In this article:
A sore tongue refers to a condition where the tongue feels painful, tender, or uncomfortable. It can be characterized by various symptoms such as a burning sensation, tenderness, redness, and swelling on the surface of the tongue. The discomfort can make it difficult to eat, drink, or speak comfortably. (1)(2)
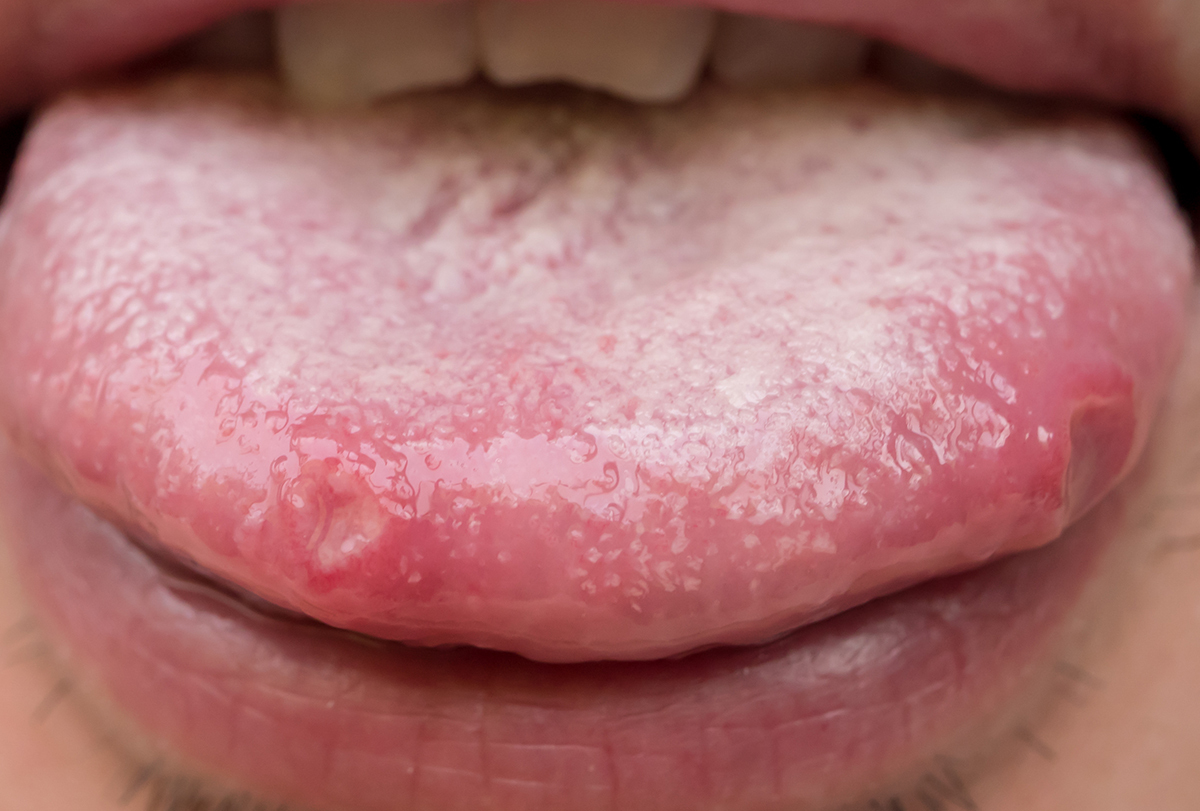
The cause of a sore tongue can be pretty obvious and easy to see, such as when you accidentally bite your tongue while talking or eating.
But sometimes, there are less obvious causes of a sore tongue that might need some treatment. If you have continuous pain/discomfort and you haven’t bitten your tongue by accident or burnt your tongue with hot food, it’s a good idea to see your GP (doctor) or dentist. (3)
A sore or painful tongue could be a sign of an underlying problem that needs attention. Your dentist can figure out what’s going on and give you advice on how to relieve the pain. In some cases, your GP might also be able to help. (1)
Causes of a Sore Tongue
A sore tongue can be due to the following factors and conditions.
1. Glossitis
Glossitis is the inflammation of the tongue, causing it to swell, change color, and have different appearances on its surface. It can happen due to various reasons including allergies, infections, injuries, irritants, immune system disorders, vitamin deficiencies, and other conditions. (3)(4)
There are different types of glossitis: (4)
- Atrophic glossitis: Your tongue becomes smooth and glossy due to the loss of the tiny bumps on its surface.
- Median rhomboid glossitis: You have a patch in the middle of your tongue that lacks those tiny bumps, often caused by an oral infection.
- Geographic tongue: Your tongue has patchy areas where the bumps are missing, giving it a map-like appearance that can change.
- Geometric glossitis: Your tongue has a deep groove down the middle with branches, commonly seen in people with weakened immune systems.
- Strawberry tongue: Your tongue’s bumps become overgrown, making it look bumpy like a strawberry. This is usually associated with bacterial infections.
2. Oral thrush
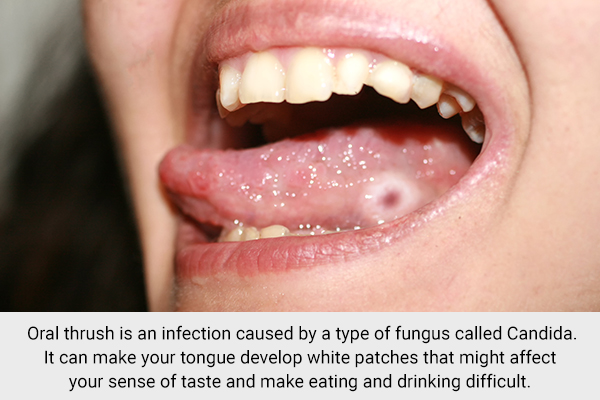
Oral thrush is an infection caused by a type of fungus called Candida. It can make your tongue develop white patches that might affect your sense of taste and make eating and drinking difficult.
Sometimes a red, smooth patch or lump can appear in the middle of your tongue. (1)(2)(5)
3. Medication uses
You’re more likely to get oral thrush if you have recently taken antibiotics, use inhaled corticosteroids for asthma, wear ill-fitting dentures, have poor oral hygiene, have certain medical conditions, or have a weakened immune system.
A sore tongue can be a side effect of NSAIDs or beta-blockers, and certain mouthwashes can also cause a sore and painful tongue in some people. (1)(2)
4. Aphthous mouth ulcers
Aphthous mouth ulcers are painful sores that can show up anywhere in your mouth, including the underside of your tongue. Sometimes, they are caused by accidentally biting your tongue or eating something hard and sharp. (6)
Stress, anxiety, certain foods, hormonal changes, and quitting smoking can also contribute to recurring ulcers.
Most mouth ulcers heal within a week or two without treatment, but you can manage the pain with over-the-counter painkillers and avoidance of eating spicy foods. (1)(2)
If you have a mouth ulcer that doesn’t improve within a few weeks or regularly recurs, it’s a good idea to see your dentist or GP.
5. Other less commonly seen causes
Occasionally, tongue pain can be caused by other factors such as: (1)(7)
- Viral infections such as hand, foot, and mouth disease, herpes zoster, and cold sores
- Candida albicans infection and bacterial infections
- Deficiencies in vitamins or iron – Riboflavin deficiency usually occurs with other B vitamin deficiencies. Symptoms and signs include sore throat, lesions in the lips and mucosa of the mouth, glossitis, conjunctivitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and normochromic normocytic anemia. Diagnosis is usually clinical.
- Conditions such as burning mouth syndrome
- Inflammation of the tongue (Moeller’s glossitis)
- Tongue cancer
- Lichen planus
- Trauma
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy
- Poor dental hygiene and ill-fitting dentures, especially in the elderly
- Diabetes
Note: If you have an ulcer, swelling, or other symptoms that persist for more than 3 weeks, especially if you are a heavy smoker or drinker, it’s essential to see your GP for further evaluation. (1)
Symptoms of a Sore Tongue
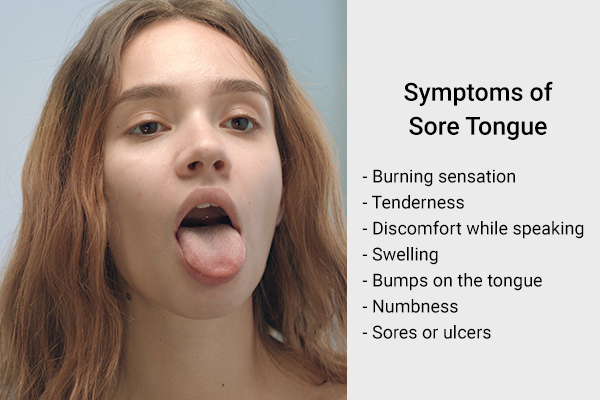
The symptoms associated with a sore tongue include: (8)
- Burning sensation
- Tenderness
- Discomfort while speaking
- Swelling
- Bumps on the tongue
- Numbness
- Sores or ulcers
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, see a doctor who can help figure out what’s causing the problem and recommend the best treatment for you. (7)
Treatment for a Sore Tongue
When it comes to treating a sore tongue, professionals say that there is no very specific solution, but they can certainly assist in managing the underlying reasons and stave off additional harm.
The medical interventions include:

- Antibiotics
- Antifungals
- Mouthwashes
- Steroidal drugs
- Nutritional supplementation
- Salivation-promoting medicines
- Analgesics (painkillers)
Testing and Diagnosing a Sore Tongue
When you visit a doctor or dentist for a sore tongue, they will ask you about your symptoms and examine your tongue closely. Sometimes, they might need to use special imaging techniques such as MRI, CT, or PET scans to get a better look. By gathering all this information, they can make a diagnosis. (8)
If there isn’t one clear sign or symptom that points to a specific problem, the doctor or dentist will consider different possibilities. This is called a “differential diagnosis.”
They make a list of all the potential causes for the signs they see on your tongue. It’s like weighing the chances of different diseases or conditions that could explain what’s happening.
For example, if you have a white patch on your tongue, the differential diagnosis might include conditions such as lichen planus, leukoplakia, or inflammation from dentures.
In some cases, when there’s a concern about cancer, a special dye called toluidine blue is used during the initial evaluation. This dye helps identify precancerous or cancerous lesions early on, which is important for prompt treatment. (7)
Final Word
A sore tongue can be caused by various factors such as infections, inflammation, trauma, and even cancer. If you experience symptoms such as pain, discomfort, or changes in the appearance of your tongue, it’s important to consult a doctor or dentist for the proper diagnosis and treatment.
While some cases can be managed with home remedies and lifestyle changes, others may require medical interventions.
 Continue Reading10 Home Remedies for Sore Tongue and Diet Tips
Continue Reading10 Home Remedies for Sore Tongue and Diet Tips
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


