In this article:
Brown spots on the skin, also known as age spots, dark spots, or sun spots, are light-brown to black spots of different sizes that generally form in the skin that is constantly exposed to the sun.
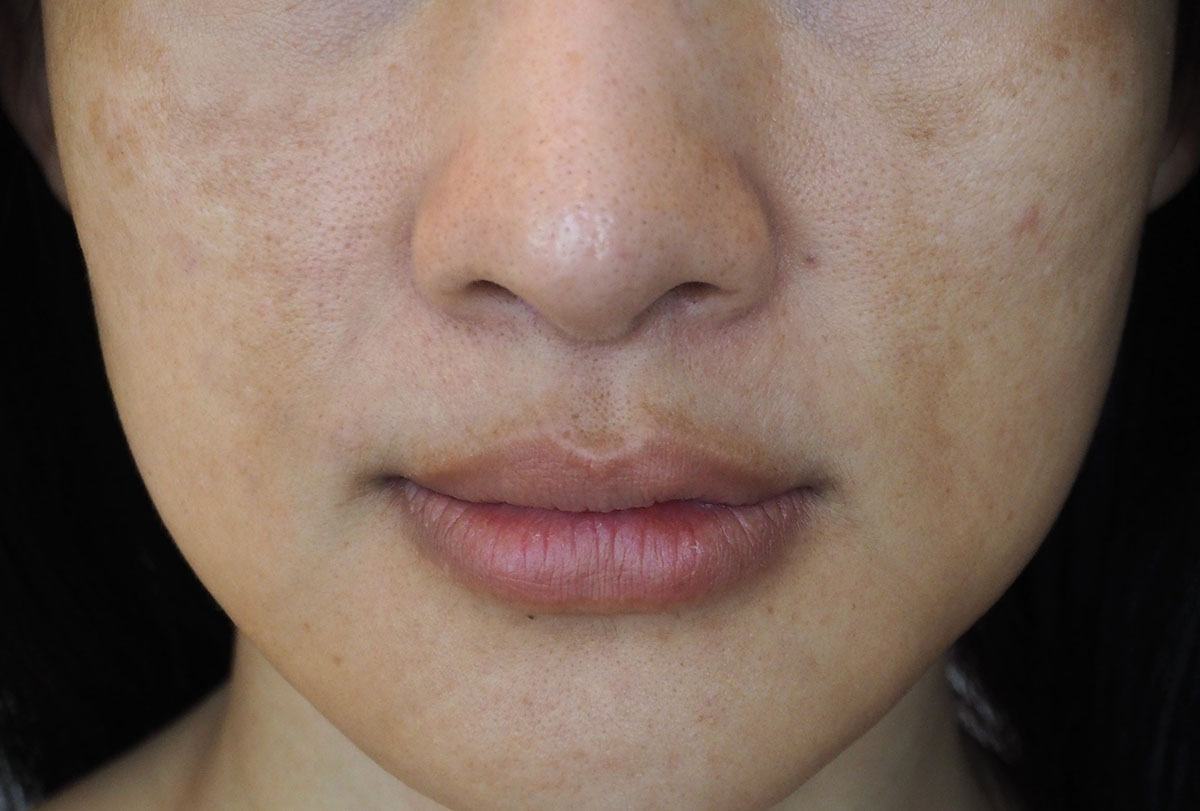
It is commonly understood that age spots are deeply associated with prolonged sun exposure and are therefore linked with photodamage of the skin. Nevertheless, the mechanism of their formation is, to date, inadequately known. (1)
Read on to know more about brown spots.
Where Do Brown Spots Commonly Develop?
Brown spots occur primarily in regions that are most prone to sun exposure. These include: (2)
- Dorsal surface of the hands
- Extensor forearms
- Upper trunk
- Face
What Conditions/Factors Can Cause Brown Spots?
Hyperpigmentation, or brown spots, can be associated with many skin disorders and other factors that include: (3)
- Acne
- Eczema
- Atopic dermatitis
- Age
- Sun exposure
- Chronic inflammation
- Skin infections
What Topical Agents Can Reduce Brown Spots?

Traditional hyperpigmentation therapy involves the use of topical agents on the affected areas. These topical agents include:
- Hydroquinone
- Retinoic acid
- Glycolic acid
- Topical corticosteroid
- Azelaic acid
- Arbutin
- Kojic acid
- Mequinol
Note: These agents can be used alone, by themselves, or in combination with another agent. Combination therapy is preferred because of its synergistic effects and fewer potential adverse effects.
Research has indicated that the triple combination of 0.05% retinoic acid, 4% hydroquinone, and 0.01% fluocinolone acetonide is the best option among all possible combinations in the treatment of melasma (a skin disorder that causes dark patches and spots on the skin). (4)
Treatment for Brown Spots
Brown spots can be incredibly troubling for some people. Fortunately, treatment options are widely available to reduce such skin issues.
The following treatments can decrease the appearance of brown spots when topical agents are not enough.
1. Chemical peels
Chemical peels work by inducing regulated damage to different layers of the skin, depending upon the type of chemical peel being done. The different agents for this technique are as follows. (5)

a. Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is a naturally derived compound from sugarcane and is used in concentrations varying from 20% to 70% based upon the requirement. This is normally deemed to be the gold standard for chemical peels for the treatment of melasma.
b. Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is derived from willow tree bark and is used in concentrations varying from 20% to 30%. It is considered useful in dealing with melasma in skin of color.
c. Jessner solution
Jessner solution is widely used in chemical peels in combination with other compounds such as ethanol. The various compounds function synergistically, lessening the strengths of each ingredient.
Side effects of chemical peels
Side effects of chemical peels vary from person to person and can include: (5)
2. Laser therapy
Laser therapy is a vastly researched treatment technique for dark spots and pigmented lesions. It can be done using the following laser types. (5)

a. Ablative lasers
Ablative lasers include CO2 lasers and erbium:YAG lasers, which work by removing layers of the skin. Even though research has indicated this technique to be helpful in the therapy of melasma, it is not desired in the skin of color because of some side effects.
b. Non-ablative lasers
Non-ablative lasers operate by inducing controlled damage in the skin. This type of laser therapy is reasonably well tolerated with rarer side effects than ablative lasers.
c. Picosecond lasers
Picosecond lasers are a quite recent class of laser that was developed to create shorter laser pulse durations that lead to minor photothermal harm to the skin.
3. Skin bleaching
Skin bleaching is described as conscious lightening of the skin tone. This transnational technique is embedded in the standards of colorism, which encourages the idea that beauty is linked with lighter skin tones.
A generally used skin-bleaching agent is glutathione, which is helpful in treating hyperpigmentation. It is hypothesized that glutathione facilitates skin lightening via multiple means such as its antioxidant action. (5)
How Are Brown Spots Different From Normal Skin?
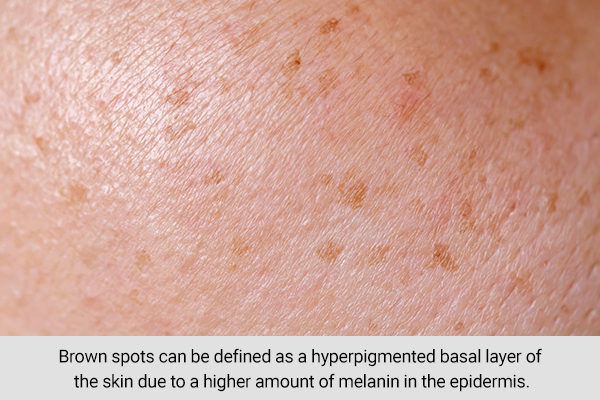
At the tissue level, brown spots can be defined as a hyperpigmented basal layer of the skin due to a higher amount of melanin in the epidermis, also known as hypermelanosis.
The structure of the epidermis in dark spots is most of the time not organized. Although there is a connection between the development of dark spots and the skin’s exposure to the sun or UV radiation, its mechanism is not yet known. (2)
What Can Aggravate Skin Hyperpigmentation?
Various factors can aggravate the problem of hyperpigmentation. These include pregnancy, oral contraceptives, endocrine disorders, and hormonal therapy.
Also, the use of some cosmetics and drugs such as anticonvulsants and photosensitizing substances can be linked to the exacerbation of hyperpigmentation. (6)
When to See a Doctor
Generally, dark spots do not call for any immediate medical attention. However, go see a doctor for spots that have gone black or changed in appearance as these transformations or changes can be indications of skin cancer.
Final Word
Brown spots on the skin, referred to as hyperpigmentation, can have a wide spectrum of reasons behind them. They are generally nothing to worry about and do not require any therapy.
However, they can be aesthetically displeasing and you may want to get rid of them. Speak to a dermatologist as, fortunately, a variety of treatments are available for dark spots.
 Continue Reading8 Home Remedies for Brown Spots on Skin and How to Use Them
Continue Reading8 Home Remedies for Brown Spots on Skin and How to Use Them
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


