In this article:
Doctors frequently encounter muscle strain, which is a prevalent type of injury. It is caused by either an excessive stretch or overuse of an active muscle, rather than just muscle contraction alone.

Improper use or overexertion of a muscle can lead to this type of injury. Muscle strain typically results in acute pain and is often noticed during strenuous activities.
The initial treatment for this injury involves rest, ice, compression, and the use of NSAIDs. Once the pain has subsided, physical therapy can be utilized to restore muscle flexibility and strength. (1)(2)
Let’s learn a bit more about muscle strain… What are the symptoms? How to diagnose? And most importantly when to see a doctor?
Symptoms of Muscle Strain
The manifestations of muscle strain may consist of redness, swelling, bruising at the injury site, weakness of the muscle, pain at rest, and inability to use the affected muscle. (3)
What Muscles Are More Prone to Strain?
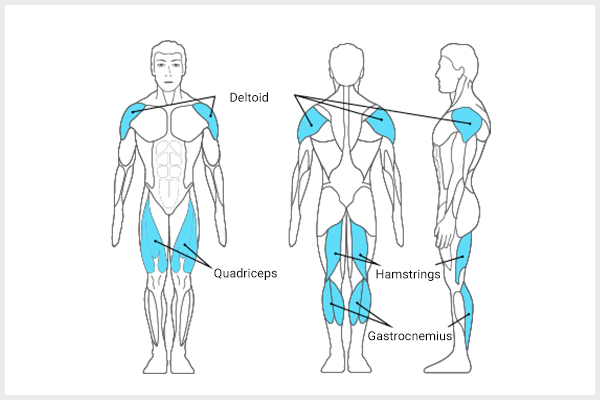
Research suggests that certain muscles are more likely to get injured because they have a lower threshold for strain when compared to other muscles. This is because these muscles either span across multiple joints or have a complex structure.
As a result, these muscles are more gullible to straining or injury. Some of the commonly injured muscles, as per experts, are: (1)(3)
- The muscles at the back of your thigh (hamstrings)
- The big muscles at the front-end of your thigh (quadriceps) (4)
- The muscles in your calf (gastrocnemius)
- The muscles around your shoulder (deltoid)
What Are the Various Kinds of Muscle Strains?
The clinical grading system for muscle strains classifies strains as: (5)
- Grade 1: This is the mildest type of strain, where there is only a small tear in the muscle fibers. There is little or no loss of strength and the pain is mild to moderate. There is no visible damage to the muscle when examined.
- Grade 2: This is a more serious strain, where there is a significant tear in the muscle fibers. There is intermediate to intense pain and loss of strength. When examined, there may be visible damage to the muscle tissue.
- Grade 3: This is the most brutal kind of strain, where the muscle fibers are completely torn. There is severe pain and total loss of strength. There may be a visible defect in the muscle tissue when examined.
Treatment of Muscle Strains

In simple terms, the first step in treating a muscle injury is to protect the injured area, rest it, and use ice therapy to reduce any swelling. Pain-relieving medicines like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs can be used.
Later, the treatment may involve ultrasound therapy to promote healing, exercises to strengthen and stretch the affected muscles, and range of motion exercises to regain mobility.
Surgery is only considered in specific cases where there is a hematoma (collection of blood) that needs to be drained, or when the muscle or tendon needs to be reattached and strengthened. (6)
What Are the Risk Factors for Muscle Strain?
There are several things that can make you more likely to get muscle strain, including:
- Having tight muscles, which can be more easily strained. Athletes should do stretching exercises regularly to keep their muscles flexible.
- Having muscle imbalances, where one muscle is stronger than the other. This can lead to the weaker muscle getting strained.
- Being in poor physical condition, which makes your muscles weaker and less able to handle the stress of exercise.
- Having muscle fatigue, which means your muscles are tired and can’t absorb as much energy. This causes them to be more likely to get harmed. (4)
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical attention if you have a muscle strain and experience severe pain that is not relieved by home remedies. Also, you should see a doctor if you heard a popping sound when the injury occurred, have substantial swelling, bruising, or can’t walk after 24 hours, as per experts.
In addition, experts suggest that medical attention is necessary if you have a muscle strain with localized abdominal tenderness, fever, weight loss, numbness, or urinary problems.
For mild muscle strains, self-treatment and precautionary measures are often enough. But you must pursue medical assistance if
- The pain doesn’t settle even after a week.
- The injured area gets very numb.
- Blood loss at the site of injury.
- You are not able to walk.
- Inability to change positions or move the muscles.
Final Word
Muscle injuries are very common, particularly in sports like soccer, cricket, and football. Based on the type of damage, you may need medical treatment or home remedies to lessen any pain and swelling.
However, the best approach is to take preventive steps to bypass getting muscle strain in the foremost place.
While we cannot always prevent muscle strains, we can control factors such as not warming up before exercise or exercising with tired muscles. It is significant to contemplate these factors before beginning any physical activity.
 Continue Reading4 Home Remedies to Relieve Muscle Strain
Continue Reading4 Home Remedies to Relieve Muscle Strain
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


