In this article:
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disease that most commonly affects the skin (central face) and is characterized by periodic eruptions and remissions.
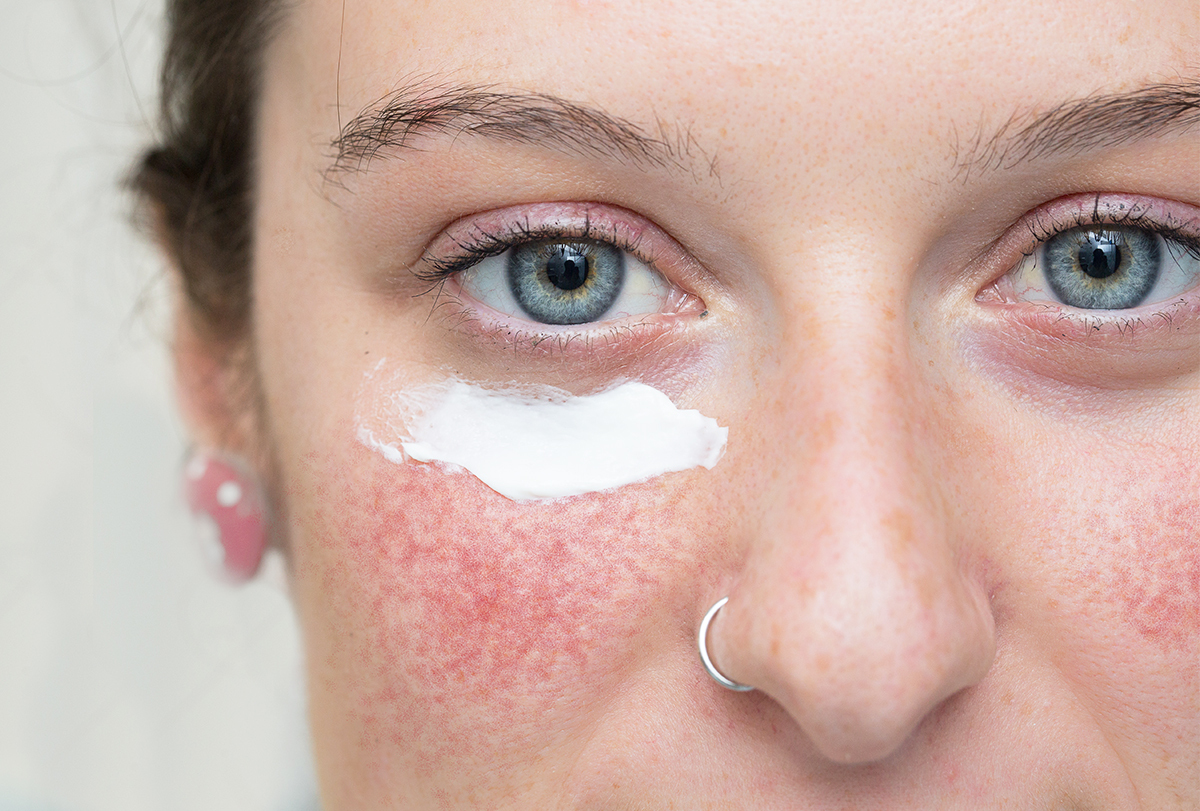

Its causes are not completely understood, but both genetic and environmental factors are currently thought to be key players. (1) Worldwide, the prevalence of rosacea is about 5%. (2) The condition usually starts between the ages of 30 and 50 years, (3) and females and males are affected equally. (4)
Is It Contagious?
It is important to note that rosacea is not contagious. Because antibiotics are used for treating this skin condition, some people mistakenly assume that rosacea is a bacterial infection.
However, there is no evidence to suggest that rosacea can be passed from one person to another through skin-to-skin contact or airborne transmission of respiratory droplets.
Certain factors have been identified for causing a disruption within the immune system and triggering rosacea, such as:
- Sun exposure
- Wind exposure
- Stress
- Heavy exercise
- Certain skin care products
- Microorganisms
- Spicy foods
- Alcohol
Avoidance or modification of these triggers can aid in symptom reduction and can guide possible treatment regimens. (1)
The National Rosacea Society (NRS) recommends keeping a diary log to record and thereby pinpoint potential triggers as they can differ from person to person. (7)
The disease process of rosacea remains unclear. However, dysregulation of the immune system, leading to increased levels of potentially disruptive compounds, is thought to be involved.
- Demodex (microscopic mites) and UV radiation appear to incite this process, but further studies need to be performed for a clear molecular mechanism. (6)
- An antimicrobial peptide called cathelicidin is found at increased levels in patients. It plays a role in stimulating the immune system and perpetuating the symptoms of rosacea. (1)
Are There Any Home Remedies and Alternative Treatments for Rosacea?
Here are some additional home remedies and alternative treatments for rosacea that may be used in conjunction with the standard medication and self-care:
- Vitamin C: Topical vitamin C has anecdotal evidence of treating rosacea. It is an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent commonly formulated with sodium ascorbyl phosphate (SAP) to improve stability. Some studies have shown that SAP alone can improve acne. (9)
- Niacinamide: Niacinamide can improve rosacea by lessening the inflammatory response and increasing epidermal barrier performance. This product is found in commercially available OTC moisturizers.
- Natural Ingredients: Skin-healing botanicals such as feverfew, licorice, chamomile, and green tea have been formulated in topical forms and shown to improve rosacea by decreasing the inflammatory response, decreasing the formation of blood vessels, or both.
- Food: Researchers have recently discovered connections between rosacea and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). Moreover, the elimination of SIBO has been shown to decrease many symptoms of rosacea. (10) Adjusting the diet to decrease fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (otherwise known as FODMAPs to include wheat, soft cheeses, and sweeteners) can favorably alter the gut microbiota. (11)
What Is the First Step to Treating Rosacea?

The first step in the treatment of rosacea is identifying and avoiding/modifying known triggers. As mentioned, keeping a diary can aid with this step.
Generalized advice to prevent epidermal water loss and dry skin (1)(5) primarily includes using:
- Sunscreen of at least SPF 30 (with the mineral zinc oxide)
- Gentle cleansers (preferably not soaps)
- Moisturizing ointments
The symptomatic treatment of rosacea involves:
- Beta-blockers and alpha-2 adrenergic agonists for flushing symptoms
- Brimonidine and oxymetazoline hydrochloride for symptoms of redness
- Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy or KTP laser
- Ivermectin, azelaic acid, metronidazole, and sodium sulfacetamide (most commonly 5% sulfur lotion and 10% sodium sulfacetamide) for mild inflammatory papules and pustules
- Doxycycline and isotretinoin for severe papules and pustules
- Oral doxycycline if the skin is inflamed and surgical/laser options if the skin is not inflamed in case of phyma (8)
Each of these medications and treatments has side effects that should be discussed with the prescribing doctor before use. Moreover, the following skin care products should be avoided:
- Waterproof makeup
- Astringents
- Cosmetics with strong fragrances
- Fruit acids
- Glycolic acids
- Witch hazel
- Exfoliating scrubs (8)
What Happens if Rosacea Is Left Untreated?

If rosacea is left untreated, the redness will persist, and the blood vessels will become more prominent from underneath the skin, causing:
- Papules and pustules
- Skin thickening
- Nose enlargement (rhinophymatous)
Moreover, several studies have documented the decreased quality of life and decreased psychological well-being of individuals with rosacea. (8)(12)(13)
Individuals with rosacea are more prone to:
- Coronary artery disease
- Celiac disease
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Parkinson’s disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Type 1 diabetes
- Migraines
However, further studies need to be conducted to establish these findings conclusively. (14)(15)
Final Word
Rosacea is a common skin problem that manifests as flare-ups of redness and pus-filled bumps on the face. It can often worsen with time. However, proper, timely diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition.
Moreover, some good skin care habits can help prevent flare-ups. Therefore, it is recommended to visit your dermatologist if you see any warning signs of rosacea.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


