In this article:
You have probably been living under a rock if you are not familiar with the delectable, natural sweetness of honey. This “nectar of the Gods” has been around since time immemorial, going as far back as the ancient Egyptians, and has been used for its rich taste and potent therapeutic value all through the ages.

In fact, such are the wondrous merits of honey that it has even been used as currency by a number of ancient civilizations. Thus, history is proof enough that honey is well worth its weight in gold.
The historical acclaim and multifarious uses of this viscous tonic continue still, with honey often figuring among the top-rated health foods available today. With the world churning out approximately 1.20 million tons of honey annually, one can get some semblance of its mammoth popularity at the global stage. (1)
Nutritional Value of Honey
If you think it’s just the simple sugars that account for honey’s nutritional goodness, you are in for a surprise.
It’s not for nothing that honey has earned the reputation for a natural healing agent and energy booster, with both ancient sages and current scientists tilting in its favor. A glance at its nutritional composition will make you a believer as well.
One cup of honey (339 g) contains: (2)
| Nutrient | Quantity | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Water | g | 97 |
| Calories | kcal | 1031 |
| Protein | g | 2 |
| Cholesterol | g | 0 |
| Carbohydrate | g | 34 |
| Total dietary fiber | g | 7 |
| Total sugars | g | 39 |
It also contains some vitamins and minerals:
| Vitamin/Mineral | Quantity | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | mg | 20 |
| Iron | mg | 42 |
| Phosphorus (P) | mg | 14 |
| Potassium (K) | mg | 176 |
| Sodium (Na) | mg | 14 |
| Zinc (Zn) | mg | 75 |
| Copper (Cu) | mg | 122 |
| Selenium (Se) | mcg | 2 |
| Vitamin C | mg | 7 |
| Riboflavin | mg | 129 |
| Vitamin B6 | mg | 81 |
| Folate | mcg | 7 |
Plus, honey has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, and healing properties. (3) Due to its powerful antiseptic, antibacterial, and healing properties, honey is used as medicine to treat many common health problems.
Health-Boosting Benefits of Honey
Here are some amazing health benefits of honey.
1. Boosts energy
Honey can spike up your energy levels in a jiffy, all thanks to its inherent natural sugar content comprising fructose and glucose, which directly enter the bloodstream.
Unlike refined sugars and artificial sweeteners, honey offers just the right number of calories for sustained energy with additional nutritional benefits, making it a widely preferred sweetening substitute for health-conscious people the world over.
This natural sweetener works as a healthy and consistent source of energy for the body, which helps maintain optimal glycogen level and satisfy the body’s innate craving for something sweet. Moreover, it’s the ideal pick-me-up snack before you dive into your daily workout routine.
While you may be tempted to gorge on honey mindlessly to indulge your sweet tooth, it’s best you exercise restraint and keep the honey intake within reason. This is primarily because 1 tablespoon of honey contains 64 calories and 17 g of sugar, and excessive intake can be a setback for your health goals. (2)
2. Reduces muscle fatigue

Athletes often suffer from muscle fatigue, which can impact their performance level. This problem can be solved easily with honey.
Honey may boost athletes’ performance and endurance levels and reduce muscle fatigue and soreness. (4)(5) This is due to the perfect combination of glucose and fructose in honey.
Glucose is absorbed instantly by the body and provides immediate energy, whereas fructose is absorbed more slowly, providing sustained energy to the body.
3. Provides antioxidants
Premium-quality honey is well endowed with a number of important antioxidants, including organic acids and phenolic compounds such as flavonoids.
This is further corroborated by a published study that found that people who consumed honey had higher levels of antioxidants in their blood. (6) This is especially true when compared with those who consumed other sweeteners, such as corn syrup, which provide no nutritional value.
These antioxidants yield the power to combat cellular damage caused by harmful free radicals, which lies at the base of a number of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer as well as premature aging.
Moreover, the antioxidants in honey have also shown some success in moderately reducing elevated blood pressure levels in both animal and human subjects.
In order to maximize this benefit of honey, choose darker-colored varieties, such as buckwheat honey, as they have been found to contain a higher number of antioxidants than the lighter-colored ones. (7)
4. Treats coughs

Several studies have found honey to be more effective in treating or suppressing cough symptoms than some conventional over-the-counter cough medicines. (8)
Honey has antibacterial properties that help soothe a sore throat and kill the bacteria that cause the infection. (9) What makes it even more appealing as a cough suppressant is that it comes without the added side effects of traditional drugs used to treat upper respiratory infections.
How to use:
- To get quick relief from coughing, mix 1 tablespoon of honey with some freshly squeezed lemon juice and drink this solution at regular intervals.
- You can also mix honey, lemon juice, and a pinch of salt in a glass of lukewarm water and use this solution to gargle.
- For cough treatment, it is recommended to use buckwheat honey over other types of honey.
Note: While honey might be an excellent natural alternative to cough medicine for your young ones, it should not be administered to children below the age of 1 as it can lead to botulism.
5. Heals wounds and cuts
The natural antiseptic, antibacterial, and antimicrobial properties of honey have made it a trusted healing agent, with its use dating back to the ancient Egyptians.
Wounds, sores, and cuts are often susceptible to infection by various strains of bacteria, such as Clostridium difficile, MRSA, and Ureaplasma urealyticum, some of which are even resistant to conventional antibiotics.
Certain varieties of honey, such as manuka honey, have been found to inhibit these pathogens and nourish the surrounding tissue. Thus, honey is a prized natural antiseptic that can keep wounds and cuts clean and free from infection, reduce odor and pus, lessen the pain, and promote speedy healing. (10)(11)
Honey has proven its mettle as a wound dressing, especially in the case of diabetic foot ulcers and other skin conditions, including psoriasis and herpes lesions. It also serves as a nifty alternative option for those who are allergic to topical antibiotics.
How to use:
- After gently cleaning the wound or cut with lukewarm water and mild soap, apply a layer of honey on the affected area and cover the area fully with a bandage.
- Change the bandage every 24 hours.
6. Heals minor burns
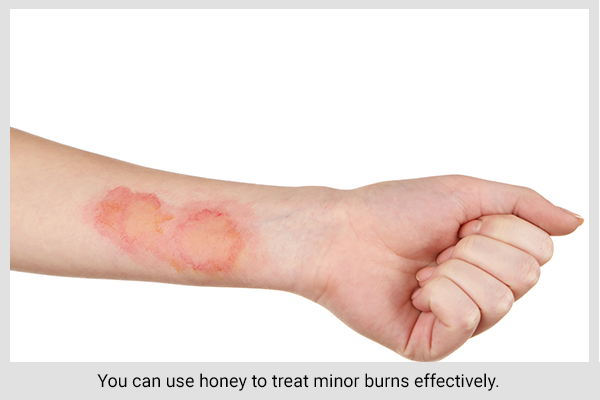
You can also use honey to treat minor burns effectively. Its antibacterial and antifungal properties can prevent bacterial growth and subsequent infection. (12)
How to use:
- If you have a minor burn, simply apply raw honey to the affected area.
- Within some time, you may feel relief from the burning and itching sensation and pain.
- You must continually apply honey on the burn site several times a day for a number of days in order to promote fast healing.
7. Beats insomnia
Honey can work as a natural aid in promoting sound and timely sleep patterns. Honey is a fast-digesting carbohydrate that stimulates the release of insulin.
This steady increase in insulin levels allows tryptophan, an amino acid present in honey, to enter the brain easily. Thereafter, the tryptophan is converted into serotonin and eventually to melatonin, which is the hormone responsible for inducing sleep and regulating sleep and wake cycles. (13)(14)
Simply have a glass of warm milk with honey before going to bed. Both honey and milk are tryptophan-containing foods that can significantly improve the length and quality of your sleep.
8. Promotes healthy skin

Owing to its potent antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties, honey is the ultimate skin-enhancing ingredient that deserves a permanent place in your beauty diet and regimen. (15)(16) This natural humectant helps restore and retain moisture and is, therefore, a savior for dry and parched skin.
Additionally, the antioxidants help mitigate oxidative stress caused by free radicals, thereby delaying signs of skin aging such as wrinkles and fine lines. It has also been found useful for unclogging pores and correcting uneven skin tone.
- For rosacea, apply a little bit of honey directly on the affected area before going to bed. This will give the skin all night to absorb the honey’s medicinal properties. (17)
- Wash it off the next morning with lukewarm water. Follow this simple remedy for several days and soon you will have clear and glowing skin.
9. Provides relief from seasonal allergies
Many people suffer from seasonal allergies, which lead to unpleasant coughing and sneezing.
A study published in 2013 found that consuming honey helped prevent unwanted symptoms of seasonal allergies. (18) The logic behind this is that honey introduces trace amounts of plant pollens into your system. When the body is exposed to these allergens in minimal quantities, an immune response is triggered, causing the body to form antibodies to the pollen.
Repeated exposure to the pollen over time leads to the buildup of such antibodies in the body, making it gradually accustomed to their presence so that less histamine is released, resulting in a diminished allergic response.
For this reason, proponents recommend choosing locally sourced honey for the most benefits.
10. Fights oral bacteria

Table sugar is a well-known cause for dental cavities. However, due to its antibacterial properties, honey can be used as an alternative sweetener that carries less risk of causing unwanted tooth decay.
Several studies have found that using honey in place of regular sugar (sucrose) and even fruit juice can reduce the risk of cavities.
Additional studies have also found that honey may protect against gingivitis and unwanted buildup of dental plaque. (19)(20) Honey helps ward off oral bacteria by releasing hydrogen peroxide, which works as an antimicrobial to inhibit their growth.
To help reduce your risk of cavities, simply swap regular table sugar for a small amount of honey in your favorite recipes.
11. Improves digestion
Honey is an effective antimicrobial agent that benefits the entire digestive tract. The enzyme (glucose oxidase) present in honey produces small amounts of hydrogen peroxide that can fight gastritis. (21)
Consuming honey in place of processed sugar has also been found to improve the quality of gut bacteria. (22) The cultivation of healthy gut bacteria can, in turn, help reduce bloating and neutralize gas commonly resulting from overeating. A small serving of honey before heavy meals may help to improve the digestion process.
With all these health benefits from honey, it’s a good item to include in your diet plan. Remember to be mindful of its calorie and sugar content – even this beneficial sweetener should only be consumed in moderation.
Precautions to Consider

- Oral consumption of honey is not recommended for infants and very young children. Intake of raw honey, in particular, can lead to botulism poisoning in children under 12 months of age.
- People with pollen allergies should avoid honey, as it might contain traces of pollen and trigger a reaction.
- All things considered, honey is still a sugar variant and, therefore, can only be healthy when consumed in moderation. The recommended dosage to optimize the health benefits of honey is a little over 2 tablespoons a day for women and 3 tablespoons a day for men.
How Is Honey Made?
While humans can’t get enough of this natural sweetener, the credit for it lies somewhere else. Honey is often touted as nature’s gift to mankind, but it’s the honeybees that put in all the grunt work to produce and deliver that gift to us.
The honey-making process entails that the worker bees swallow, digest, and regurgitate the nectar they gather from various flowers. They then transfer the honey to the honeycomb until it’s completely saturated with the liquid.
Thereafter, the arduous worker bees buzz around the comb to dry and thicken the liquid until their labor pays off and the fully finished, dense, and sticky honey as we know it comes to be. At the outset, this might seem like a fairly simple task but one that requires acute precision that only honeybees are capable of.
What makes honey even more of a treasure is the fact that it takes eight bees their entire lifetime to manufacture just a single teaspoon of pure organic honey.
Honey’s Peculiar Nature

The most important determinant of good-quality honey is its color with the clear golden-amber varieties often fetching a higher retail price than the darker ones. Moreover, there is no uniformity in flavor, and the taste varies depending upon the flower from which the nectar was derived.
It’s not hard to come across both raw and pasteurized forms of honey in the market, with the two differing purely in terms of filtration. While the former is extracted from the hive and bottled directly, the latter goes through a pasteurization process that involves heating and removal of impurities.
Raw honey tends to contain trace amounts of yeast, wax, and pollen and has an extended shelf life compared with the commonly used pasteurized honey. Furthermore, it has been found to be effective against seasonal allergies, due to repeated exposure to pollen in the area.
What makes honey especially compelling to fitness enthusiasts is its efficacy as an energy food. Unlike regular sugar, which is nothing but empty calories, honey is made up of simple sugars, including fructose, maltose, glucose, and sucrose, that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream without digestion.
No prizes for guessing then that honey works exceedingly well as a healthier sugar alternative, which not only goes well with nearly all foods but also mixes well as a sweetener in hot and cold drinks.
Besides, the moisture-absorbing quality of honey works to keep bread, cakes, cookies, and candies from turning stale quickly. (23) If these weren’t enough, this sweet-tasting boon can also be used to add browning and excess moisture to a dish.
Expert Answers (Q&A)
Answered by Mr. Jonathan Valdez (RDN)

Certain studies have shown that honey can improve gut microbial balance, which would end up relieving digestive problems as the more microflora you have, the better your GI tract is going to function.
If you have to watch your carbohydrate and caloric intake, consider eating other foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains that contain other nutrients besides calories and carbohydrates to maintain or improve the microflora environment.
Most studies have shown that raw honey provides more health benefits, nutrients, and enzymes than pasteurized honey. Pasteurized honey can be heavily processed and overly filtered, destroying those good nutrients and enzymes.
Raw honey is safe for most adults. However, it can contain spores of the bacteria Clostridium botulinum which are dangerous for pregnant mothers and infants. Consider the ingredients in honey before consuming it.
Over-consumption of honey can lead to blood sugar issues in individuals as well as unwanted weight gain as it is a calorie-dense food that is high in sugar. A single tablespoon contains 64 calories and 17 grams of carbohydrates. There are traces of potassium, zinc, and iron, but the amounts are less than 1% of the Reference Dietary Intake.
There is no definitive evidence that suggests the best time to consume honey.
Final Word
Honey can be incorporated into one’s daily diet by adding it to your tea, coffee, drizzling it on your morning toast, or pretty much whatever way you prefer to enjoy your honey. Not to take away from the nourishing potential of honey, but honey alone cannot be expected to fix all your health troubles.
The best way to reap its benefits is to incorporate it as part of a balanced and wholesome diet. There are no one-trick wonders or shortcuts to perfect health, but a diversified diet that takes the best from a variety of food options instead of concentrating on individual foods is the best way to get you started.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


