In this article:
A bacterial infection in the hair follicles can cause the development of swollen, red, painful bumps on the skin, known as boils. These boils can enlarge due to the accumulation of pus and can form an abscess.

While boils and abscesses usually resolve after 10 days, prolonged infections can lead to complications. This article discusses various home remedies and self-care tips that can help aid recovery from boils and abscesses.
Home Remedies for Treating Boils and Abscesses
The following home remedies can help in the treatment of boils and abscesses. However, make sure to perform a patch test to rule out any allergies or skin reactions.
1. Use bleach baths or wipes
Sodium hypochlorite, commonly known bleach, possesses antimicrobial properties against S. aureus. Since it can irritate the skin, it is recommended to use diluted bleach.
How to use:
- Fill your bathtub up to ¼ height with water and mix 1 tsp of bleach per gallon of water. Soak yourself in it for 10 minutes and rinse your body with lukewarm water. (1)
- Soak a cotton ball with diluted bleach solution and use as a wipe.
Caution: Keep the water away from your head and eyes. Refrain from adding any other cosmetic, oil, or solution to the bathwater. Avoid using the remedy for children or asthmatic patients.
2. Try tea tree essential oil

Tea tree oil contains antiseptic and antibacterial properties (2) that can target the infection-causing bacteria and thus help control the infection at the early stages.
How to use:
Dilute 3–5 drops of tea tree oil with a teaspoon of carrier oil, such as castor, coconut, or olive oil, and apply the oil blend to the infected area using a cotton ball. You can also add turmeric to it. You may use black seed oil or clove oil in place of tea tree oil.
3. Use castor oil
Castor oil contains ricinoleic acid that provides an antibacterial effect. (3) Moreover, it has anti-inflammatory properties that can help control redness and swelling.
How to use:
Apply castor oil to the affected area with the help of a cotton ball.
4. Apply turmeric paste
The active compound in turmeric, known as curcumin, helps control infection and inflammation when applied topically. (4) It helps boost the immune system and purifies the blood when taken orally.
How to use:
Form a paste by grinding equal parts of turmeric and ginger together, and apply it to the affected area. Cover the area with a clean cloth and leave it on for a few hours. Use this remedy 3–4 times a day.
You can also consume turmeric milk every night. Simply mix 1 tablespoon of turmeric in a glass of warm milk and drink at bedtime.
5. Use neem leaves

Neem contains anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties (5) that can help control the growth of bacteria that cause boils and abscesses. (6)
How to use:
- Make a paste by grinding a few neem leaves in some water, and apply it to the affected areas. Leave it on for around half an hour and rinse.
- Boil neem leaves in water to form an antiseptic solution, which can be used to wash the skin.
- Try using diluted neem essential oil as spot treatment.
6. Try garlic
Garlic has antibacterial properties that can help inhibit the growth of staphylococcus bacteria. (7)
How to use:
Crush a garlic clove and mix it with honey, turmeric, and garlic to form a paste. Apply the paste to the affected skin and leave it on for 10 minutes before rinsing. You can also use crushed garlic clove and onions.
7. Apply honey
Honey possesses wide antibacterial properties that can even help control the growth of bacteria resistant to standard antibiotic treatment. (8)(9) It is recommended to use only raw, organic, or medical-grade honey.
How to use:
Apply honey to the affected areas, or mix it with turmeric before applying. Leave it on for 15 minutes and rinse with lukewarm water.
8. Try colloidal silver
Colloidal silver also exhibits antibacterial activity. It is commonly used for wound dressing to help prevent the growth of infectious bacteria. (10)(11)
How to use:
- Apply colloidal silver solution to the boils topically.
- Use ointments containing colloidal silver.
Caution: Avoid the oral intake of colloidal silver to prevent complications.
9. Apply apple cider vinegar
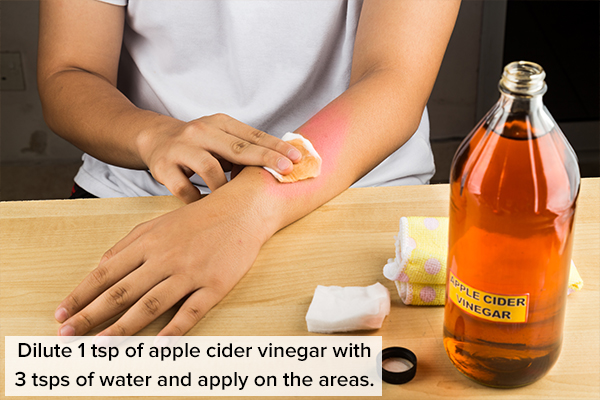
Vinegar is a common anecdotal remedy used for the treatment of boils. However, there is no scientific evidence to support its efficacy.
How to use:
Dilute 1 teaspoon of apple cider vinegar with 3 teaspoons of water, and apply the solution to the affected areas.
10. Take an Epsom salt bath
The use of Epsom salt bath is another anecdotal remedy that can help manage boils and abscesses.
How to use:
Add ½ cup of Epsom salt in your bathwater, and soak in it for 15–20 minutes.
Self-Care Measures for Boils and Abscesses

The following self-care measures should be kept in mind to aid the healing of boils and abscesses and prevent complications:
- Avoid picking on the boils. Refrain from scratching, squeezing, pinching, popping, or draining the boils as it can push the infection deeper into the skin.
- Keep your skin clean. Wash the affected areas gently with a mild cleanser twice a day. Pat the skin dry instead of rubbing it.
- Maintain hygiene. Clean draining abscesses with antiseptic solutions twice a day. Make sure to wash your hands properly if you touch a boil to prevent the spread of infection.
- Apply a warm compress. Soak a clean cloth in warm water and wring out the excess water. Put the cloth on the affected area for half an hour approximately, up to four times a day, to help open up and drain the boil. You can also use a heating pad wrapped in a damp towel.
- Apply a bandage. Cover the open abscesses with a clean bandage every day.
- Do not share towels. Refrain from sharing towels or washcloths with other people. Moreover, use separate washcloths for the affected areas and other body parts.
- Wear loose clothes. Do not wear tight clothes as it can cause untimely drainage of abscesses.
- Wash the infected clothing. Wash your cloths and towels or washcloths with warm water.
- Observe proper wound care after surgery. You can remove the gauze packing surgical draining yourself upon consulting your healthcare provider. Wash the area and clean it, and reapply clean gauze if directed.
How to Prevent Boils and Abscesses
The following tips can help prevent the development or recurrence of boils and abscesses:
- Wash your hands with antibacterial soaps and use alcohol-based hand sanitizers frequently, especially before touching your face.
- Take showers daily instead of baths to get rid of staph bacteria present on your skin.
- Do not pick your nose. Around 30% of individuals have staph bacteria in their nose. (12)
- Avoid shaving too close to the skin as it can increase the risk of bacteria entering the skin.
- Maintain optimum weight.
- Consume a balanced diet to avoid or correct any nutritional deficiencies, such as iron deficiency, that increase the risk of boils and abscess. (13)
- Consume probiotic-rich foods such as kimchi and yogurt. Additionally, include vitamin C-rich fruits such as berries, lemons, and oranges. These foods help boost your immune system. (14)
- Refrain from consuming refined sugars as they support bacterial growth.
- Quit smoking. (15)
- Wear clean clothes daily. Wash your bedding and clothes properly.
- Avoid the use of antiperspirants as they block the sweat glands, often leading to boils.
Final Word
Boils and abscesses are a common occurrence that can generally be managed with self-care measures and home remedies.
Keep the affected area clean using antiseptics and pat it dry. Use creams or ointments to help manage the infection. If the boils persist for more than 10 days or recur, make sure to contact your doctor, as they can indicate other medical conditions.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


