In this article:
Muscle injuries have been seen to be the most common injuries in sports persons. Muscle strains make up roughly 55% of all sports damages. But don’t think that you can’t get them if you don’t play sports as they’re not only booked for soccer or football players.
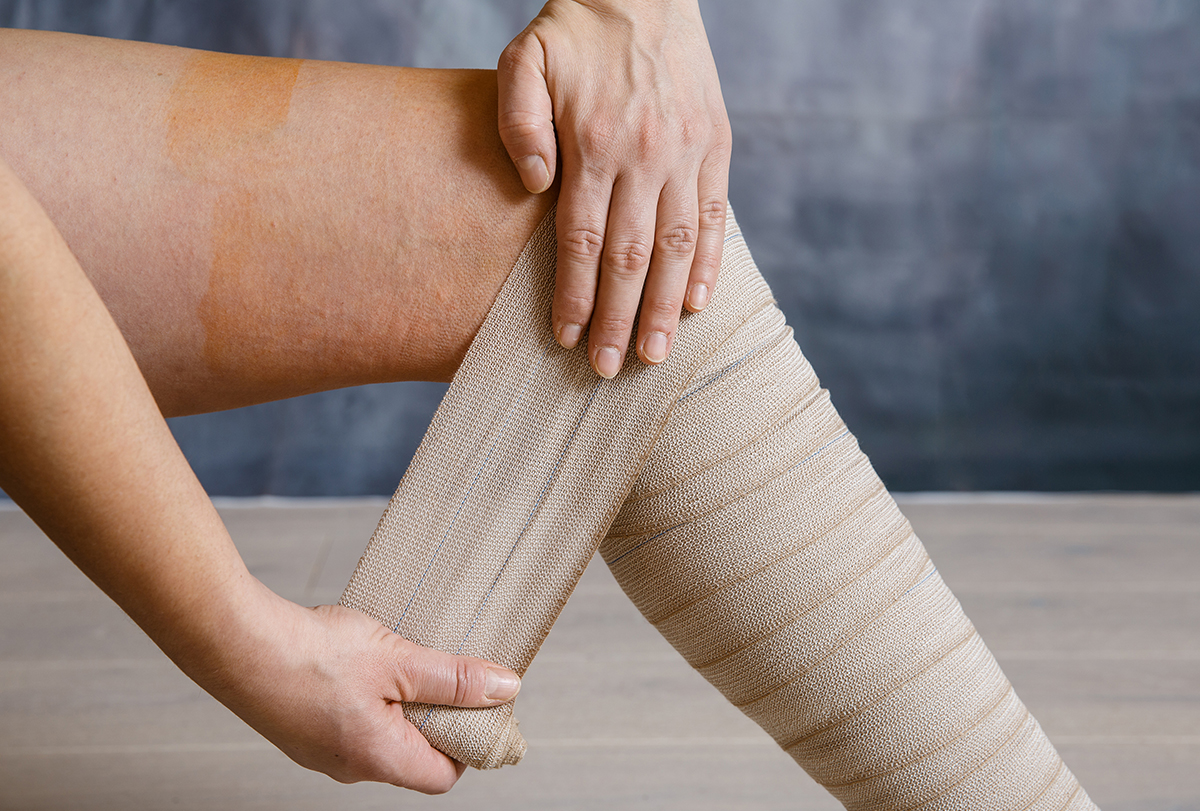

Non-athletes can also suffer from muscle strains for various reasons. A muscle strain occurs when the muscle gets overstretched or if it’s forcefully contracted
Muscle strains can be painful and full of discomfort, but this doesn’t mean that you’ll always have to run to the emergency room because, if they’re not very severe, you can manage them at home with many remedies. (1)
Here are some at-home treatments for muscle strains:
Home Remedies for Muscle Strain
Here are some at-home remedies that can help soothe mild to moderate cases of muscle strain.
1. PRICE therapy for 2–3 days
Muscle injuries like mild sprains and strains can usually be managed at home using PRICE therapy for the initial 2–3 days following the injury. (2)
PRICE means:
- Protection
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
Protection and rest

It is of supreme significance to safeguard the affected area from added damage. You can protect your muscles by getting proper rest. Letting the muscle rest discourages the worsening of the initial injury. Rest means avoiding any exercise and reducing your day-to-day physical action.
Additionally, you can invest in crutches or a walking stick to help you if you are not allowed to put weight on your ankle or knee if the muscle strain is suffered by your leg. Similarly, a sling may be of assistance if you’ve hurt your shoulder.
It is advised that the injured limb should be immobilized because both prohibiting activity and practicing immobilization should prevent hampering the healing of the injury. This safeguards the affected muscle from further retraction. (3)(4)(5)
Ice
Generally, cryotherapy is used for soft tissue sports injuries by applying an ice-soaked sponge or an ice pack covered by a towel to the affected area.
The application of ice causes vasoconstriction (constriction of blood vessels) and decreases the local blood flow by roughly 50% after 10 min. This causes a lessening of swelling and bleeding.
The use of cryotherapy has also been established to reduce inflammatory responses. Another effect of ice application is the decrease in pain by improving the pain threshold levels in the free nerve endings.
Ice spray can also be used, especially for pain relief. Normally, direct contact between the ice and skin should be prevented to discourage blistering or necrosis of the skin.
Cryotherapy, followed by compression, should be used for 15–20 min at a time with a 30–60 min gap between consecutive applications. (3)(5)(6)
Compression
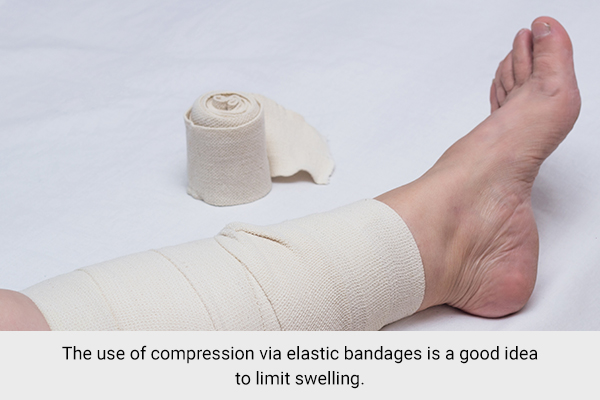
The use of compression via elastic bandages is a good idea to limit swelling. Although, the trick here is to use the compression devices correctly because when used properly, compression can be viewed as the most effective technique in the initial stages of managing structural injuries by promoting haemostasis and decreasing intramuscular bleeding.
The choice of compression load should be increased as high as possible to target the blood vessels accountable for apparent bleeding. Elastic compression bandages are often available in different styles to adjust to the size and the area of injury.
The compression load can be decreased after 20–30 min. You must jot down that constant, intermediate compression should be used to promote the decrease of further swelling. (3)
Elevation
Keep a note that you should keep the affected body area elevated. This may help lessen any swelling. It can also be beneficial in restricting bleeding and the accumulation of interstitial fluid. (3)
ALSO READ: RICE Treatment: Benefits, Steps, and Side Effects
2. Active management via exercise after 3–5 days of injury
The PRICE remedy for the initial stages of injury management is thereafter followed by an active phase of management when the affected leg is healing well.
This stage normally starts roughly 3–5 days after the initial injury depending on its seriousness. Stretching, strengthening, range of motion exercises, and aerobic fitness are the main elements of this phase.
Stretching exercises

Stretching is important for treating muscle tightness which causes a reduced range of movement. Stretching exercises should be performed with utmost care to the point of discomfort, but not pain.
Numerous methods can be used including static, and dynamic stretching. Typically, ballistic stretching is not advised due to the danger of re-tearing of the muscle fiber. (5)(7)
- Static stretching: The conventional and most familiar type is static stretching, where a particular position is held for 20–45 seconds with the affected muscle as far as it can go without feeling any pain to a point of a stretching sensation. The same is confirmed by the Hospital for Special Surgery.
- Dynamic stretching: Active stretching commonly refers to moving a limb through its complete range of motion and repeating the same several times.
Note: A diligent warm-up should invariably come before any type of rehabilitation exercise. Speak with a healthcare advisor or professional about the type of exercise suitable for your injury before performing any.
3. Epsom salt soak for the injured body part
The foremost use of magnesium in medicine can be tracked all the way back to the 17th century. Epsom salt, the primary component of magnesium sulfate, was taken advantage of to deal with ailments like muscle strains.
Even in modern medicine, magnesium is very much employed for preventing and looking after or managing pain. (8)
Here’s how you can use Epsom salt for muscle strain management:
- Add 2 cups of Epsom salt to warm water.
- Soak the injured body in the water for 30 minutes.
- Dry the region with a clean fabric and wrap it with an elastic bandage.
- Do this one time every day for some weeks.
4. Deep massage with olive oil
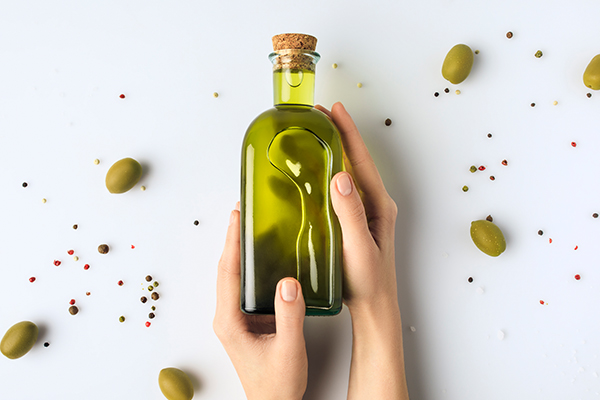

The ancient Greeks acknowledged the benefits of massaging the body with olive oil.
Research to analyze and verify the beneficial effects of a massage with olive oil to prevent and treat sports injuries concluded that the practice of massage, concurrently with olive oil rub may help reduce muscle fatigue and lower the chances of sports injuries in athletes. (9)
Here’s how you can use olive oil:
- Take 1–2 tablespoons of olive oil and apply the oil over the affected area.
- Nicely massage the area for some time.
- Do this 2–3 times every day for a few days.
How to Prevent Muscle Strains?
To prevent muscle strain, you can take the following precautions:
- Exercise regularly: Talk to your doctor to develop an exercise program that is right for your age and activity level.
- Warm-up schedule: Before physical activity or sports, make sure to warm up. This helps get your blood circulating well, increases your muscle temperature, and improves your breathing rate.
- Cool down: After exercising, take the time to cool down. Stretch unhurriedly and slowly, keeping up each stretch to provide the muscle with time to react and lengthen. Ask your doctor or coach for help developing a routine.
- Let your muscle get better: If you get injured, take a moment to let the muscle feel healthier before returning to sports. Recovery time can range from 1–3 weeks for a mild strain, and around 24 weeks for an intense strain like a hamstring strain. (10)
- Best not consuming stimulants (eg, caffeine, ephedrine, pseudoephedrine) unless prescribed by doctors for a specific time.
- Drink a lot of fluids (especially liquids that have potassium) after working out, unless contradicted by a doctor.
Taking Care of Muscle Strains if You’re an Athlete

As per experts, people who enjoy sports should carefully consider the intensity, volume, frequency, and progressive overload of their exercise routines. The appropriate balance of these factors depends on an individual’s physical capacity and limitations.
For example, if intensity increases, it may be necessary to decrease volume and frequency, while increasing volume may require decreasing intensity. It’s possible to increase all three factors at once, but only to a certain extent because everyone has a limit to the amount of strain they can handle.
The aim is to determine the right amount of exercise that provides the best results based on the patient’s goals. Typically, experts explain that exercise routines should cover four main areas known as the 4 core components:
- Stretching and improving flexibility
- Building strength
- Enhancing balance
- Boosting aerobic capacity
Most-Asked Questions About Muscle Strain
When can I start playing sports following a muscle strain?

Orthopedics recommends that return to sports or full activity is generally permitted when the patient is pain-free, has a complete range of motion, and has regained full strength.
If an athlete attempts to come back to their full activity before these benchmarks are reached, there is an elevated possibility of hurting the muscle again.
Are muscle sprains and strains the same?
No, muscle sprains and strains are not the same thing. Sprains and strains are 2 varieties of injuries, but they involve different parts of the body.
A sprain is damage to a ligament, which is the tissue that attaches two bones at a joint. Ligaments help to stabilize and support joints, such as those in the knee or ankle.
A strain is induced by overstretching or even tearing of a ligament, which can happen from a tumble, twist, or smash to the body.
Furthermore, strains damage muscles and tendons. Muscles are the tissues responsible for movement, while tendons are lines of tissue that attach muscles and bones.
Acute strains occur when a muscle or tendon is stretched or pulled suddenly, often from a quick, forceful movement. (11)
Does stretching help with or causes muscle strains?
As per experts, stretching can actually help attend to muscle strains by increasing the flexibility and span of motion of your muscles. When muscles are better at flexibility, they are less probably going to get strained or injured during physical activities.
However, stretching incorrectly or overstretching can also lead to muscle strains, especially if the muscle is already weak or fatigued, experts explain.
What are the complications of muscle strains?
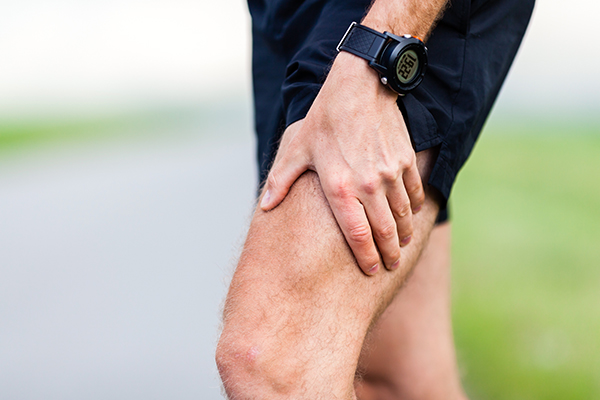

Muscle strains may cause muscular rupture, which may lead to oedema or haematoma within the muscle. (12)
Do I need muscle strain surgery?
It’s uncommon to require surgery for a muscle strain. But if you have experienced a serious strain (Grade 3), you might require surgery to restore the torn muscle. Your doctor will tell you the best about what surgery you’ll need.
What can I anticipate in terms of healing if I suffer from a muscle strain?
You should be able to bring in a complete comeback from a muscle strain. You should recover your strength and the ability to move your muscle after it gets better.
Can I go to work if I’ve muscle strain?
If you can do your work and not place pressure on your affected muscles you shouldn’t have to stop work. It’s better to take advice from your healthcare provider about which kind of work you should avoid while you’re healing.
Final Word
While uncomfortable, muscle injuries are usually manageable. In case of minor strains, home remedies for the management of injuries will aid in relieving your pain and swelling in a few days. But if your pain is intolerable, seek medical attention.
 Continue ReadingMuscle Strain: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and More
Continue ReadingMuscle Strain: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and More
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


