In this article:
The cysteine treatment is a popular procedure for softening and straightening curly hair. The treatment uses a non-essential amino acid called cysteine complex to turn your curls straight. Cysteine is an amino acid that is a building block of proteins. It also helps your body to produce glutathione, a powerful antioxidant. (1)
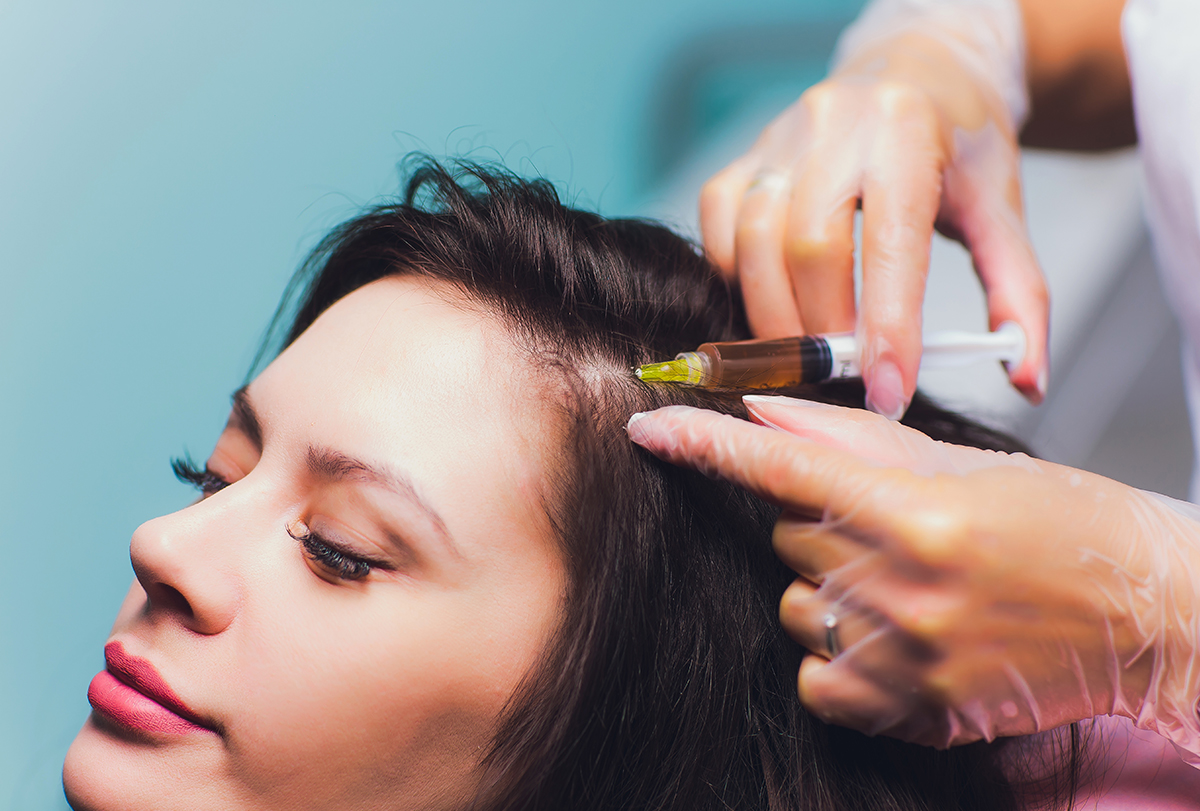

Hair botox is a new hair care treatment that claims to be the ultimate solution to thinning hair and balding. (2)
Which hair treatment should you use? There’s no definitive answer, as it depends on your individual hair type, preference, and needs. However, this article can give you some general guidelines to help you decide.
Generally, if you want to impart a straight look to your curly hair and reduce frizziness, then cysteine treatment may be a better option for you. (3) This is because it can help to straighten and thicken your hair strands. (1)
Hair botox, on the other hand, is better suited for hair types that are in need of a little tender loving care. It can help to add volume and shine to your hair while also boosting hair regrowth, when injected. (4) Generally, hair botox is done in a salon as topical application to add more volume and deep conditioning treatment is applied.
But for a more scientific answer as to which one is better, continue reading.
Cysteine or Hair Botox – Which One Is Better According to Research?
Permanent relaxers, which were the first type of hair straighteners used in salons, eventually gave way to formaldehyde-free hair-straightening techniques such as hair botox and cysteine, which are currently popular.
Both are chemical free and make hair more manageable but there are slight differences in their results as cysteine lasts up to 6 months and hair botox effects wear in about 4–5 months. However, in terms of choosing which one is better, it depends on your own choice.
But as per the latest research, hair botox makes hair more manageable, stronger, and less frizzy while causing less chemical damage to the hair and preserving its natural waves, giving the hair a more natural-looking appearance. (5)
Types of Cysteine
Cysteine is an amino acid that gives nourishment to keratin, which is a natural protein that protects cells in the body. There are two main types of cysteine:
- L-cysteine. L-cysteine is the form of cysteine found in proteins, and it is also the form used in supplements as N-acetyl cysteine (NAC). (6)
- D-cysteine. D-cysteine is a synthetic form of cysteine that is not found in nature. It helps in the formation of sulfide bonds, which strengthen hair strands. (7)
Both forms of cysteine have been shown to be effective in boosting hair growth, but L-cysteine is generally more widely used as it is well-tolerated, at least according to the results of one randomized controlled trial, which found good results with NAC on the synthesis of glutathione. (8)
Types of Hair Botox
Hair botox, or Brazilian keratin treatment, is a popular hair treatment that uses chemicals to straighten hair. Hair botox is a supplement made up of an antiaging complex that contains more than 20 proteins including cysteine, keratin, and other essential elements. (5)(9)
There are three main types of hair botox:
- Sodium hydroxide-based: Sodium hydroxide-based hair botox is the most common and popular type. (10) It works by breaking down the bonds between the protein chains in your hair, making it easy to straighten. (11) Sodium hydroxide is a strong chemical, so it can cause some irritation if it comes into contact with your skin or eyes.
- Guanidine hydroxide-based: Guanidine hydroxide-based hair botox is less common than sodium hydroxide-based, but it is gentler on the scalp and doesn’t cause as much irritation. Guanidine hydroxide works by breaking down the disulfide bonds in your hair, making it easy to straighten. (10)
- Formaldehyde-free: Formaldehyde-free hair botox is the newest type of hair botox. It uses chemicals such as glycolic acid and thioglycolic acid to break down the disulfide bonds in your hair, making it easy to straighten. Formaldehyde-free hair botox is gentle on the scalp and doesn’t cause irritation. (12)
Pros and Cons of Cysteine Treatment and Hair Botox

When it comes to hair treatments, there are a lot of different options to choose from. Two of the most popular options are cysteine treatment and hair botox.
Here are the pros and cons of each treatment.
Cysteine hair treatment
Pros:
- Cysteine is a protein that can strengthen and repair your hair. (2)
- It can protect your hair from damage caused by heat styling or coloring. (3)
- It can add shine and luster to your hair. (3)
Cons:
- Cysteine can be expensive.
- It may not be suitable for all hair types. (3)
Hair botox
Pros:
- Hair botox is less expensive than cysteine treatments.
- It can smoothen frizzy or unruly hair. (4)
- It can give your hair a sleek and shiny appearance. (5)(9)
Cons:
- Hair botox uses chemicals to straighten and smoothen hair. (2)
- It needs to be repeated after several months; the results are not permanent.
- It is not as widely available as cysteine treatments.
- It may not be as effective for very damaged or unhealthy hair.
How to Take Cysteine and Hair Botox
If you’re looking for a way to improve the health and appearance of your hair, you may be wondering which between cysteine treatment and hair botox is better. Both can offer benefits, but it’s important to understand how each works before making a decision.
Cysteine is a protein-based treatment that helps to strengthen and protect your hair. Cysteine is an amino acid that helps to strengthen and repair hair follicles. It can be taken orally in supplement form or applied topically to the scalp. When used topically, cysteine can help to stimulate new hair growth and prevent further hair loss.
Hair botox, on the other hand, is a treatment that uses chemicals to straighten and smoothen the hair shaft. It is a fairly new treatment that’s becoming increasingly popular.
It works by infusing your hair with nutrients and vitamins that help to repair hair damage and give your hair a healthy boost. It can also be used to add volume and body to thinning hair. Hair botox treatments typically last for several months before needing to be repeated.
So, which is better – cysteine or hair botox? Ultimately, it depends on your individual needs and goals. If you’re looking for a treatment that will offer long-lasting results, cysteine hair treatment may be the better option. However, if you’re interested in something that’s more natural, hair botox may be the better choice for you.
Most-Asked Questions
I have dry, limp locks. Which treatment should I go for?
A hair botox treatment will work great on your dry and limp hair. Make sure that you do a patch test beforehand to ensure that it is suitable for your hair type.
Final Word
There is no easy answer when it comes to choosing between cysteine treatment and hair botox. Both have pros and cons, and ultimately, the best option for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences.
If you are looking for a safe and natural option, cysteine may be the better choice. However, if you are looking for a more affordable option that can treat existing damage, hair botox is the way to go.
Whichever treatment you choose, make sure to consult with a professional stylist or dermatologist to ensure that it’s the right fit for you.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


