In this article:
Melanin is the pigment that gives the skin, hair, and eyes their natural color. The more the melanin, the darker the color. Melanocytes are specialized cells found in the epidermis, iris, and hair follicles that produce melanin through the oxidization of an amino acid called tyrosine. (1)

Melanin also serves a protective function against the harmful UV rays of the sun. These UV rays can penetrate deep into the skin and break down the very DNA of the skin cells.
This kind of persistent sun damage can trigger a number of skin problems such as dark spots, early skin aging, and premature graying of the hair at the very least and cancer at the very worst. In fact, UV exposure is one of the major contributors to skin cancers such as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and malignant melanoma.
But melanin helps minimize this kind of sun damage by absorbing the UV rays before they can reach the healthy cells. (2)(3) It’s the body’s natural SPF, which springs into action whenever you go out in the sun. This is how tanning happens.
When the sun-induced UV radiation falls on the skin, the melanocytes are stimulated to produce extra melanin, which makes your skin darker. This article will focus on the role of melanin in hair health.
Importance of Melanin for Hair
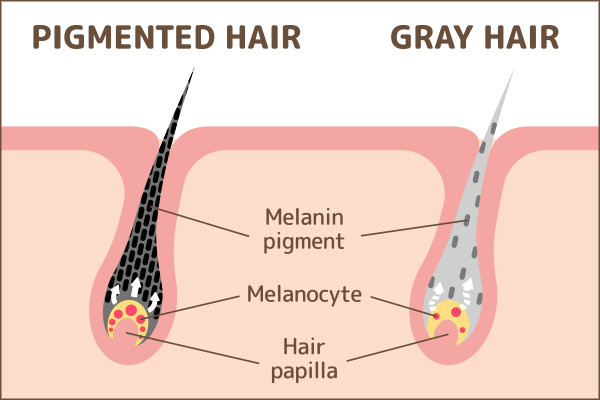
Melanin plays a significant role in hair development and health.
1. Melanin regulates hair color
You’ll be surprised to know that your hair is originally white but changes color once it emerges out of the hair follicle.
Each strand is made up of a tough protein called keratin, which is carried by cells called keratinocytes. The melanocytes supply melanin to these keratinocytes as your hair grows and give them their natural dark color.
The melanin responsible for your hair color can be of two types, namely, eumelanin and pheomelanin. Both these pigments are mainly found in the cortex or the middle layer of the hair shaft.
Different combinations and concentrations of these two forms of melanin produce five natural hair colors: black, dark brown or brunette, light brown, yellow or golden blonde, red or ginger, and white. Thus, your hair color depends on the type, amount, and combination of melanin found in your hair. Melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) is the gene that decides what type of melanin will be produced by the melanocytes. The activity of this gene is what ultimately determines your hair color. (4)
Eumelanin refers to the dark form of melanin and is further divided into brown eumelanin and black eumelanin. This is the most common variant of melanin found in humans, and it gives your hair a black, brown, blonde, or gray color.
A high concentration of black eumelanin in the absence of other pigments will result in black hair, whereas a high concentration of brown eumelanin will result in brown hair. A low concentration of black eumelanin without any other pigment will make your hair grey, while a low concentration of brown eumelanin devoid of other pigments will make your hair blonde.
Pheomelanin refers to the bright shade of melanin with a reddish hue. A high concentration of this pigment in the absence of other pigments will give your hair a red color.
But when a small amount of this pigment mixes with a small amount of brown eumelanin, the result is orange-colored hair, which is popularly termed ginger.
| Eumelanin:pheomelanin ratio | Hair color |
|---|---|
| High eumelanin and low pheomelanin | Brown or black |
| High pheomelanin and low eumelanin | Red (very high pheomelanin) or yellow |
| None or very little eumelanin or pheomelanin (albinism) | White |
The production and distribution of melanin are affected by an array of internal and external factors. (5)
Intrinsic factors:
- Genetic defects
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Body distribution
- Age
Extrinsic factors:
- Climate
- Pollutants
- Toxins
- Chemical exposure
There is a natural decline in melanocyte activity as you grow older, resulting in decreased melanin production. It is this progressive melanin loss that makes your hair lose its color and turn white or gray in the later years of life. (6)
2. Melanin protects the hair against sun rays
As discussed earlier, melanin in the hair and skin forms a barrier that blocks out the UV rays of the sun. Sun exposure triggers melanin production in the body to neutralize the damaging effects of the UV rays.
Eumelanin is more photostable than pheomelanin, which essentially means that it’s less likely to breakdown when exposed to light. Thus, people with more eumelanin in their hair will get better sun protection than those with more pheomelanin.
In other words, darker hair is less vulnerable to sun damage than lighter ones. (7)
Restore Melanin in Hair Naturally
The following measures can help maintain or improve the melanin content in your hair:
1. Eat foods that increase melanin production

Certain nutrients can help keep your hair from graying either by stimulating melanin production or reducing its degradation. Conversely, various nutritional deficiencies are often held culpable for the premature or increased graying of hair.
The best way to get your required dose of these hair-friendly nutrients is by consuming a well-balanced, wholesome diet. If you fail to meet your nutritional needs through foods alone, you may ask your doctor to put you on supplements.
Here are some of the must-have foods that help you retain your natural hair color:
a. Iron
Some of the best dietary sources of iron are dark green vegetables (such as spinach, legumes, and broccoli), quinoa, tofu, dark chocolate, fish, bananas, tomatoes, soybeans, lentils, nuts, and seeds (cashew, peanuts, flax seeds, pumpkin seeds, etc.).
b. Copper
You can meet half of your recommended copper intake through cereals, organ meats, and seafood alone, and you can compensate the rest by adding nuts or seeds to an overall balanced diet.
Some of the best copper-rich foods to include in your diet are chickpeas, dark chocolate, almonds, cashews, sweet potatoes, avocados, poppy or sunflower seeds, liver, and oysters.
c. Catalase
Catalase is an enzyme found in all living organisms, including several plant-based foods. It works as an antioxidant by neutralizing hydrogen peroxide, which is a strong oxidizing agent.
Normally, hydrogen peroxide breaks down into hydrogen and hydroxyl radicals that attack healthy cells. In fact, graying of the hair is partly the result of this kind of oxidative damage.
Hydrogen peroxide builds up in hair follicles over time and releases oxidative stress on the melanocytes. As a result, the melanocytes become damaged and are unable to produce enough melanin to retain your natural hair color. (8)
But catalase can neutralize this process. It acts as a catalyst in decomposing hydrogen peroxide into hydrogen and water, which are safe for hair cells and do not hamper melanin production. You can increase your catalase intake through vegetables such as sweet potatoes, onions, spinach, celery, cucumbers, and kale as well as fruits such as pineapple, cherries, apricots, watermelon, and peaches.
d. Antioxidants
Antioxidants neutralize the activity of free radicals that unleash a lot of oxidative stress in the body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that target and damage healthy cells, paving the way for a number of health issues.
These free radicals attack the melanin-producing cells in the hair to cause premature graying. Thus, it may be a good idea to up your intake of antioxidant-rich foods such as dark chocolate, blueberries, beans, pecans, artichokes, and leafy greens.
e. Vitamins and its supplements
The lack of vitamin A, C, or B12 is often linked with melanin deficiency, which makes your hair lose its color. So, you should aim to include foods rich in these vitamins if you are concerned about premature graying or greying in general.
Certain supplements can boost melanin content in your hair, but you must consult your doctor before starting them. Supplements are usually recommended when your diet is unable to make up for the vitamin deficiency.
Here are the foods and supplements that can help fight graying of the hair:
- Vitamin A-rich foods help keep the hair moisturized by stimulating the oil glands attached to the hair follicle. You can get this vitamin from foods including carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, and some animal foods, or you can take it in supplement form but only after consulting your doctor. You need to consume enough fatty acids such as omega-3 and omega-6 to help your body absorb the vitamin A supplements properly. Dairy products, bread, fruit juices, chia seeds, dark chocolate, and avocados are some of the best sources of fatty acids. Add these to your diet when you start your vitamin A supplement.
- Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps prevent melanin breakdown due to free radicals. Citrus and naturally pigmented foods such as oranges, lemon, strawberries, plums, guavas, cherries, broccoli, sprouts, and papaya are richly endowed with vitamin C.
- Vitamin B6 and B12 are known to aid the formation of both melanin and hair. (9) Various illnesses and deficiencies can accelerate the loss of melanin from your hair, but taking vitamin B6 in the form of turkey, beans, potatoes, and spinach during the recovery period can help undo this damage and restore your natural hair color.
- Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) and pantothenic acid belong to the family of B complex vitamins and are known to delay the onset of hair graying. Both these vitamins are sold as supplements at health food stores and pharmacies.
- Brewer’s yeast is a supplement that contains a powerful concoction of nutrients that help strengthen and stimulate the hair follicles. Healthy hair follicles result in better melanin production to reduce or delay greying. The star ingredient of this supplement is biotin which is essential for hair growth and cell regeneration. (10)
- Inositol and niacin also help nourish the hair follicles so that they produce enough melanin to keep your hair color intact.
2. Try some home remedies

Massaging your scalp with a hair-nourishing oil or tonic can help stimulate blood circulation in the head. The enhanced blood flow will deliver more nutrients and oxygen to the hair follicles and help the melanocytes perform better. The activated melanocytes will produce more melanin to restore and maintain your true hair color.
Two of the top-rated ingredients for this purpose are coconut oil and onion juice, but there aren’t enough scientific studies to confirm their effectiveness.
However, these anecdotal remedies have delivered good results for a lot of general users with no side effects reported. So, even though there is no guarantee for success, there is no harm in trying as well.
Simply massage your scalp with coconut oil or onion juice, and let it sit for at least 30 minutes before rinsing it out.
3. Reduce stress
Stress inhibits melanin production, which is why you must keep it under control to prevent loss of hair color. (11) Try relaxing activities such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises to calm your mind and body.
Topical Application of Dyes With Artificial Melanin
Many melanin-based topical hair products are available on the market. However, there isn’t enough scientific research to confirm their mechanism or efficacy.
A synthetic melanin-based hair dye developed by Northwestern University was found to mimic the natural process of human hair pigmentation to reverse hair graying. This product can be used as a gentler and safer alternative to regular hair dyes that are loaded with harsh hair-damaging chemicals. (12)(13)
Plus, hair products that contain lutein, lycopene, astaxanthin, and probiotics generally deliver the promise of increased melanin production and should be a part of your hair care regimen if you are struggling with gray hair.
Melanin Supplements

There is no scientific evidence supporting the intake of melanin supplements to increase melanin production, but certain nutrient supplements can certainly engender this effect. However, these nutrient supplements are only meant to compensate for deficiencies rather than reverse natural hair graying.
In other words, these supplements help you meet your required intake of certain nutrients that are needed for melanin production. If you are getting enough of those nutrients through your diet, the supplements will have no effect on melanin production.
Final Word
Graying of the hair is caused by the loss of melanin, which is brought on by a number of biological and environmental factors. Genetic and age-related graying is impossible to control or reverse.
You can help delay the rate of melanin loss by eating right and observing proper hair care. It is also very important to protect your hair from the toxins present in the environment and hair products. These chemicals and pollutants can wreak havoc on the hair follicles and destroy the melanin-producing cells within them.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


