In this article:
The face has sensitive skin, and it’s important to take care of it.
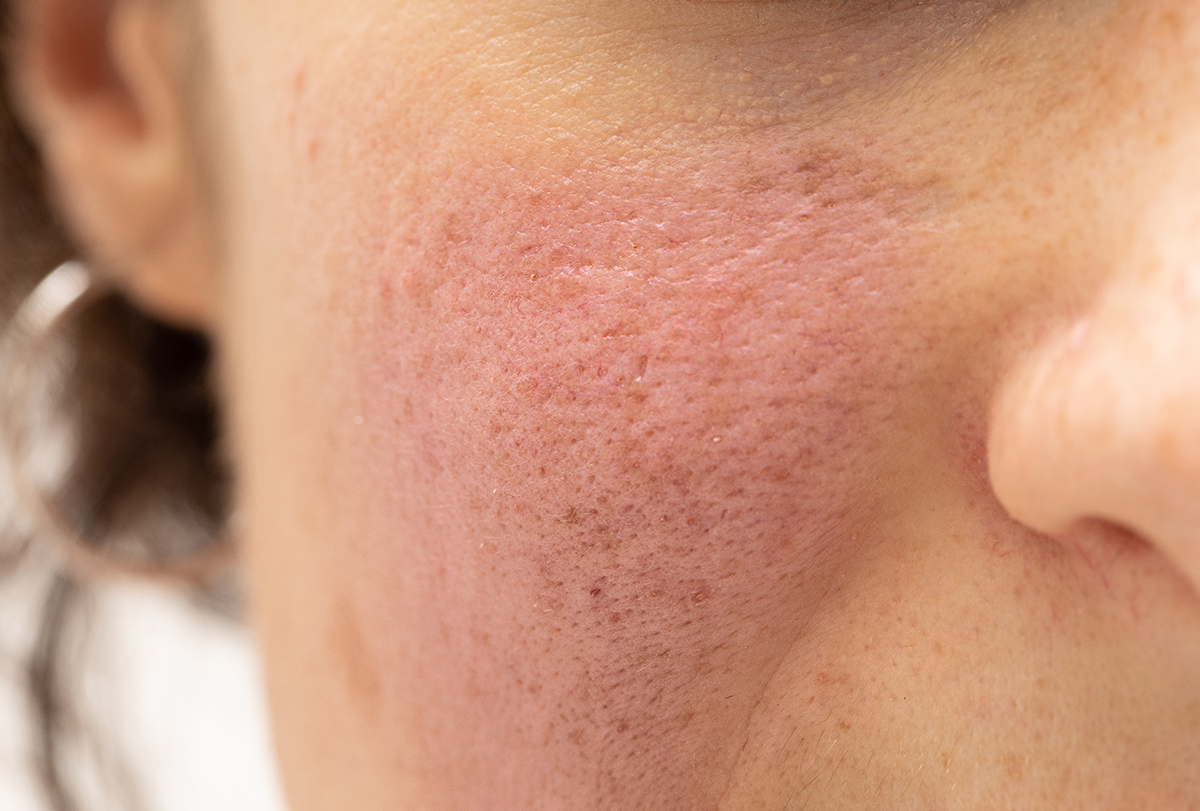
When the skin becomes too cold due to the weather or ice application, the vessels that carry blood in the epidermis (the uppermost layer of skin) are constricted due to a reflex action. This can cause redness on your face or make your acne worse if you have it. (1)
What Causes Redness After Applying Ice
It’s not uncommon to experience redness on the face after applying ice. This is because when you apply ice to your skin, the blood vessels dilate suddenly at the sudden drop in skin temperature.
This dilation occurs because your body tries to normalize your skin temperature. During this sudden dilation, some blood vessels may burst. This causes the area to become red. (1)
If you find that your skin turns red after applying ice, it is important to pay attention to other symptoms that you may be experiencing. If you have any pain, swelling, or blistering in addition to the redness, see your healthcare provider right away as this could be an indication of frostbite or frostnip. (2)
How to Fix Redness on the Face
If you have applied ice to your face and it has caused redness, don’t worry – there are a few things you can do to alleviate the problem.
- First, make sure that you’re not applying the ice directly to your skin. Instead, wrap the ice in a cloth or paper towel before applying it to your face. This will help to prevent direct contact between the ice and your skin.
- Second, try applying the ice for shorter periods. If you find that the redness is still occurring, use a different method of cooling down such as a cold compress. (3)
- Another option is to apply a warm compress to the area for a few minutes before reapplying the ice. You can also massage the area lightly with your fingers. After you apply the warm compress, wash your face with cold water. This will help to soothe the skin and reduce the redness by reducing inflammation. (3)
- Finally, if the redness is still present, apply a topical cream or aloe, honey, or glycerine-based gel designed to reduce redness and inflammation. (4)(5)(6) Be sure to follow the instructions on the packaging carefully, and always test a small area of skin first to ensure that you are not allergic to the product.
- If the redness does not go away after following these steps, you should see a doctor or dermatologist to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
How to Prevent Redness From Applying Ice

Applying ice to your face can cause redness and inflammation. This is because the ice leads to blood vessels bursting at the skin’s surface when the temperature drops suddenly.
To prevent this from happening, you can do a few things:
- Wrap the ice in a cloth before applying it to your skin. This will help in insulation and prevent the ice from coming into direct contact with your skin.
- Hold the ice on your skin for shorter periods. If you keep the ice on your skin for too long, it will cause more redness and inflammation, similar to a cold-induced injury such as frostbite. (2)
- Apply a thin layer of Vaseline or petroleum jelly to your skin before applying the ice. This will create a barrier between your skin and the ice, preventing the ice from causing redness and inflammation. (7)
Why Is Ice Good for Your Face?

Even though ice can cause redness, it’s still a great tool for your skin care routine. Ice can help to reduce inflammation, redness, and swelling. It can also help to diminish the appearance of pores and wrinkles. (8)
When used correctly, ice can be a powerful tool in your skin care arsenal. Just be sure to use it sparingly and never apply it directly to your skin.
Most-Asked Questions
My face still has some redness even after following these remedies. What do I do?
If home remedies have not been effective for you, you may need to consult a dermatologist who can figure out your specific condition and suggest treatments accordingly.
I live in a cold city and my skin turns red every winter. What should I do?
Ensure that your skin is protected and covered with a scarf or any protective clothing when you are stepping out into the cold.
You can use occlusive (thick, barrier-forming) creams such as Vaseline, other forms of petroleum jelly, or other thick creams to protect your skin against the cold wind.
Final Word
Skin redness and irritation after ice application is a common reaction that can occur when the cold temperature of the ice causes the blood vessels in your skin to dilate and burst.
While these reactions are usually not serious, they can be painful and uncomfortable. If you want to avoid them, you can try some of the remedies mentioned above to prevent redness and protect your skin.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


