In this article:
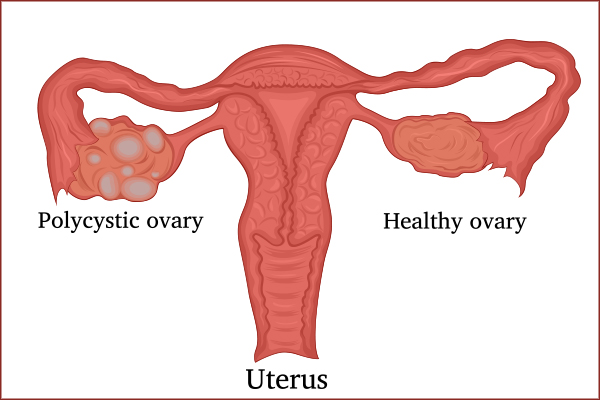
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder characterized by an increase in androgen levels in women. This common problem results from the development of cysts in the ovaries, which hampers its proper functioning. (1)

PCOS manifests different symptoms in women, but the common ones include irregular periods, excessive body hair (hirsutism), and hair thinning.
The increase in male hormones also causes hair shedding or hair loss from the scalp, medically known as androgenetic alopecia or female-pattern baldness. This article discusses the different aspects of PCOS-related hair loss and its treatment options.
Role of Testosterone in PCOS and Hair Loss
The female human body releases both female hormones (estrogen and progesterone) and male hormones (testosterone). The female hormones are responsible for developing the characteristic features of women.
The male hormones, on the other hand, circulate throughout the body for various functions and the development of different features such as the growth of underarm and pubic hair.
Generally, the female body maintains a balance between the hormones so that the level of female hormones remains significantly higher to enable the uninhibited development of female features.
However, in women with PCOS, the formation of cysts in the ovaries causes a hormonal imbalance. This results in the development of masculine features, such as enlarged clitoris, deep voice, shrinking of breast size, and hirsutism.
Hair on the body increases and grows thicker, but the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) negatively impacts the hair follicles in the scalp. DHT disturbs the hair growth cycle, causing shortening, thinning, and falling of vertex and frontal hair, (2) which is known as female-pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia. (3)(4)
Medical Treatments to Stop the Hair Loss

To treat hair loss associated with PCOS, it is best to target the root cause, which is hormonal imbalance. The current medical treatment aims at restoring hormonal balance and ovary function. This, in turn, improves the health of hair follicles.
If you have PCOS-related hair loss, you may need to undergo a combination of the following treatments:
1. Birth control pills
Oral contraceptives or birth control pills are hormone pills that increase female hormones in the body, thus helping prevent a high level of androgens from affecting the hair follicles. (5)
This may be combined with anti-androgenic drugs that work by blocking the action of androgen hormones. Some common examples of anti-androgenetic drugs include spironolactone and flutamide.
However, women who are trying to get pregnant should not use birth control pills or anti-androgenetic drugs but explore other treatment options instead.
2. Minoxidil
Minoxidil, available in liquid and aerosol forms, is an FDA-approved topical treatment for androgenetic alopecia. This OTC medication has been shown to improve hair growth and thickness by various studies. (2)(6)
Newer formulations, such as nanoxidil, are being introduced on the market while currently being studied for their long-term use.
ALSO READ: Can We Use Nanoxidil for Hair Loss
3. Tretinoin
The topical use of tretinoin or retinoid A may help treat androgenetic alopecia and is commonly used in combination with minoxidil.
4. Other drugs
Ketoconazole may be prescribed; it is primarily an antifungal agent, but it can help lower androgen levels. Another commonly used drug for treating PCOS-related androgenic alopecia is Diane-35.
Medications such as finasteride and dutasteride, which are primarily used for the treatment of male-pattern baldness, may also help manage female-pattern baldness in rare cases.
5. Platelet-rich plasma therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves injecting blood plasma into the scalp to improve the symptoms of androgenetic alopecia with minimal side effects.
PRP therapy is currently used as an adjunct treatment, until further large-scale, randomized studies can confirm its efficacy as a single treatment.
6. Laser therapy
Laser therapy, (7) including photobiomodulation, soft laser, biostimulation, and red-light laser, can help boost hair growth and thickness. It is, however, essential to closely regulate the use of laser therapy as its long-term effects are still being studied.
7. Hair transplant surgery
Hair transplant is a surgical procedure wherein a skin graft with healthy hair follicles and hair from the body is cut out and transferred to the area of hair thinning and hair loss on the head.
This procedure offers a quick solution to the targeted area, but you must also undergo additional treatments to address the root cause and thus prevent future hair loss.
Diagnosing PCOS as the Cause of Hair Loss
While hair loss is a common manifestation of PCOS, various other conditions can cause symptoms that represent PCOS, including hair loss and irregular periods. Therefore, it is vital to consult a doctor so that other causes can be ruled out before confirming PCOS as the underlying cause.
The following tests may be performed to confirm a PCOS/PCOD diagnosis:
- Physical test. The doctor may check for physical symptoms of PCOS, such as excess hair, acne, and male-pattern hair loss.
- Blood test. This includes measuring hormonal levels in the blood. A high amount of androgens in the blood signifies PCOS.
- Imaging tests. An ultrasonography of your ovaries will detect an increase in the size of the ovaries and the presence of follicles.
Home Remedies to Manage Hair Loss

The following home remedies may help manage PCOS and its related symptoms, especially hair loss:
Caution: Only try these remedies if you are not allergic to them. Moreover, consult your doctor on using supplements and OTCs as these may not be FDA regulated. Regardless, it is best to advise your doctor about these treatments to determine if they are suitable for you, based on your medical history and symptoms.
1. Drink spearmint tea
Spearmint tea is shown to have anti-androgenetic activity. However, research on it is limited in various aspects. (8)(9) While spearmint tea is reported to have better efficacy by users, you can also opt for spearmint capsules.
2. Take inositol
Inositol, commonly known as vitamin B8, is a carbocyclic sugar.
Different forms of inositol are shown to be effective in PCOS treatment. Myoinositol helps improve the metabolic profile, including insulin levels in women with PCOS, while D-chiro-inositol helps control testosterone levels. (10)(11)(12)
3. Increase zinc intake
Zinc can help control hair loss by blocking the activity of the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme that is responsible for testosterone metabolism in the hair follicles. (13)(14)
You can increase your zinc intake by consuming oysters, poultry, nuts, crabs, lobster, beans, fortified breakfast cereals, and whole grains. You may also consider the use of zinc sulfate supplements and zinc-containing cold lozenges.
4. Consume cinnamon
Cinnamon is shown to help improve lipid and insulin profiles in women with PCOS. (15) The use of cinnamon to help improve PCOS symptoms is also supported by anecdotal evidence. Moreover, it is safe for consumption and, therefore, can be safely tried.
5. Have green tea
Green tea is rich in epigallocatechin that exhibits anti-androgenetic effects. Moreover, the antioxidant in green tea boost metabolism and control hormonal imbalance. (9)
6. Take help of maca root
Maca root is shown to boost estrogen production and improve ovary functioning, (16) and it is commonly recommended for PCOS management by physicians in Europe. (17) Maca root is available in capsule and pregelatinized powder forms.
7. Use N-acetyl cysteine
Studies showed that the use of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) can improve ovary functioning in women with PCOS. (18)(19)
NAC can be taken in supplement form or can be acquired through the diet by increasing the intake of lentils, beans, tuna, spinach, eggs, salmon, banana, and yogurt.
Self-Care Measures

In addition to medical and at-home treatments, it is recommended to adopt the following self-care measures to manage PCOS-related hair loss and other symptoms of the condition:
1. Modify your diet
Adopt a healthy diet, such as the keto diet, if you have PCOS. Moreover, increase your intake of antioxidants, including vitamin E, selenium, and coenzyme Q10, through foods such as cherries, tomato, berries, and bell pepper to improve hormone balance.
Omega-3 fatty acids can help treat PCOS, (20) along with magnesium, chromium, and calcium. (20) Vitamin D is another essential nutrient that helps by improving endocrine functioning. (21)
You can include anti-inflammatory foods to help manage the inflammation associated with PCOS. These foods include yogurt, turmeric, ginger, kimchi, sauerkraut, cayenne pepper, cinnamon, garlic, cloves, green leafy vegetables, and olive oil.
Avoid consuming processed sugars, refined foods, trans fat, saturated fats, and white bread. Substitute red meat with lean meat such as fish and beans. (22) Finally, limit the use of dairy as this helps improve PCOS symptoms in some women. (23)
2. Stay hydrated
It is essential to keep your body hydrated for proper metabolism and functioning. Drink at least 8 glasses of water each day.
3. Manage your weight
It has been shown that weight loss of even 5%–10% of your body weight has significant effects on androgen levels and other PCOS symptoms. (24)(25) Maintaining a healthy weight helps lower the number of circulating androgens, thus controlling hair loss and thinning.
4. Try different hairstyling techniques
You can use wig falls, partial wigs, scarves, hair bands, root cover-up powders, and volumizing hair products to make your hair look full and thick. For hair fall at the midline, you can try side parting your hair.
Avoid using heat tools such as straighteners, rollers, curling irons, and hair dryers.
5. Avoid pulling your hair
Always handle your hair gently. Detangle your hair using a wide-toothed comb and brush it softly after a shower. Avoid combing the hair while it is still wet. Avoid hairstyles that pull on the hair and cause damage, such as buns and braids.
6. Do not use chemical-containing products
Avoid the use of chemical-laden hair products such as dyes and bleach. Additionally, refrain from using endocrine-disrupting synthetic products such as cosmetics and soaps that contain glycol ether, phthalates, and dioxins.
7. Manage stress
Stress can exacerbate the symptoms of PCOS. Therefore, it is advised to try stress management techniques such as aromatherapy, Epsom salt baths, meditation, and yoga. You must also get 7–8 hours of sound sleep every day.
8. Exercise regularly
Exercise for 30 minutes daily, including both strength and cardio exercises. You can start with skipping and bicycling.
9. Quit smoking and limit your alcohol intake
These habits have negative impacts on your general health, including metabolism and hormonal profile.
10. Join a support group
Getting in touch with women undergoing similar problems can help you overcome the psychological implications of PCOS and the associated hair loss.
Can Biotin Supplements Help Induce Hair Growth?

The role of biotin in boosting hair growth has not been widely studied. However, you can increase your biotin intake through the diet. You must consult your doctor before considering the use of supplements.
Final Word
PCOS is a pervasive problem among women that manifests a wide range of symptoms due to increased androgen levels in the body. One such frequent complaint associated with PCOS is female-pattern baldness, which is characterized by hair thinning and hair loss.
Several medical treatments are available to manage androgenetic alopecia. You can also try home remedies to aid treatment. However, always consult a doctor to determine what suits you the best. In addition to treatments, observe self-care measures that help prevent hair loss and manage PCOS.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


