as a result of infection with bacteria such as Staphylococcus. These bacteria enter the hair follicle through a cut, injury, or scrape on the skin. The hair follicle may also get irritated due to friction and swell up, often leading to a boil.
Other factors that increase the risk of boils include:
- Shaving: Improper shaving techniques on the inner thighs can cause cuts and boils.
- Poor genital hygiene: Not maintaining cleanliness around the genital area can lead to clogging of hair pores with dead skin cells, sweat, and sebum. This eventually gives way to bacterial infections, leading to pus-filled boils on the inner thighs.
- Medical conditions: Medical conditions such as diabetes or skin conditions such as eczema increase the risk of boils.
- Medications: Immune-suppressing medications such as cortisone drugs (prednisone and prednisolone) and chemotherapy can increase the chances of boils.
- Exercising: Friction on the inner thighs during exercises such as walking, jogging, or cycling can also increase the risk of developing boils on the inner thighs.
- Contact: Close contact with a person with a skin abscess may lead to the development of boils.
Symptoms of Boils
A boil may manifest the following signs and symptoms:
- Redness and swelling of the skin
- Pain
- Pus formation at the center of the boil
- Bloody or whitish discharge from the boil
Treatment for Boils

Treatment for boils generally involves the use of antibiotics. Over-the-counter antibiotics may be sufficient for mild cases, but prescription-strength topical or oral drugs may be given for severe conditions. In addition, in-office treatments may be suggested to drain the boils and prevent further infection.
Here are the specific treatment options for boils:
Medicated creams
Prescription medicated creams help control the infection and aid healing.
- Mupirocin: This is an antibacterial cream that fights skin infections by killing the infection-causing bacteria.
- Fusidic acid: This antibiotic cream is commonly used in the treatment of boils. It controls bacterial growth by preventing bacteria from multiplying.
- Clindamycin: Clindamycin-based creams are used for severe infections caused by staphylococci, pneumococci, and streptococci. These creams control bacterial growth and should only be used if other antibiotics don’t work.
Antibacterial soap
When the boil begins to drain, wash the area with antibacterial soap, apply antibiotic cream, and then bandage it. Use the soap 2–3 times a day and apply fresh bandages until the skin heals.
Oral antibiotics
For severe infections, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics. Make sure to complete the recommended dosage to prevent antibiotic resistance. The antibiotics may include:
- Cephalosporins: This is an effective antibiotic often used in the treatment of boil-causing bacterial infection.
- Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid: Amoxicillin is another antibiotic that can help treat boils caused by bacterial infection. Clavulanic acid prevents the bacteria from degrading amoxicillin.
Surgical incision
A small cut is made on the boil using a sterile needle or blade to drain the abscess. Once the pus is removed, the area is cleaned and bandaged to prevent infection and to speed up recovery.
Diagnosing Boils
Boils can generally be diagnosed through a simple physical exam.
In certain cases, the doctor may order a culture test by draining the boil wound and sending the sample to the lab to identify the bacterial source of infection. This helps in determining the suitable antibiotic treatment.
Home Remedies for Boils
Boils often resolve on their own; however, they may be discomforting and painful, warranting treatment. The following at-home remedies can ease the symptoms of boils and promote healing:
1. Use a warm compress
Applying a warm compress to the boil improves blood circulation in the area. This, in turn, elicits a better immune reaction by speeding up the transfer of antibodies and white blood cells to fight the infection.
A warm compress also helps in draining the boil, enabling faster healing. You can use plain water for the warm compress or mix it with Epsom salt for its antiseptic properties.
How to use:
- Dip a clean, soft cloth in a bowl of warm plain water or a mixture of 2 tbsp of Epsom salt and 1 cup of warm water.
- Wring out the excess water and place the cloth on the boil until it comes to room temperature.
- Re-apply the warm compress a few times until the pus discharges.
- Clean the area once the boil drains to prevent infection.
2. Apply turmeric

Turmeric is known to have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help control infections caused by bacteria, such as those of Staphylococcus aureus, and also manage the pain. (2)
In addition, oral consumption of turmeric helps detoxify and purify the blood, helping relieve itching and boosting immunity.
How to use:
- Mix turmeric powder with water to form a thick paste.
- Apply the turmeric paste to a bandage place it over the boil.
- Leave it on for 20–30 minutes.
3. Dab some tea tree oil
Tea tree oil has antiseptic and antibacterial properties that can help fight boils caused by bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. (3)
How to use:
- Dilute tea tree oil with coconut oil.
- Using a cotton swab, apply the oil blend to the infected area.
- Dispose of the swab immediately to avoid infection.
- Repeat this remedy 2–3 times a day.
4. Use neem
The anti-inflammatory properties of neem have been shown to help manage the pain and swelling associated with boils. Also, neem extract has been effectively used as an antibacterial agent even in low concentrations. (4)
How to use:
Grind neem leaves into a paste and mix in some turmeric powder. Apply the paste to the boil and rinse it off after half an hour. Alternatively, you can boil neem leaves in water until it reduces to a third. Apply the infusion to your boil multiple times a day.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Boils

Boils can be quite painful and discomforting, even after they drain. Making a few lifestyle changes can help in managing the pain better and preventing complications. Here’s what you can do:
- Maintain good hygiene. It is recommended to wash the affected area with warm water and antibacterial soap twice a day. Then, gently pat the area dry. Make sure to use separate towels for the boil-affected area and the rest of the body. Always wash your hands after touching the boil.
- Use powders. Applying talcum or baby powder to the area can help prevent friction and irritation with your clothes, which can otherwise cause pain.
- Refrain from shaving. Do not shave the affected area until the boil has completely healed to prevent the spread of infection.
- Wear cotton clothes. It is best to wear loose cotton pants until your boil heal. Cotton fabric helps keep the area clean and dry and prevents friction.
- Improve your diet. Eat more fresh fruits and vegetables and foods rich in vitamins A, E, and C and zinc to boost your immunity.
- Maintain your weight. Boils often develop in the folds of the skin as the environment is hospitable for bacterial growth. That is why overweight people are at a higher risk of boils. Recurring boils can thus be prevented by losing weight.
- Drink plenty of water. You must consume at least 8 glasses of water daily to maintain optimum hydration and fight infections.
Preventive Tips

Boils, especially recurrent ones, often can be avoided with a few simple steps. Follow these tips to prevent the development of boils and their spread:
- Avoid going to the pool or gym: It is best to steer clear of such public utilities as you run the risk of spreading the infection to others.
- Do not share personal items: Refrain from sharing towels, washcloths, clothing, razors, or bath waters with others as you may contract the infection from them or spread your infection to them through these items.
- Resist popping the boils: Popping the boil allows bacteria to enter the bloodstream and spread infections. Consult your doctor for the procedure if necessary, rather than performing it at home.
- Wear loose clothes: Tight clothes cause friction and irritate the hair follicles, leading to a boil. Therefore, it is recommended to wear loose clothes.
- Go for laser hair removal: When you don’t have an active infection, you can consult a professional for laser hair removal as it helps get rid of unwanted hair without damaging or irritating the skin or causing flare-ups, lesions, or infections.
Complications Associated With Boils
If not treated timely, boils can easily spread to other parts of the body causing severe pain and discomfort. Improper healing of the boil or puncturing them forcefully can cause a scar as well. Also, if the bacteria enter the bloodstream, sepsis may result.
When to See a Doctor
It is recommended to consult a doctor in the following cases:
- The boils are recurrent, as this may be symptomatic of uncontrolled diabetes.
- The affected area is red and irritated.
- You have fever, immense pain, or other symptoms.
- The boils occur in a cluster and are persistent for more than a week.
- You have medical problems (such as diabetes) or immune problems or are taking immune-suppressing drugs.
Is Black Seed Oil Helpful in Treat Boils on the Inner Thighs?
It has been shown that the topical use of black seed oil can cause an allergic reaction. It can also aggravate bleeding issues and lower blood sugar levels in some people. Additionally, there is no evidence to support the benefit of black seed oil in the treatment of boils. Therefore, it is best to avoid the use of black seed oil.
Final Word
Boils are a common occurrence and generally develop on the inner thighs due to a number of factors. However, they can often be avoided by observing good hygiene and using natural skin-friendly products.
You can try different home remedies and OTC treatments to help treat your boils. Make sure to consume a well-balanced and nutritious diet. If the boils don’t resolve within 10 days, consult a doctor.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


