In this article:
Immunity is the body’s ability to fight infections and foreign pathogens that include disease-causing bacteria and viruses.

Several components of blood (white blood cells) are involved in building the body’s immunity: neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, basophils, and eosinophils. Each cell performs a different function, from killing microbes locally to responding to infections and defending against allergens. (1)
Some nutrients can regulate the immune system by boosting the activity of cells involved in protecting the body against infections.
Minerals such as zinc and selenium, proteins such as glutamine, and vitamins such as vitamins D, A, C, E, K, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12 are all necessary for a well-functioning immune system. (2)(3)
Needless to say, a deficiency of any of these nutrients can result in an increased risk of infection and ultimately illness. (2)
Foods for a Strong Immunity
Consume these foods to build a healthy immune system.
1. Broccoli

Broccoli is rich in a bioactive compound called sulforaphane, which has many known health benefits. (4) It improves cells’ defenses against toxicity and prevents them from turning cancerous. It can also boost the antioxidant activity within white blood cells, which is important in lowering inflammation.
Some studies also suggest sulforaphane can fight against viruses, mainly HIV, influenza, and hepatitis C, by improving the immune response. (4) In addition, it can trigger a response against bacteria by improving the activity of macrophages, which can kill disease-causing bacteria. (4)
Broccoli can be steamed, stir-fried, or included in salads, soups, and side dishes.
2. Colored bell pepper

Bell pepper comes in a variety of colors, ranging from green to yellow, orange, and red. They are abundant in beta-carotene, vitamin C, lycopene, and bioactive polyphenols that can improve the body’s immunity and antioxidant status. (5)
Studies have shown bell pepper to have antimicrobial activity against disease-causing bacteria by killing them. (6) Compounds in bell pepper can also affect the activity of immune cells, boosting overall immune function. (6)
Bell peppers can be consumed raw in salads or side dishes. They also taste wonderful when roasted and turned into dips.
3. Kiwi

Kiwifruit has been known to influence immune function due to its vitamin C content. It also contains carotenoids, polyphenols, and dietary fiber. (7)
Both green and gold kiwis contain vitamins K, C, E, and K and folate, which all work together to reduce cholesterol levels, protect the body against oxidative stress, and improve the symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections such as colds and flu in both children and adults. (8)
One kiwi each day as part of a healthy diet can boost your body’s immunity to fight infections.
4. Citrus fruits

Citrus fruits such as oranges, limes, lemons, and tangerines are rich in vitamin C and folate, which can maintain the activity of the immunity barrier and support the activity of cells involved in immune responses. (9)
Vitamin C also acts as an anti-inflammatory agent and can reduce the inflammatory response during infections. (9)
Citrus fruits can be consumed by themselves or as fruit juices.
5. Berries

Berries including strawberry, blackberry, blueberry, cranberry, and raspberry have tremendous health potential. (10)
They are chockful of nutrients including vitamins C and K, manganese, anthocyanins, catechins, flavanols, flavonoids, and resveratrol. All of these nutrients exert beneficial effects on the immune system by improving the activity of cells involved in immune function. (10)
Studies done on humans have shown berries and their juice to be beneficial against bacterial infections from H. pylori. Patients receiving 500 ml of cranberry juice for 3 weeks had reduced infection. (10)
Berries are a great addition to smoothies, parfaits, oatmeal, and even salads.
6. Ginger

Ginger is a well-known spice in many parts of the world and finds its place not only in multiple recipes but also in medicine cabinets as it is used in traditional medicine to treat several ailments. (11)
The healing potential of ginger comes from its many bioactive compounds and polyphenols. It is known to be effective against inflammation, acts as a strong antioxidant, and can help fight microbial infections. (11)
By reducing substances that create inflammation, ginger plays a role in protecting against diabetes, allergies, asthma, arthritis (an immune response where the body attacks itself), osteoporosis, and even psoriasis. (11)
Ginger can be consumed by using it as a topping for dishes and soups, or it can be turned into a delicious warming tea with or without the use of honey.
7. Garlic
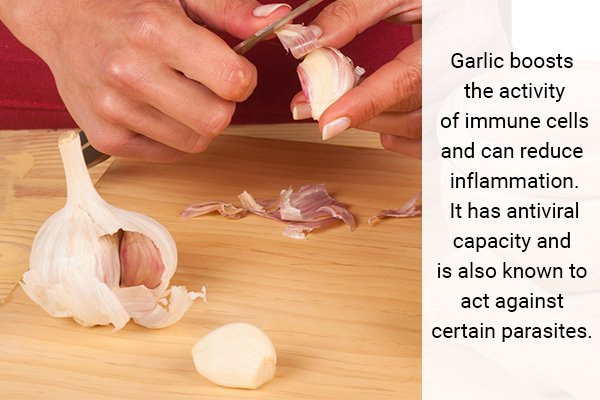
Who isn’t a fan of extra garlic on their pizzas? But did you know garlic can be used to strengthen your immunity too?
Garlic boosts the activity of immune cells and can reduce inflammation. It has antiviral capacity and is also known to act against certain parasites. (12)
In recent studies, garlic has been evaluated for its role in reducing the symptoms associated with COVID-19. (12)
Aged garlic obtained by cutting and soaking garlic in an alcoholic solution for up to 20 months is now being studied for its role in improving immune response and antioxidant activity.
In one study, consumption of 3 g of aged garlic each day during the cold and flu season reduced the severity and duration of illness and symptoms in adults. (13) Therefore, consuming even 1 garlic pod a day in meals, salad dressings, or dips can be beneficial in boosting immunity.
8. Turmeric

Turmeric owes most of its health benefits to curcumin, which is its main polyphenol. It can reduce inflammation and pain, benefit the kidney, and even reduce the risk of some diseases. (14)
Turmeric has potent antibacterial and antiviral properties in topical applications. It is also consumed to help the body fight off infections from the common influenza virus. (15)
Turmeric capsules are available as supplements and can be consumed after consulting your physician. A common way of consuming turmeric is boiling 1 tsp of it in a cup of milk and drinking it warm. You can also add a pinch of black pepper as it improves the bioavailability of curcumin. (14)
9. Green tea

Tea made from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant is a rich source of catechins and other flavonoids that act as antioxidants. But it also exhibits some antimicrobial effects. (16)
Studies have shown that drinking green tea regularly reduces the duration and symptoms of influenza in healthcare workers. It can also inhibit parasitic infections by disrupting their DNA. (16)
Consume at least 1 cup of green tea each day to build strong immunity.
10. Honey

Honey has been used by many ancient cultures including the Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians for its many benefits. This golden sweet liquid exhibits antimicrobial activity against disease-causing bacteria and fungi. (17)
Through its anti-inflammatory function, honey can improve the activity of white blood cells involved in immune responses and the death of foreign bodies (such as bacteria). Honey also has wound-healing properties by which it can direct immune cells to begin repair and healing at the site of injury. (17)
Honey is a great sugar substitute and can be used to top oatmeal and yogurt parfaits and to sweeten drinks and teas. It can also be consumed as a dip or glaze for toasts.
11. Nuts and seeds

Hazelnuts, peanuts, almonds, and sunflower seeds contain good amounts of vitamin E. Animals and human studies have shown nuts and seeds to have the ability to lower enzymes that increase inflammation and enhance the body’s immune function. (3)
Most-Asked Questions
Can I take supplements to improve immunity?
Supplements that boost immunity often contain vitamin C, zinc, selenium, and other nutrients involved in immune functions. They can help strengthen the body during infections and aid recovery.
Taking a supplement may be a good idea, but don’t forget to consult your doctor before doing so.
What can weaken the immune system?
An improper diet with lots of processed foods and added sugar as well as illnesses can weaken the immune system.
Can children be given these immune-boosting foods?
Children above the age of 2 can be given any of the foods discussed in this article. Most natural foods are safe to consume and have no side effects. However, individual allergies need to be taken into consideration, and allergy-inducing foods must be avoided.
Final Word
A good immune system can help the body naturally fight illnesses and infections. It keeps the body healthy and strong from within and even reduces the risk of chronic illnesses.
Certain nutrients influence the immune system by boosting the activity of white blood cells involved in immunity.
Some foods also have antimicrobial activity that is beneficial when it comes to fighting off certain bacteria or viruses, such as the flu. Include these immune-boosting foods in your diet to aid and speed up recovery.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


