In this article:
Fungi are organisms that can be found everywhere, especially in warm, moist environments. They can be macroscopic or microscopic in size. Fungi can often grow on their own, but some types may depend on host organisms, such as humans, for their growth.
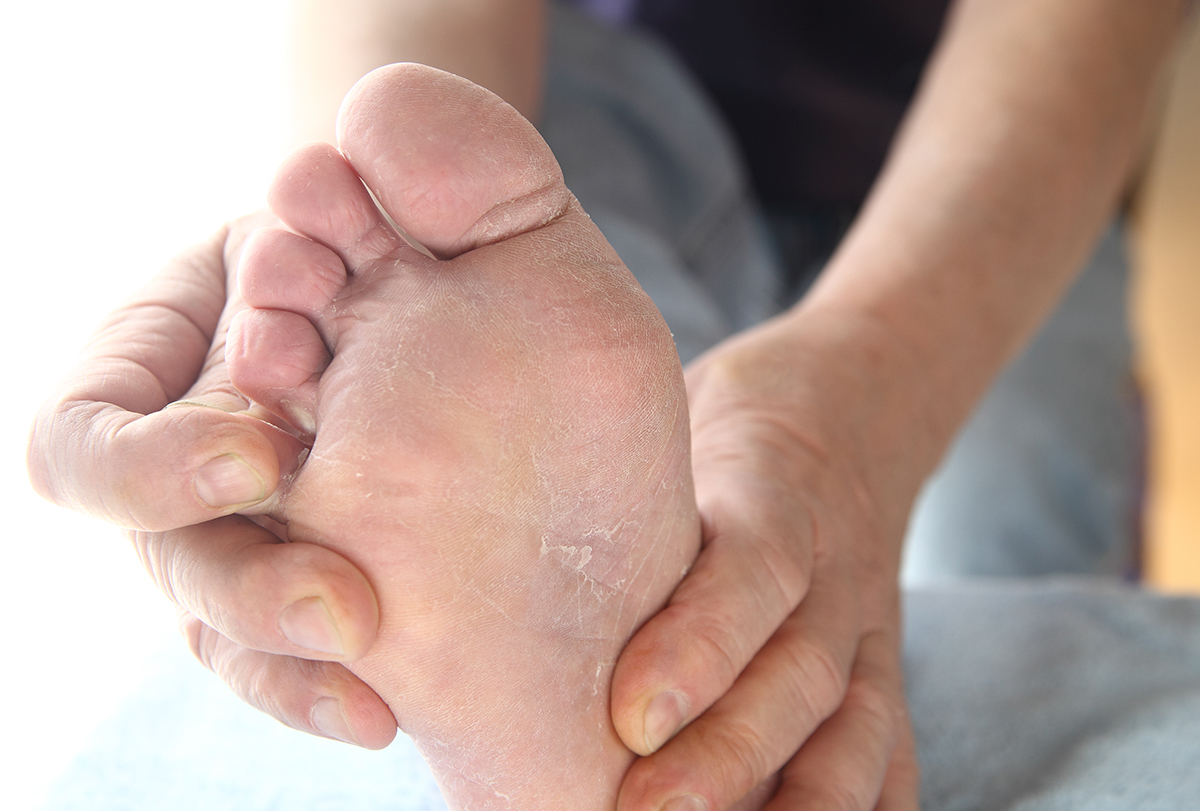
Some fungi, including cryptococcus, aspergillus, and rhizopus, (1) can be pathogenic and cause infections. It is vital to treat the infections they cause at the earliest for easy management and to prevent complications.
How Common Are Fungal Infections?
Fungal infections, also known as mycosis, are very frequent, with around a billion people having a nail, skin, hair, or mucosal fungal infection. Of these infections, the most common is yeast or candida infections, such as thrush.
Moreover, about 150 million people suffer from fatal fungal diseases. Fungal infections have a high mortality rate, approximately equivalent to that of tuberculosis and three times more than that of malaria. (2)
Types of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are highly common and can affect various body parts, including the exposed skin, internal organs such as the lungs, and even hidden skin folds.
Fungal infections are often categorized into different types according to the area they affect:
- Athlete’s foot, affecting the feet and hands
- Candidiasis or thrush, including oral thrush, urinary tract infection, and vaginal thrush
- Ringworm, infecting the scalp and skin
- Intertrigo, present in the skin folds
- Jock itch, affecting the groin
- Penile yeast infection, affecting the penis
- Onychomycosis of the nails
- Pityriasis versicolor, or discoloration of the skin
- Seborrheic dermatitis, affecting the scalp
- Trichosporonosis, which can affect the blood, heart, or lungs
- Zygomycosis of the sinus and nose
- Hyalohyphomycosis present in the blood, meninges, and urinary tract
Other fungal infections include:
- Blastomycosis
- Valley fever
- Histoplasmosis
- Fungal eye infection
- Mycetoma
- Cryptococcus gattii infection
- Paracoccidioidomycosis
- Sporotrichosis
- Mucormycosis
- Aspergillosis
General Signs and Symptoms of Fungal Infections
Most fungal infections manifest the following common symptoms:
- Itching (pruritus)
- Smelly skin
- Stinging sensation
- Burning sensation
- Pain or discomfort while urinating or during sexual intercourse
- Flaking, cracking, and peeling of the skin
- Rash
- Erythema
- Skin discoloration
- Nasal congestion
- Thick or discolored nails
- Sinus problems
Medical Treatment for Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are generally mild and can be managed with antifungal medications, which are available both over the counter and on prescription. The doctor may recommend oral or topical medications of different strengths upon analyzing the severity of your infection.
The most commonly prescribed antifungal medications include: (3)
- Polyenes (amphotericin)
- Echinocandins
- Azoles such as fluconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole
- Fluorocytosine
You may also be prescribed steroids if you have a swollen, large lesion known as kerion. If you are undergoing any surgery, you may be required to take empiric and prophylactic therapies to prevent invasive fungal infections.
Diagnosing a Fungal Infection

Fungal infections are diagnosed with a close inspection of the infected site. Ultraviolet light may be used to observe the site of infection more clearly.
The doctor may also take a sample from the site of infection and send it for culture to identify the strain of fungi. In some cases, you may require blood cultures and enzymatic immunoassays to detect certain invasive fungal infections. (3)
Additionally, the doctor may evaluate your medical history and current medications to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Risk Factors for Fungal Infections
The following factors can make you more susceptible to contracting fungal infections:
- Weak immune system (4)
- Medical conditions, including diabetes, cancer, and other diseases that affect blood circulation (5)
- Medications such as cancer drugs and antibiotics
- Hormonal imbalance, such as in hormone therapy or menopause (6)
- Warm, humid climate
- Skin or nail injury
- Close contact with an affected person, animal, soil, or air
- Lack of skin care or poor hygiene
- Use of tight clothes and footwear
- Walking barefoot, especially in damp places
- Sharing personal hygiene items, such as towels and clothes
- Poor ventilation
Complications of Severe Fungal Infections

Fungal infections, especially the invasive types that affect internal organs such as the brain and lungs, that are not treated at the early stages can cause complications, including:
- Fever
- Sinus problem
- Seizures
- Paralysis
- Lung inflammation
- Blood in the sputum
When to See a Doctor
While mild fungal infections can usually be treated with OTC medications, it is vital to consult your doctor if the symptoms do not alleviate after 3–4 days. Make sure to get a proper diagnosis if you have a severe infection accompanied by any of the following symptoms:
- Pain
- Inflammation
- Skin discoloration
- Blisters
- Hair loss
Final Word
Fungal infections are a common occurrence and manifest a range of symptoms, commonly including itching and rash formation. There are various kinds of fungal infections, depending on the causative organism and the area they affect. Regardless, all infections should be treated at the earliest to prevent any complications.
You can use antifungal creams, sprays, ointments, oral medications, and even antifungal cosmetics to help manage the infections. Always observe your condition, and contact your doctor at the earliest if you notice worsening of the symptoms.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


