In this article:
The skin on your neck may easily turn dark due to simple and common reasons such as hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, unprotected sun exposure, polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD), and diabetes.
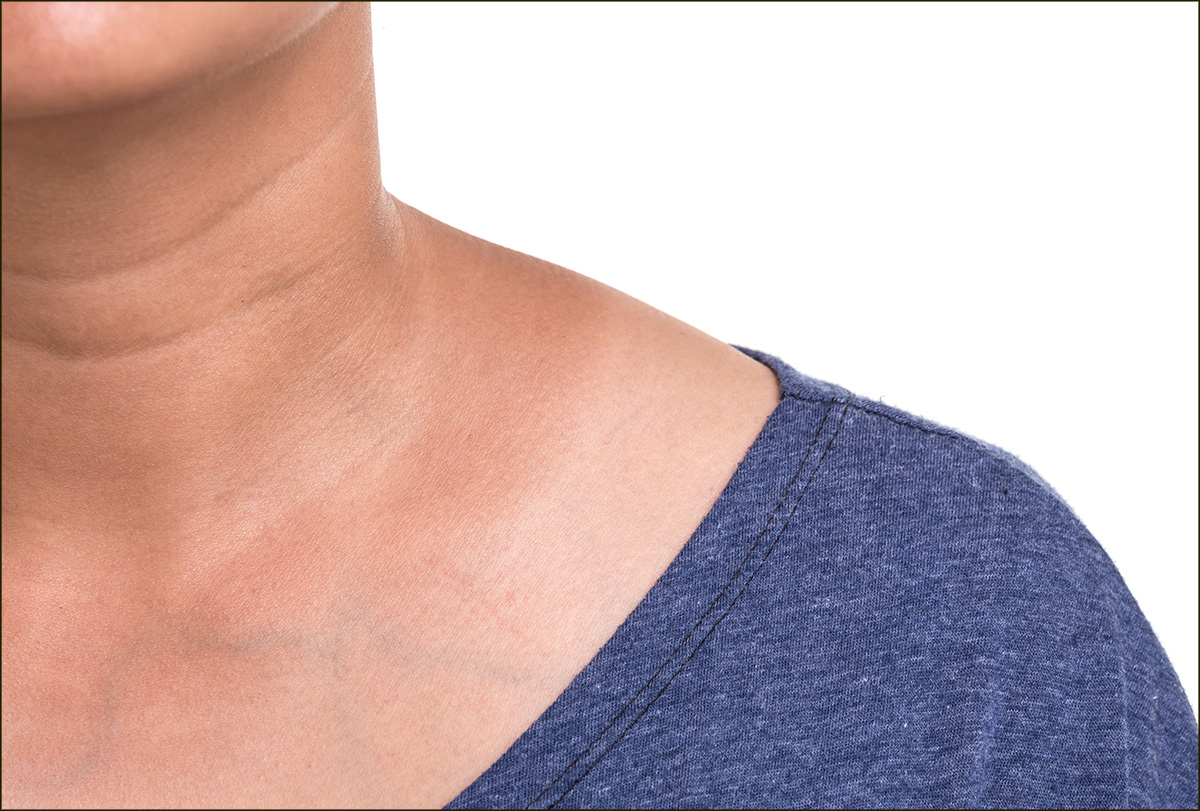
This hyperpigmentation may be accompanied by other symptoms such as changes in skin texture from soft to rough or dry. These secondary symptoms mainly depend on the underlying medical condition that is causing your neck to turn dark.
Most causes of neck darkening such as sunburn or exposure to environmental pollution are not medical concerns, but some of them are, such as:
- Acanthosis nigricans, in which your skin will turn thick and velvet-like. People who are diabetic or obese are at a higher risk of developing this condition, although, generally, it does not pose a serious threat to your health.
- Zinsser-Engman-Cole syndrome is characterized by dark patches on the neck.
- High insulin levels, such as in people with diabetes or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), may cause hyperpigmentation on the neck.
- Autoimmune disorders such as lichen planus pigmentosus, are characterized by greyish-brown itchy patches on the face and neck.
- A hyperpigmented variant of a fungal infection called tinea versicolor.
- Dermatitis neglecta, is characterized by skin discoloration due to the buildup of dead skin cells in areas that are either not cleaned properly or cleaned too rigorously. While face washing is a daily ritual for everyone, the neck is often neglected, contributing to this problem. The same thing happens when you apply too much force, friction, or harsh products to clean your neck.
- Sudden weight loss or weight gain, may also make the neck appear dark.
Home Remedies to Lighten Dark Neck
Home remedies only work for mild skin darkening caused by nonmedical factors such as staying in the sun for too long without sunscreen or exposure to environmental pollutants.
The UV rays of the sun can travel deep into the skin to damage it at the cellular level. Fortunately, your skin has a built-in mechanism to block out these radiations in the form of melanin. This skin pigment is produced by specialized cells deep inside the skin called melanocytes.
When sunlight falls on the skin, it over activates the melanocytes to produce more melanin, which then absorbs the UV rays and prevents them from penetrating further. The excess melanin saves you from sun damage but makes your exposed skin darker, which is referred to as tanning.
While tanning leads to uniform darkening of the skin, certain medical conditions can anomalously stimulate melanin production in sporadic areas, leading to patchy hyperpigmentation, such as age spots.
Whatever the cause may be, the physiology of skin darkening remains the same. It is an extensive biochemical process that requires several biological tools. One such tool is the tyrosinase enzyme. It is a copper-based enzyme present inside the melanocyte cells. It acts on the premature melanin pigment and converts it into an active one.
The solutions mentioned below have been studied to inhibit the activity of this enzyme, which then halts the production of melanin. Subsequently, as the already-present melanin degrades gradually, your skin becomes lighter.
But before using any of these remedies on your skin, ensure that you are not allergic to them by doing a patch test first.
1. Alpha hydroxy acids

Milk, yogurt, milk cream, and Indian gooseberry are all good sources of alpha hydroxy acids, which, when used topically, dissolve the bond between dead skin cells so that they shed easily. As the damaged upper layers peel away, new brighter skin forms in its place.
The natural exfoliating properties of alpha hydroxy acids are so impressive that some types of these acids, such as lactic acid and glycolic acid, are even used in in-office chemical peeling procedures. (4)(5)
You can prepare a skin-peeling mask at home using the kitchen ingredients mentioned above.
How to use:
- Mix 1 tablespoon of rose water or 1 teaspoon of lemon juice in milk, yogurt, milk cream, or mashed Indian gooseberry.
- You may add a little bit of sandalwood or oatmeal powder to build its consistency.
- Apply the paste to your neck and let it sit for 10–15 minutes before rinsing it off.
2. Lemon or lime juice
Lemon or lime contains citric acid, which is known to lighten skin naturally when used topically.
Its bleaching properties can also be traced back to its rich vitamin C content. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that fights free radical damage, promotes collagen synthesis, and facilitates the removal of dead skin cells. (6)
How to use:
- Dip a clean cotton ball in lemon juice, and dab it all over the affected skin. Undiluted lemon juice can irritate or sting sensitive skin, but you can make it milder by mixing in some water. Leave it on your skin for about 20 minutes before rinsing it off with cold water.
- Alternatively, you can take 1 part lemon juice, 1 part rose water, 2 teaspoons of turmeric, and a few drops of vitamin E oil or almond oil in a bowl and mix them all to make a smooth paste. (7) Apply this mixture to your neck area and let it dry. It’s best to do this at night before going to bed.
Use these remedies every day for about a month to see noticeable improvement.
Note: Excessive application of lemon juice can make your skin highly susceptible to solar damage (photosensitive). Therefore, if you are using the lemon remedy, take extra precautions to protect your skin from the sun. The first thing is to avoid going out during the day for long periods. Plus, always wear broad-spectrum high-SPF sunscreen during the day, even if you are indoors.
3. Aloe vera gel

Aloe vera gel contains aloin, which has been shown to induce skin lightening. (8)
How to use:
- You can scoop out this gel from a freshly cut aloe leaf at home and directly apply it all over your neck.
- You can also mix 1 teaspoon of lemon juice in 2 tablespoons of aloe gel to make a mask, and then smear it over the affected area. Let your skin soak it in for about 20 minutes, and then wash it off.
4. Honey
Studies have shown that the polyphenols and flavonoids in honey inhibit tyrosinase activity. (9) Raw, organic, locally produced honey has the highest nutritional value and is, therefore, the best choice for home remedies. But if you can’t get your hands on it, regular medical-grade honey should work fine.
How to use:
- Mash half of a ripe avocado to a smooth pulp.
- Pour in 2 teaspoons of honey and 1 teaspoon of milk, and mix all the ingredients well to form a thick, lump-free paste.
- Apply the paste all over the darkened skin and let it dry.
- Wash it off with lukewarm water.
5. Rose extracts or pomegranate juice
Both rose (10) and pomegranate (11) extracts can be used to lighten the dark skin around the neck because of their antityrosinase activity, which ultimately curbs melanin synthesis.
How to use:
- Mix a few drops of rose water in 2 tablespoons of sandalwood powder to make a thick paste. Smear the paste all over the affected area. Wait for half an hour, and then rinse it off with lukewarm water.
- Alternatively, rub some pomegranate juice on the back of your neck, and rinse it after 10–15 minutes.
Note: It has been shown that alcohol-based rose extracts work better than other extracts. (12) But the alcohol concentration should be just right for it to be safe for your skin. Too much alcohol can lead to extreme skin dryness. So, it’s best not to use alcohol when preparing the extract at home. You can buy alcohol-based rose extracts that are safe for topical use from any cosmetic store.
6. Potato juice
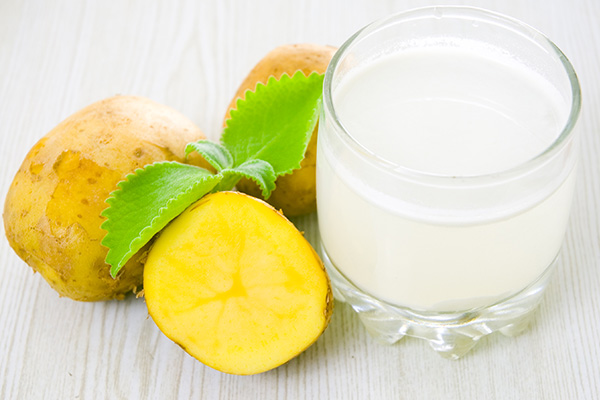

Potatoes contain an enzyme called catecholase, which may exhibit bleaching properties that can help reduce the hyperpigmentation on the neck, although there is no scientific evidence to back this claim.
Nevertheless, this remedy has gained considerable anecdotal support by delivering good results to a number of general users. Plus, it is completely safe to use, so there is no harm in trying. Even if you don’t get the desired results, you won’t suffer any side effects.
How to use:
- Grate a potato or extract its juice. You can add some lemon juice to it for added skin-lightening effect.
- Apply the juice all over your neck and let it sit for 15 minutes.
- Rinse it off with cold water.
7. Skin-lightening oils
The oils that have been shown to reduce hyperpigmentation include rosehip oil, (13) almond oil/any vitamin E oil, and sandalwood oil.
Sandalwood oil is an essential oil, which can be too strong at its original potency, so be sure to dilute it with a carrier oil when using it. Direct application of essential oils can corrode and irritate your skin, leading to further darkening.
How to use:
- Massage your skin with these oils daily.
- Add them to your DIY skin-lightening masks.
Self-Care Measures

Here are some tips that will assist in recovering the natural color of your neck:
- Wash your neck properly. You can prepare your own scrub with rice grains, crushed walnuts, salt, or sugar, and some lemon juice.
- Never step into the sun without wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30. Also, wear hats with a wide brim to protect your neck when you are out in the sun.
- If you have metal allergies such as a nickel allergy, don’t wear artificial neck jewelry made with metals that can further irritate and darken your skin.
- People who are overweight or have diabetes usually suffer from poor regulation of insulin levels that can contribute to skin darkening, especially at the back of the neck. In such cases, proper sugar control and healthy weight management can help regulate insulin levels to gradually fade the hyperpigmentation.
- You can also use makeup to cover the hyperpigmentation and even out your skin tone. Start by applying a primer or moisturizer to the affected area. Choosing the right shade of concealer and foundation is paramount to ensure that the product blends seamlessly into the surrounding skin, or else it’ll look blotchy. When buying a concealer or foundation, look for products that match your skin’s undertones, but avoid those that seem too pink or yellow. Apply the concealer first and then the foundation. Make sure to blend them well, either with your finger, makeup brush, or sponge.
Treatment Options to Lighten Dark Neck
The medical treatment for hyperpigmentation on the neck depends upon the diagnosis made by the expert. Since there can be several possible reasons why your neck is turning black, it is important to consult a doctor for a complete diagnosis.
After the evaluation, your doctor may suggest some measures to treat your hyperpigmentation. These may include the following.
1. Medicated creams and ointments
Severe hyperpigmentation may be treated with prescription creams containing tretinoin (vitamin A derivative) or cortisone (steroid), which can irritate your skin at first and take 3–6 months to show results.
Several different kinds of medicated skin creams and ointments, serums, soaps, and lotions can be suggested by the doctor and may contain active ingredients such as glutathione.
Some other ingredients that you should look for in your product include alpha hydroxy acids (serums), beta hydroxy acids, deoxyarbutin, glycolic and/or kojic acid, quercetin, N-acetyl glucosamine, and extracts of mulberry, soy, grapefruit, rose, aloe vera, marine algae, vitamins C and E, and green tea.
2. Laser treatment
Laser therapy involves exposing the darkened skin to laser radiation, which destroys the melanocytes (pigment cells) in the targeted area to reduce the unwanted pigmentation and even out the skin tone. This intervention is fairly non-invasive and delivers the most drastic results with minimal risk of scarring.
Many different types of lasers can be used for this purpose, such as PDL laser, Q-switched Nd:YAG laser, Q-switched ruby laser, intense pulsed light (IPL), and carbon dioxide laser, to name a few. Your dermatologist will assess your skin condition and then recommend the appropriate one for you. (1)
You may experience slight redness or swelling in the skin post treatment.
3. In-office chemical peeling procedures
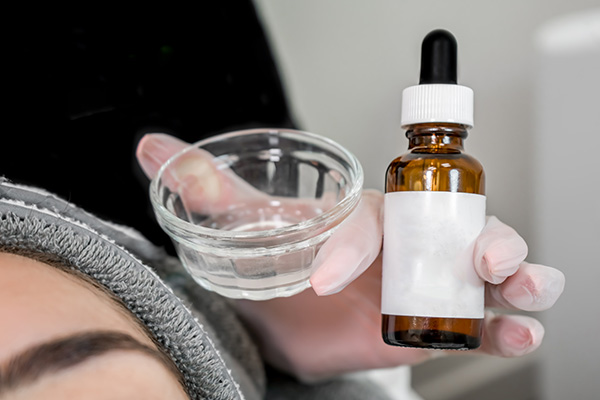

In-office chemical peeling procedures promote cell renewal and scattering of epidermal melanin. The chemicals used include mild acidic formulations containing glycolic, salicylic, mandelic, lactic acid, or trichloroacetic acid.
These treatments, depending upon the agent being used, can also stimulate collagen production and enhance cellular turnover. (2)
4. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion (3) is an exfoliating procedure that removes the darkened superficial skin and is a common dermatological procedure. This treatment uses a diamond- or crystal-tipped brush with tiny particles to sand away superficial skin cells.
Microdermabrasion is best for mild hyperpigmentation conditions. You must discuss with your doctor which procedure will benefit you the most. Microdermabrasion devices for home treatment are now available, but such practice is not advisable as it will not be as safe as that done by an expert.
When to See a Doctor
Your neck can turn black due to many possible reasons, and usually, it is nothing to fret about. Exposure to chemicals, improper skin care routine, and unprotected exposure to the sun is usually responsible for the darkening of the neck.
Simple measures can fix this problem, but it is advised to consult a doctor when the neck hyperpigmentation is accompanied by:
- Itching
- Peeling or flaky skin
- Rashes
- Pain
- Blistering
- Thickening of the skin
Certain medications such as NSAIDs, tetracyclines, cholesterol-lowering drugs like nicotinic acid, phenytoin, and antimalarials can also darken your neck as a side effect. If this bothers you, you can ask your doctor to suggest an alternative medication, if available.
Can Rubbing Diluted Vinegar Lighten the Dark Skin Around the Neck?

There is no scientific evidence to suggest that the topical use of diluted vinegar can help fade hyperpigmentation, but its main component – that is, acetic acid – is often used as a peeling agent in chemical exfoliation procedures.
It is important to note that these procedures are performed in-office by a trained specialist who decides what concentration or strength of acetic acid to use. So, it is rather impossible to reap the same skin benefits through amateur usage at home. If anything, it could lead to deleterious side effects that can make your condition worse.
Thus, simply diluting vinegar at home to lighten your darkened neck may not be all that effective, especially when there are other more efficacious treatments that you can try.
Final Word
Skin darkening around the neck can make you self-conscious of your appearance, but it is generally nothing to get worked up about. In most cases, hyperpigmentation is triggered by common day-to-day factors such as excessive sun exposure, wearing metallic jewelry that you may be allergic to, and buildup of dirt or dead skin due to negligent skin hygiene, all of which can be fixed with proper skin care and home remedies.
In some cases, however, the skin darkening may be a warning sign of something more serious such as hormonal imbalance or an increase in your sugar levels, which warrants immediate medical attention. The doctor will assess your condition to make a diagnosis and then recommend the appropriate treatment best suited for you.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


