In this article:
Herbal medicines are growing in popularity, with 80% of people worldwide using them as part of their primary health care. (1)
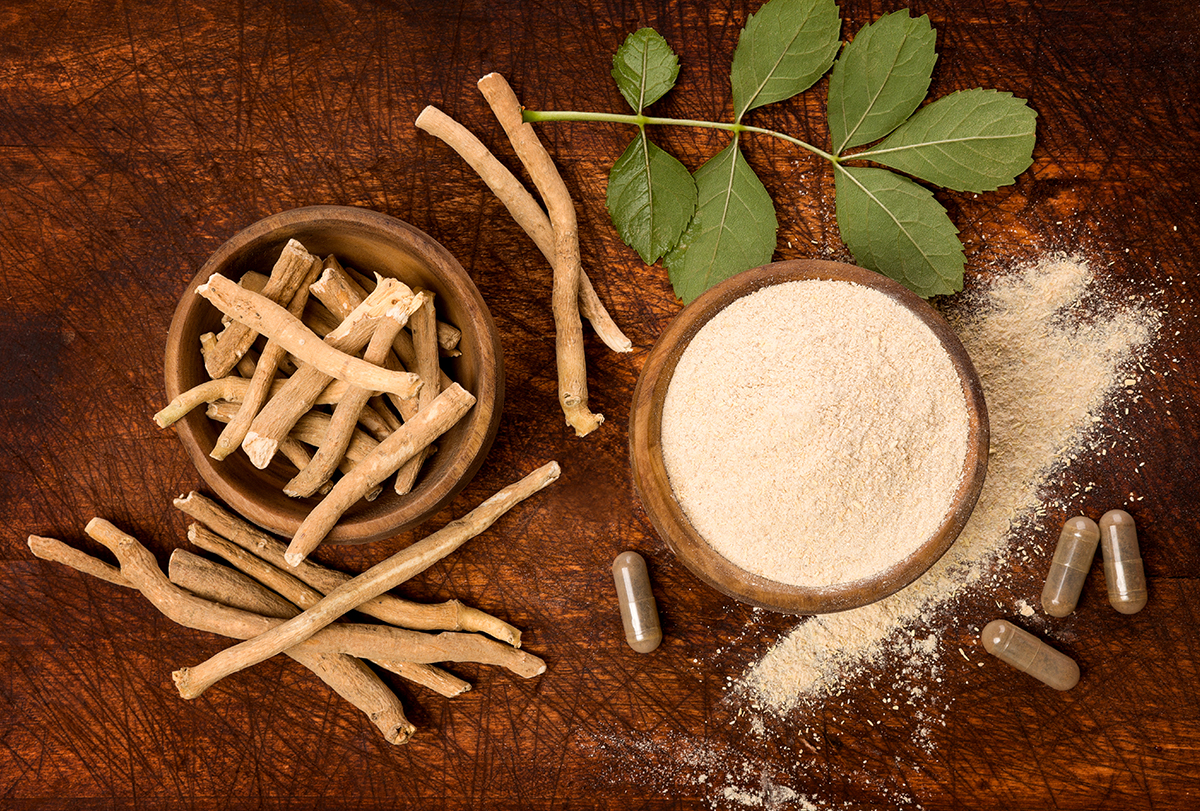

Withania somnifera (L.), also called ashwagandha, is used to reduce stress and to improve cognition and memory in Ayurvedic medicine. It’s commonly known as Indian ginseng.
Ashwagandha is a shrub that belongs to the Solanaceae family. It’s found in the dry regions of South Asia, Central Asia, and Africa. Every part of the ashwagandha herb exhibits medicinal properties, but most of them are concentrated in its roots.
You can get fresh, dried, or powdered ashwagandha root from Asian stores, health stores, and some grocery stores that you can either chew or consume in the form of a tea. Ashwagandha is also available in the form of supplements or liquid extracts.
Therapeutic Potential of Ashwagandha
The healing potential of ashwagandha can be traced back to its bioactive components.
For instance, its roots contain steroidal lactones known as withanolides, whose preventative and therapeutic properties have been upheld by traditional medicine for centuries. (2)
Ashwagandha also contains alkaloids, 18 fatty acids, polyphenols, saponins, phytosterols, iron, and choline, all of which can be good for health.
Possible Health Benefits of Ashwagandha

Ashwagandha is credited with multiple health benefits, but there isn’t enough research to corroborate most of them. However, the calming properties of this herb have been verified by preliminary studies. Ashwagandha may have the potential to reduce stress and lower cortisol.
In a double-blind randomized controlled trial, participants supplementing with ashwagandha had reduced anxiety and cortisol, a stress hormone, after 8 weeks. (3) Supplementing with 300 mg of ashwagandha twice daily for 60 days significantly lowered the participant’s cortisol levels and improved their quality of life. (4)
Other Possible Uses of Ashwagandha
Research has shown the following potential benefits of ashwagandha, although there’s insufficient evidence to support the therapeutic use of the herb for these conditions.
1. May improve sleep and mental alertness
In one study, sleep quality and mental alertness improved in older adults after 12 weeks of taking ashwagandha. (5) Supplementing with 300 mg of ashwagandha twice daily showed some sleep-inducing potential, but more large-scale studies are needed. (6)
2. May affect hormones

Ashwagandha’s ability to decrease stress may be through its action on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. (7)
The hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis regulates hormones that control stress and regulates body functions such as digestion, immune system, sexuality, mood and emotions, and energy expenditure and storage.
Cortisol and testosterone
In a 60-day trial, participants taking ashwagandha had lower stress and anxiety and had decreased depression based on a rating scale. (7) The hormones cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEA-S) decreased and testosterone increased in men. (7)
Thyroid
Ashwagandha may affect thyroxine and T4 levels. In one study, the thyroid hormones of adults with bipolar taking ashwagandha were monitored. Twelve of the 60 participants had altered thyroid function after 8 weeks. (8) The thyroid markers TSH, T3, and T4 were outside the reference range for the 12 participants.
Insulin
There is some evidence that ashwagandha improves insulin sensitivity. (2) Cortisol is a stress hormone, which has an “anti-insulin” effect. When cortisol is high, insulin isn’t as efficient at lowering blood sugar.
Ashwagandha’s potential to lower stress could improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar. If you have diabetes, you may need to adjust your medication and monitor your blood sugar closely.
3. May improve cardiovascular health
Ashwagandha may improve cardiorespiratory endurance. In some studies, oxygen consumption and quality of life scores improved after healthy athletic adults supplemented with ashwagandha. (9)(10)
4. May have an anticancer effect
Some animal and cell studies show ashwagandha’s potential for preventing and treating cancer. (11) However, more human studies are needed to support ashwagandha’s use in cancer prevention and treatment.
Dosage and Consumption of Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha root extract is taken in pill form. For stress, 300 mg is taken twice daily after food or 240 mg daily for 60 days. Ashwagandha shouldn’t be taken for more than 3 months as there are no studies on the safety of taking ashwagandha long term.
Safety of Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is considered safe for healthy adults in the recommended dosages for a short period. (12) It is important to consider the side effects and interactions with other medications before taking herbal supplements.
Possible side effects of ashwagandha
In large doses, ashwagandha may cause an upset stomach, diarrhea, and vomiting. Liver problems are rare.
Underlying medical problems and drug interactions
When taking ashwagandha, use caution when you have the following medical problems:
1. Diabetes
Ashwagandha may increase insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar and it may interfere with medications for diabetes. Your blood sugar could go too low.
2. High or low blood pressure
Ashwagandha may increase or decrease blood pressure and can interfere with blood pressure medication.
3. Stomach ulcers
Don’t use ashwagandha if you have a stomach ulcer. It may irritate the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
4. Autoimmune diseases
Avoid ashwagandha if you have multiple sclerosis (MS), lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), or other autoimmune conditions. Ashwagandha might increase immune system activity, which could increase the symptoms of these diseases.
5. Surgery
Stop taking ashwagandha at least 2 weeks before surgery. It may interfere with anesthesia.
6. Thyroid disorders
Use ashwagandha cautiously or avoid it if you have a thyroid condition. Ashwagandha may alter thyroid hormones and interfere with thyroid medications.
Most-Asked Questions About Ashwagandha

Does ashwagandha promote growth?
Ashwagandha does not promote growth in height. In Ayurvedic medicine, ashwagandha paste is given to emaciated children. (13)
Does ashwagandha improve immunity?
Ashwagandha is an adaptogen. It enhances the body’s resilience to stress and improves immunity by improving the body’s cell-mediated immune response. (13) Human studies are needed to study ashwagandha’s effect on immunity.
Is ashwagandha safe for kids and pregnant women?
Ashwagandha is considered unsafe for pregnant women and may even cause a miscarriage. Safety has not been determined with breastfeeding, so you should avoid use. Clinical trials are needed to confirm the safety of ashwagandha for kids.
Final Word
Stress increases oxidative stress and inflammation and may increase the risk of certain diseases. Ashwagandha’s potential to reduce stress could have many other health benefits.
Ashwagandha shows some therapeutic potential in treating other conditions, but this is not sufficiently supported by clinical studies. Herbal supplements should not replace medical care.
Every country has safety regulations for herbal supplements. While ashwagandha is generally recognized as safe (GRAS), you should consider its side effects and interactions with other medications before use.
Ashwagandha can be part of a healthy lifestyle for stress reduction by taking it as recommended and after consulting your doctor.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


