In this article:
Different people have different problem areas when it comes to fat accumulation. Some people are prone to gaining weight around the belly, some on their hips and thighs. Certain hormones determine where your body will store its fat reserves, and this in turn determines your body type.

Each body type responds in its own way to different foods and has its own nutritional demands. Certain foods that may suit one body type may prove quite unhealthy for others.
So, your body type must be taken into account when planning a healthy diet for proper weight management.
What Is Body Type?
Body type is the individual physical makeup that determines how you metabolize food, what foods help you feel great and make you feel bad, and what training or eating methods work best for your type.
Characteristics and Nutritional Needs of Different Body Types
There are 3 main body types: apple shape, pear shape, and hourglass shape.
a. Apple-shaped body
In an apple-shaped body, most of the mass is in the midsection above the waist.
Apple-shaped individuals often have larger amounts of visceral fat. Visceral fat accumulates around the organs deep beneath the skin. Apple-shaped individuals also often struggle with their weight and may have a harder time keeping weight off.
Dietary recommendations for apple-shaped body
Apple-shaped bodies often have trouble with refined carbohydrates.
What are refined carbohydrates? These are carbohydrates that have been broken down and processed to make them more shelf-stable. Some examples are white bread, white pasta, and pastries.
What to eat:
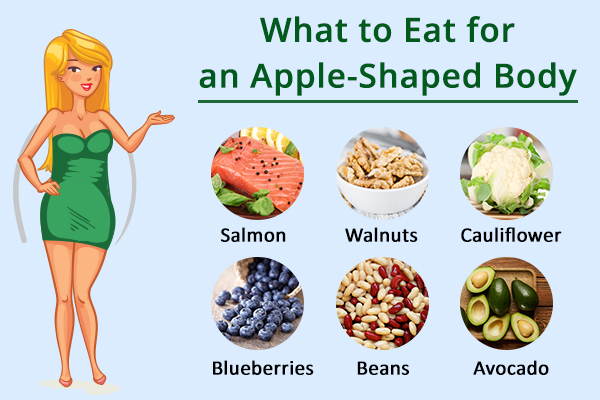
It is important to focus on high-fat and protein-containing foods such as the following:
1. Salmon
Salmon is a great source of omega-3 fatty acids. These fats are anti-inflammatory and can combat the inflammatory effect of visceral fat. (1)
2. Walnuts
These nuts are also high in omega-3 fatty acids and have been shown to improve heart health, which apple-shaped bodies can struggle with.
3. Cauliflower
This cruciferous veggie is great not only because it can be used in so many dishes but also because it is a very low glycemic vegetable that is high in volume and low in calories.
Low glycemic simply means cauliflower doesn’t raise your blood sugar as other high-carbohydrate foods do.
4. Blueberries
Not only are blueberries high in antioxidants, which also bring down inflammation, but they are also low glycemic. (2)(3) By keeping your blood sugar stable throughout the day, you reduce cravings and allow your body to burn more fat.
5. Beans
Incorporating high-quality beans into your diet also helps to control blood sugars, not just during your meal but for up to 24 hours after you have eaten your meal! Beans are high in protein and provide a wide variety of vitamins and minerals to keep you nourished. (4)
6. Avocado
Different from salmon and walnuts, avocados are high in oleic acid, which is an omega-9 fatty acid. Omega-9 fatty acids are also anti-inflammatory and can benefit the skin, eyes, and immune system. It is important to get a wide array of fats into your diet every day.
What not to eat:

Because apple-shaped bodies struggle with insulin control, it is important to limit your intake of high-glycemic foods such as:
1. Pasta
Because pasta has been stripped of its fiber, it triggers a big spike in your blood sugars, causing inflammation and potential weight gain.
2. Juice
Even 100% juice with healthy ingredients may not benefit apple-shaped bodies. Once again, because juice no longer contains the fiber from the fruits and vegetables, your blood sugar can rise very quickly.
3. Fruit
No, you should not avoid all fruits, but only certain types. Fruits such as pineapple, mango, and bananas are high glycemic, meaning they are higher in sugar content compared to other fruits such as berries.
4. Pizza
Because of the mix of refined carbohydrates and saturated fat, pizza is a disaster for apple-shaped bodies. This combination is terrible for insulin control and reducing weight.
5. Cereals
Unfortunately, there aren’t many healthy cereal options at the store. Most have added sugar and extra ingredients that are not beneficial to an apple-shaped body.
6. Alcohol
Drinking too much can cause inflammation and cravings for the foods listed above.
b. Pear-shaped body
A pear-shaped body has more weight near the hips and thighs. Although having fat in this area isn’t as detrimental as the belly, it is still important to manage it. Holding fat in these areas can lead to high estrogen levels in the body. (5)
Dietary recommendations for pear-shaped body
Reducing foods that either contain estrogen or can raise estrogen is crucial.
What to eat:

1. Broccoli
This cruciferous veggie can reduce estrogen in the body by decreasing overall insulin. (6)
2. Whole grains
Not only high in B vitamins that provide energy, but whole grains also bind to toxins and excess hormones such as estrogen and pull them from the body.
3. Flaxseeds
High in omega-3 fatty acids, flaxseeds also promote healthy estrogen levels. (7)
4. Mushrooms
High in healthy fibers, mushrooms reduce insulin spikes, helping control estrogen levels.
5. Apples
High in fiber and low glycemic, this fruit will keep your blood sugar levels normal and will prevent excessive estrogen.
ALSO READ: Apples: Health Benefits, Nutrition, and Other Things to Know
6. Low-fat yogurt
Too much fat can be detrimental to estrogen levels, plus yogurt has beneficial probiotics.
What not to eat:
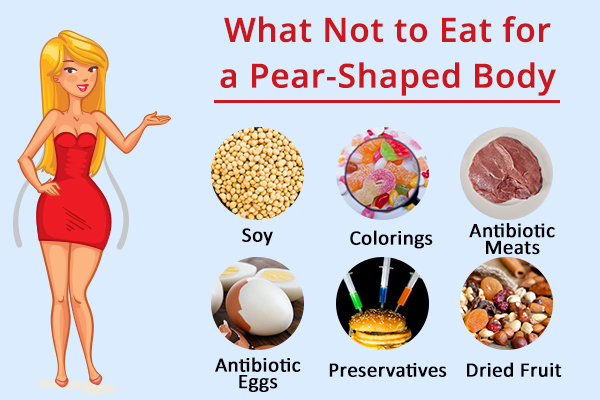
1. Soy
One of the most genetically modified and pesticide-ridden foods on the market, soy can cause estrogen dysregulation.
ALSO READ: Soy: Nutrients, Health Benefits and Allergy Symptoms
2. Antibiotic meats
Most animals are raised with antibiotics to reduce infection and disease. However, studies have shown that these antibiotics can affect the immune system and endocrine system. (8)
3. Antibiotic eggs
Like meat, egg-producing chickens are often treated with antibiotics, which pass down to the eggs and then to consumers.
4. Colorings
If you see a color such as red or blue on an ingredient list, avoid it. These colorings have been shown to affect the endocrine system in a very negative way. (9)
5. Preservatives
When looking at canned foods or packaged foods, avoid ingredients you simply don’t recognize. Some preservatives mimic estrogen. These are called xenoestrogens. An example of a xenoestrogen perseverative is propyl gallate.
6. Dried fruit
Dried fruit has been shown to raise estrogen levels, which for a pear-shaped body isn’t ideal as excess estrogen is the issue. (10)
c. Hourglass-shaped body
An hour-glass shaped body is one that can tolerate much higher amounts of carbohydrates than the other body types. A representation of an hourglass body is a thin waist, bigger hips, and a slightly strong and wide upper body.
Dietary recommendations for hourglass-shaped body
Because hourglass-shaped bodies thrive with higher carbohydrate content in their diet, basing the diet on whole fruits and vegetables is the way to go.
What to eat:
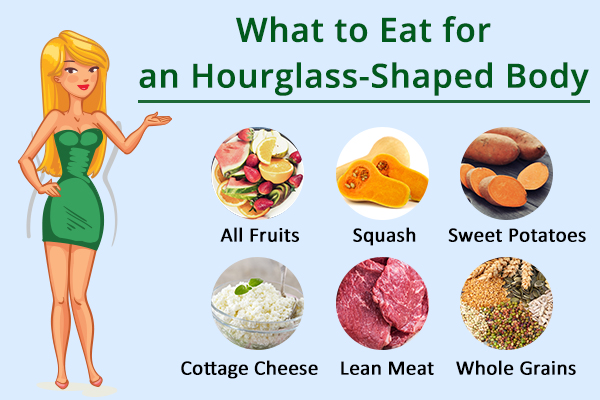
1. All fruits
Fruits provide healthy carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. All fruits are acceptable for hourglass-shaped bodies except for dry fruit.
2. Sweet potatoes
Low on the glycemic index and a healthy source of carbohydrates, sweet potatoes make for a versatile option.
3. Squash
Squash is another starchy veggie that is rich in vitamins and minerals, low in calories, and high in water content.
4. Cottage cheese
Low in fat and high in protein, cottage cheese is a great protein source for hourglass-shaped bodies.
5. Lean meat
Chicken, which is a lean meat, provides a great source of protein while remaining low in fat. (11)
6. Whole grains
Rich in carbohydrates and also in fiber, this food provides a great source of energy while keeping you full.
What not to eat:
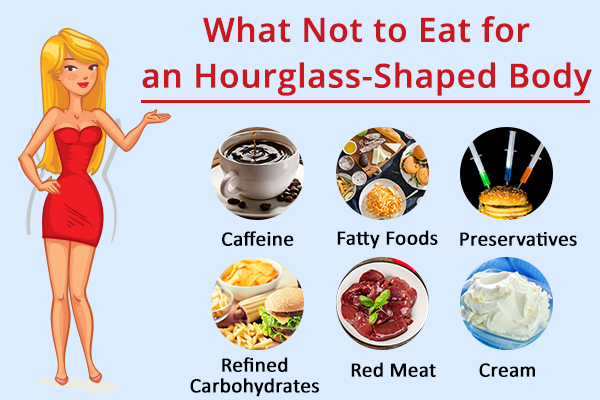
1. Caffeine
Found in many beverages and even chocolate, caffeine can impair metabolism, leading to weight gain, fatigue, and sleepiness. (12)
2. Fatty foods
Greasy foods are disastrous for weight management and will make staying lean quite difficult.
3. Preservatives
Hourglass-shaped bodies thrive most on a clean diet with no additives or preservatives.
4. Refined carbohydrates
Although whole-food carbohydrates are important, refined carbs spike insulin and can result in weight gain.
5. Red meat
High in saturated fat, red meat should be limited to keep overall fat consumption low.
6. Cream
Nearly 100% fat, cream is not well metabolized by hourglass-shaped bodies.
Final Word
Eating according to your body type can help you lose weight faster, provide you with greater energy, and improve nutritional uptake.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


